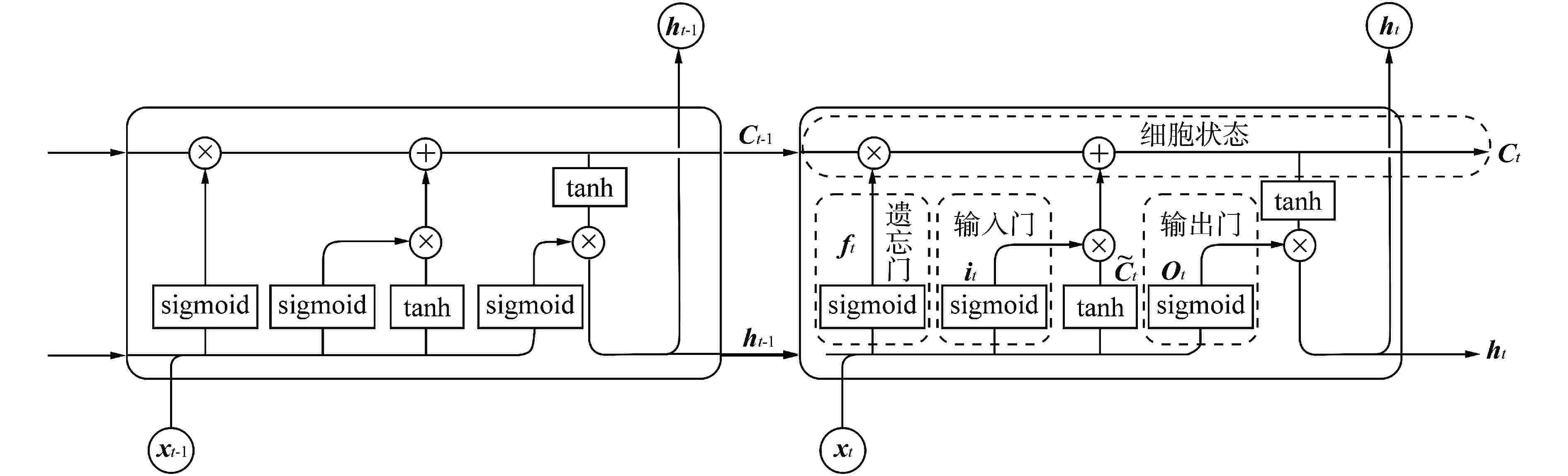
Condition Prediction of Reactor Coolant Pump in Nuclear Power Plants based on the Combination of ARIMA and LSTM
-
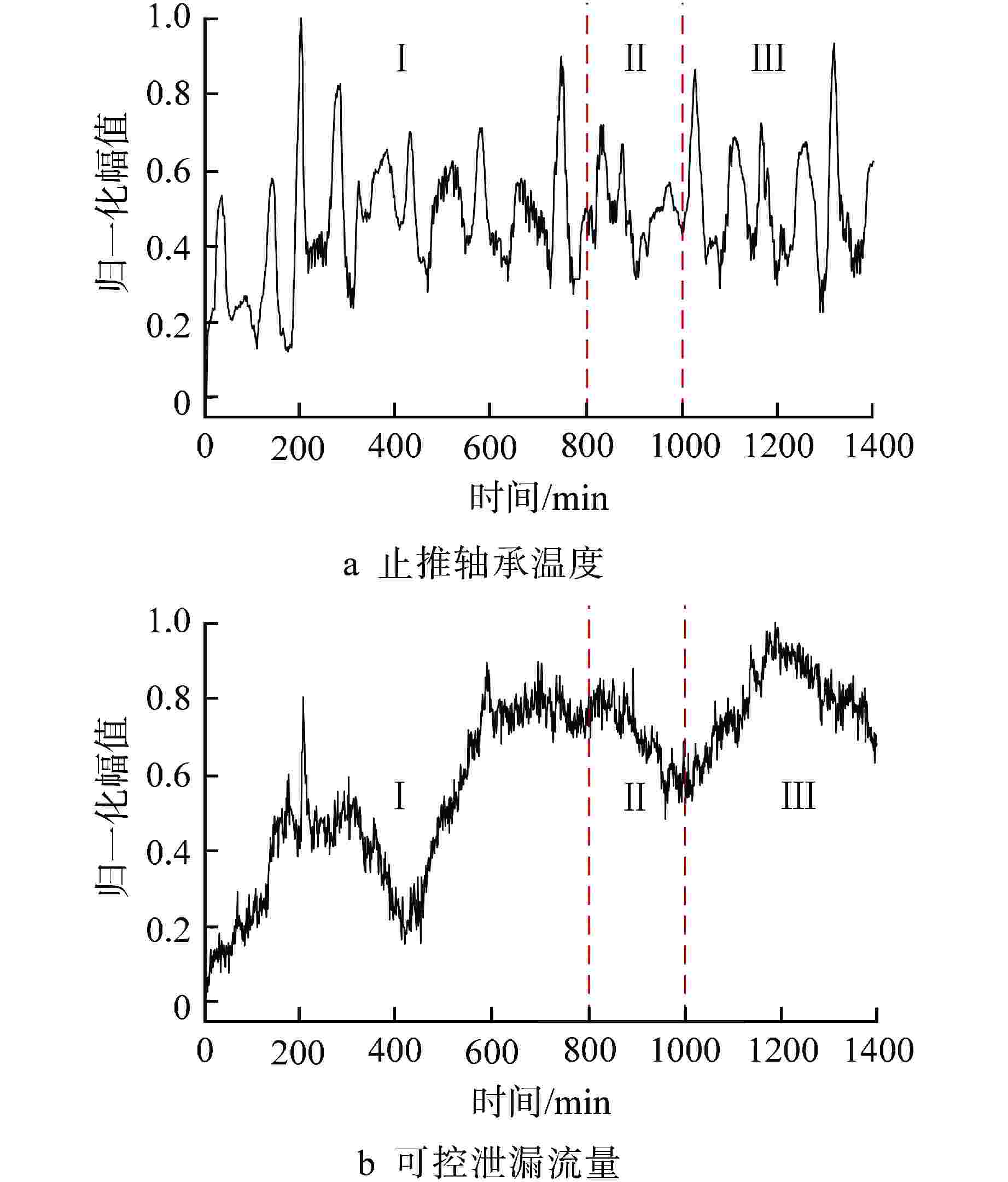
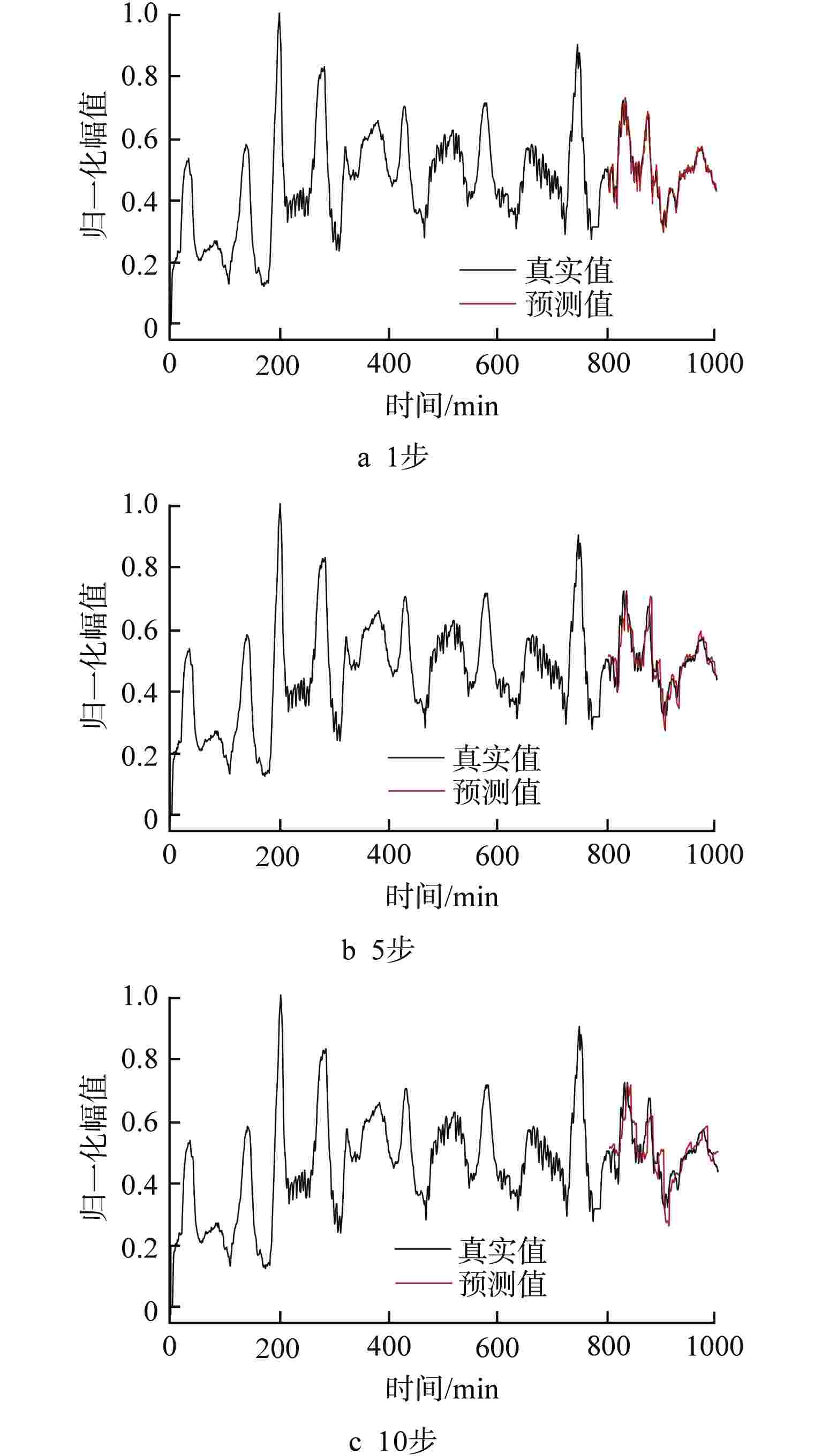
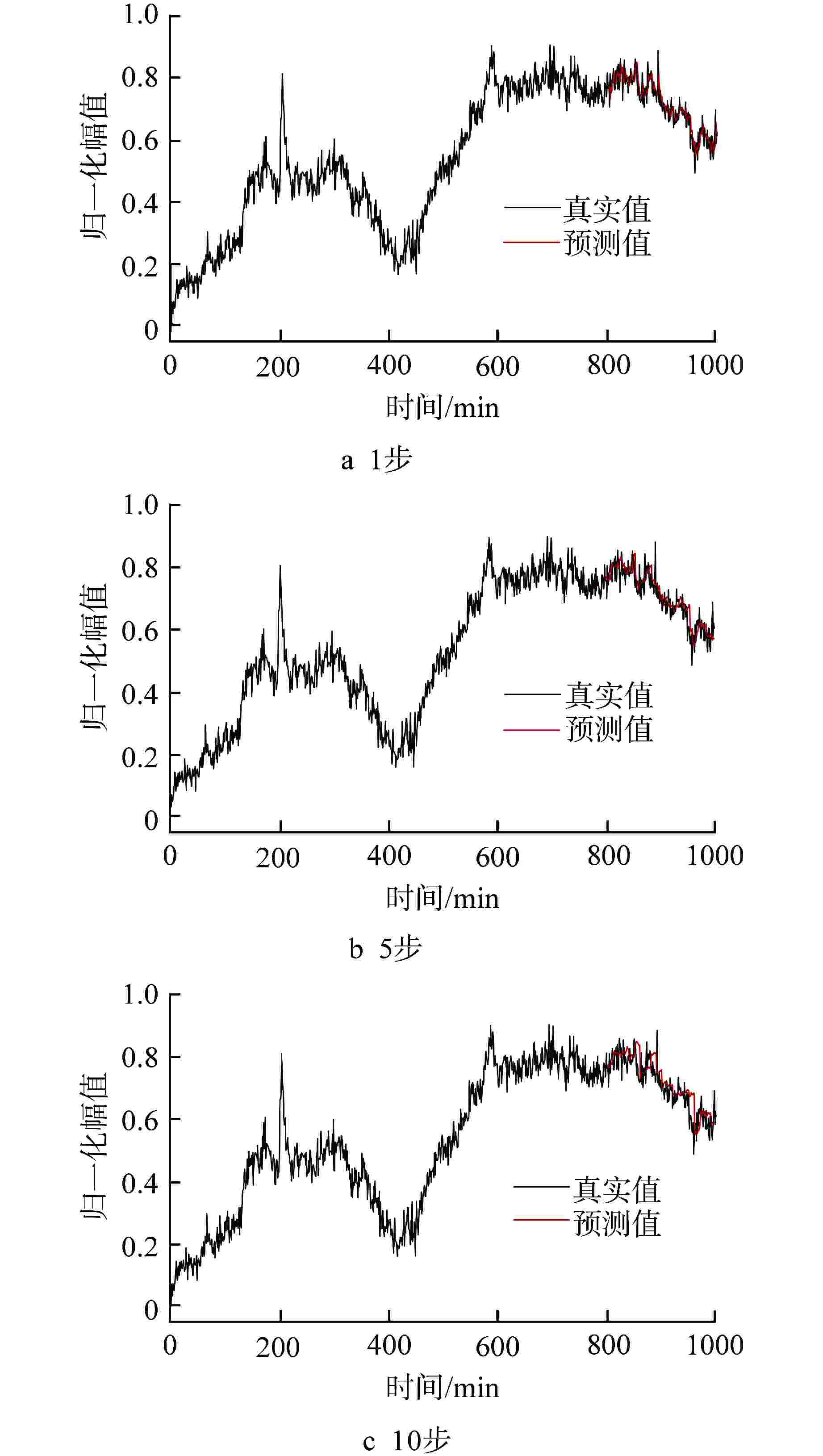
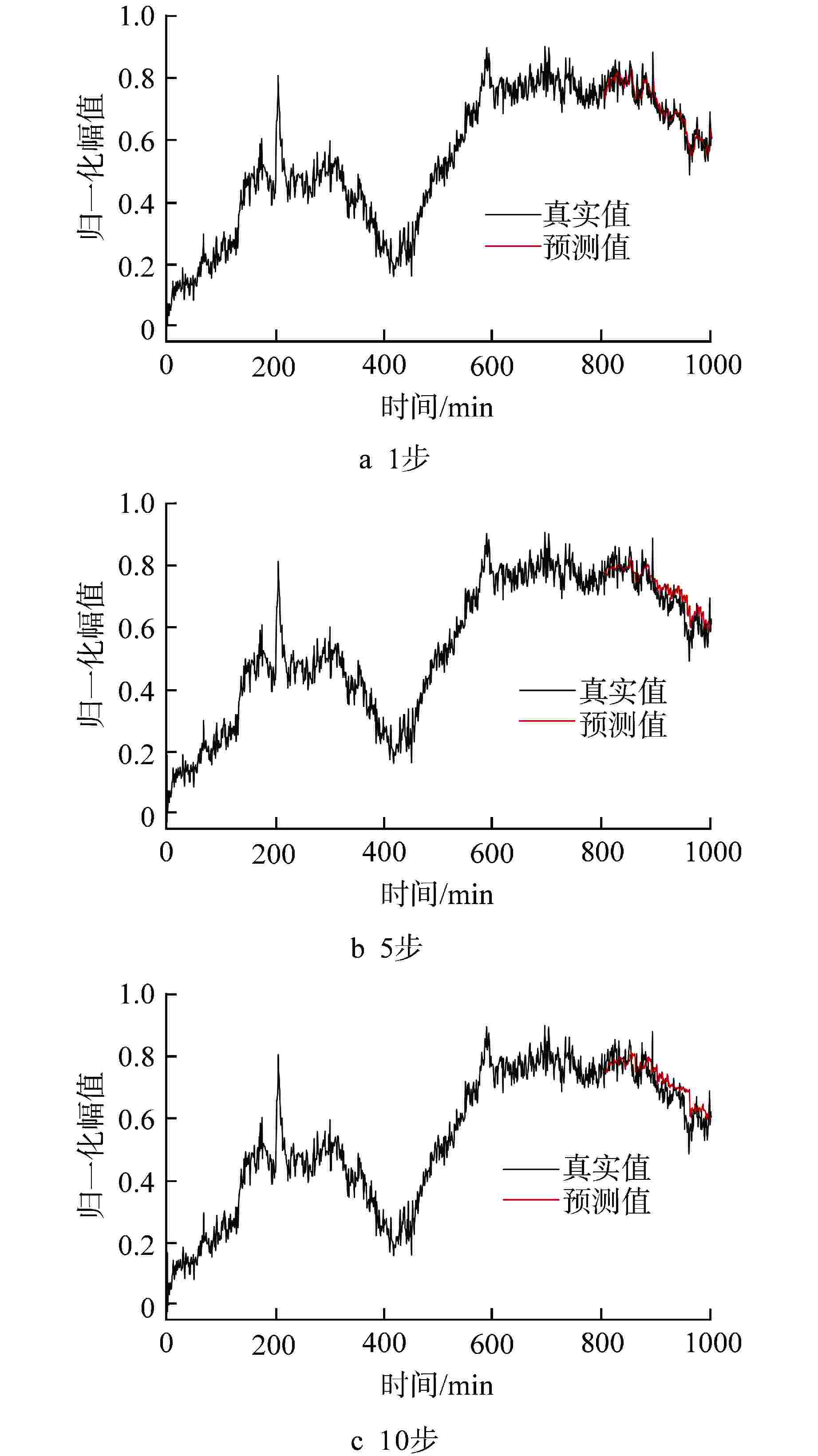
摘要: 为了对核电厂主泵的运行过程进行监测和追踪,进而提高主泵的预警能力,提出了基于差分自回归移动平均(ARIMA)和长短期记忆(LSTM)神经网络组合模型的主泵状态预测方法,并用该方法对某核电厂主泵止推轴承温度和可控泄漏流量进行单步和多步预测,以根均方误差(RMSE)为指标对预测精度进行评估。结果表明,所建立的ARIMA和LSTM神经网络组合模型能够对主泵的状态进行准确的预测和追踪,并且组合模型的预测精度要优于ARIMA和LSTM单一模型,尤其在多步预测中,组合模型的优势更加明显。Abstract: To monitor and track the operation process and improve the early warning of the reactor coolant pump (RCP) in nuclear power plants (NPPs), a hybrid RCP condition prediction approach based on autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model and long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network is proposed in this paper. This method is used to predict the thrust bearing temperature and controllable leakage flow of the RCP of a nuclear power plant in one step and multiple steps, and the prediction accuracy is evaluated with the root mean square error (RMSE) as the index. The results show that the combination model of ARIMA and LSTM neural network can accurately predict and track the state of the RCP, and the prediction accuracy of the combination model is better than that of single ARIMA or LSTM model, especially in the multi-step prediction, the advantage of the combination model is more obvious.
-
Key words:
- ARIMA /
- LSTM /
- Combination model /
- Reactor coolant pump /
- Time series prediction /
- Condition monitoring
-
表 1 LSTM网络超参数
Table 1. Hyperparameters of LSTM Network
超参数 设置情况 LSTM层数 1 初始学习率 0.005 学习速率衰减系数 0.2 隐藏层神经元个数 20 输入序列长度 20 输出序列长度 {1, 5, 10} 迭代次数 500 目标函数 均方根误差(RMSE) 训练优化算法 Adam 表 2 单一预测模型的权值
Table 2. Weight of Each Prediction Model
预测步数 1步 5步 10步 止推轴承温度 $ {\omega }_{\mathrm{A}} $ 0.6637 0.7020 0.5020 $ {\omega }_{\mathrm{L}} $ 0.3363 0.2980 0.4980 可控泄漏流量 $ {\omega }_{\mathrm{A}} $ 0.6061 0.7935 0.7798 $ {\omega }_{\mathrm{L}} $ 0.3939 0.2065 0.2202 表 3 组合模型与单一模型预测效果对比
Table 3. Comparison of Prediction Performance between Combination Model and Single Model
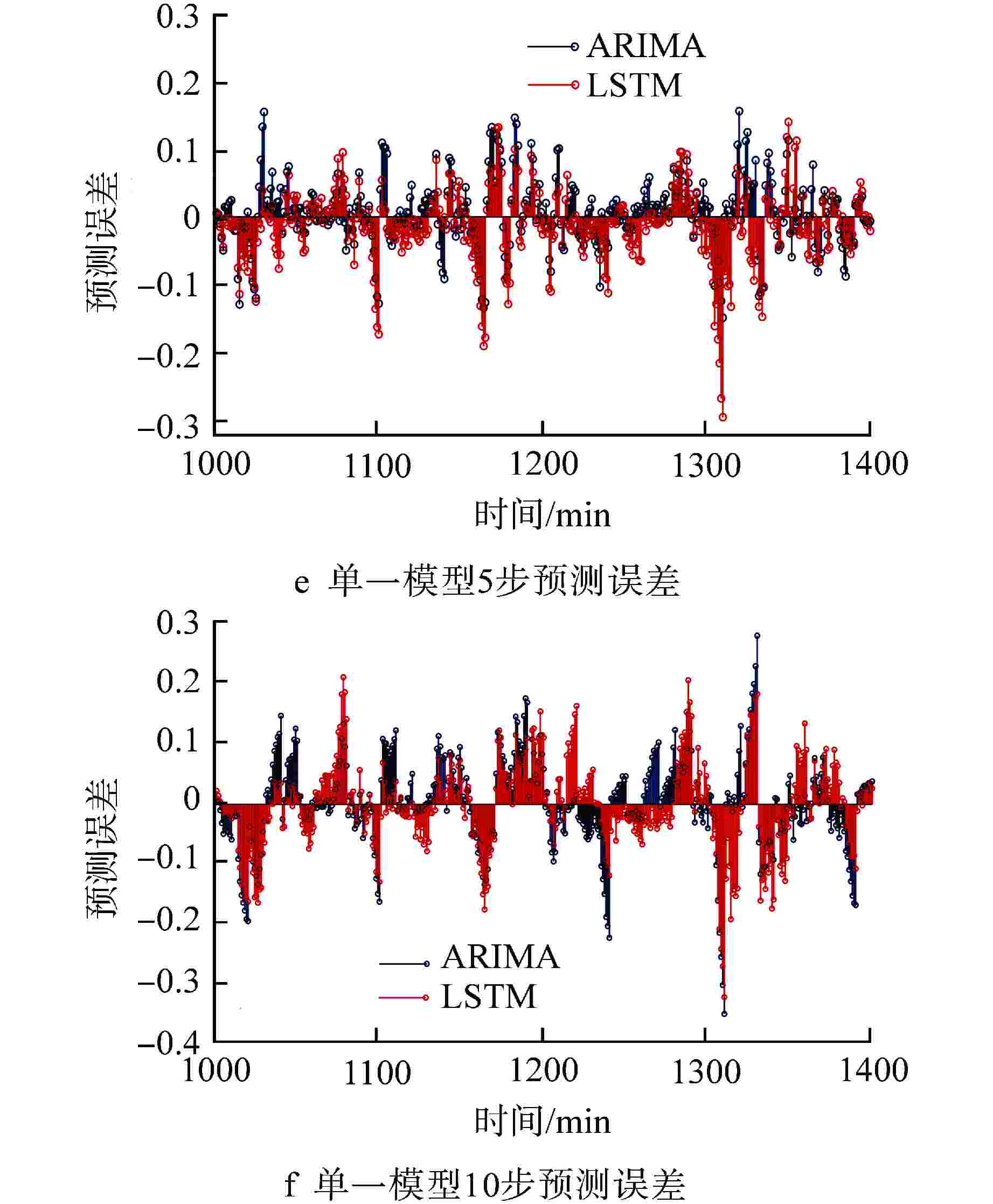
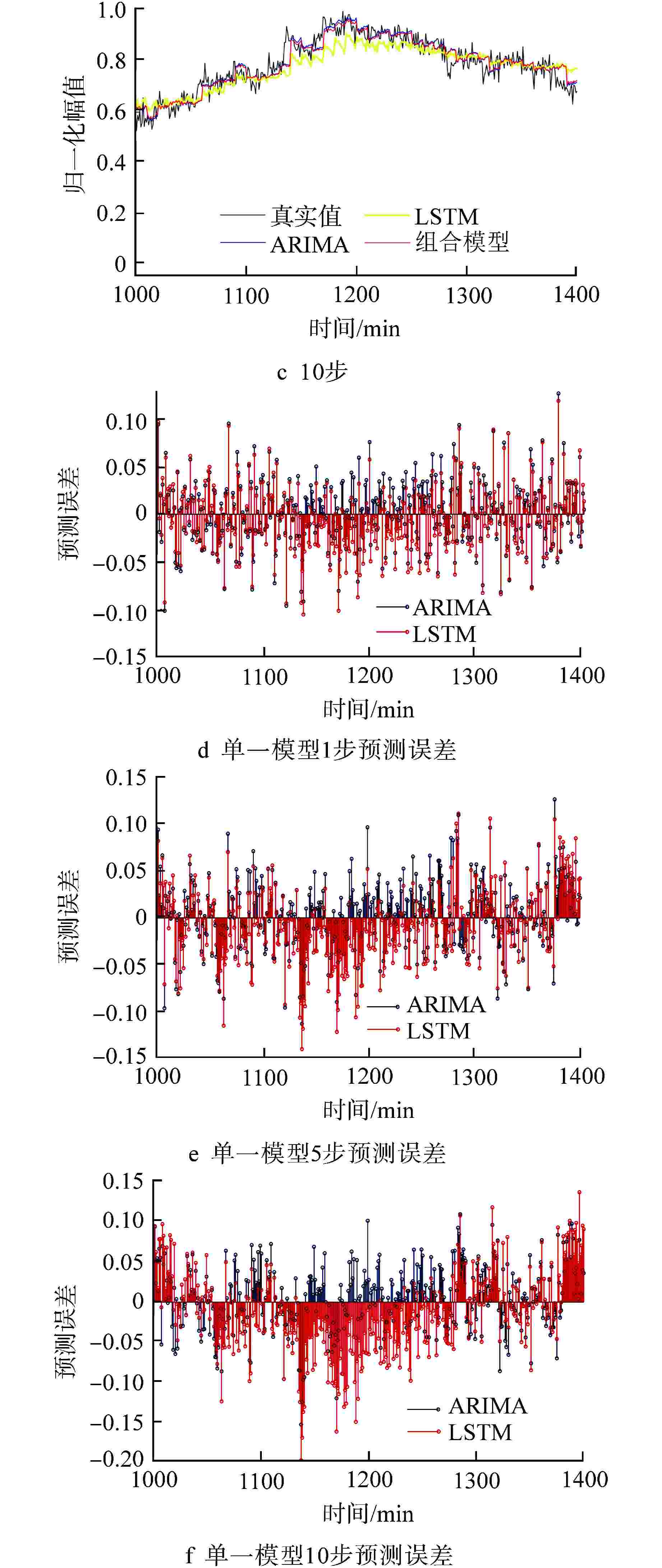
预测参量 预测模型 RMSE 1步 5步 10步 止推轴承温度 ARIMA 0.0221 0.0511 0.0782 LSTM 0.0237 0.0579 0.0782 组合模型 0.0215 0.0494 0.0728 可控泄漏流量 ARIMA 0.0343 0.0373 0.0460 LSTM 0.0348 0.0410 0.0539 组合模型 0.0340 0.0370 0.0407 -
[1] 朱少民,夏虹,彭彬森,等. 主泵故障诊断系统人机界面设计[J]. 自动化仪表,2019, 40(6): 84-86,92. [2] 朱少民,夏虹,彭彬森,等. 基于PCA的主泵传感器状态监测模型[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(3): 170-176. [3] 胡晓东,王秀勇,刘在伦,等. 基于核主泵性能预测的数值模拟精度研究[J]. 核动力工程,2019, 40(4): 127-133. [4] 张学清,梁军. 基于EEMD-近似熵和储备池的风电功率混沌时间序列预测模型[J]. 物理学报,2013, 62(5): 050505. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.050505 [5] 陈强强,戴邵武,戴洪德,等. 基于SPA-FIG与优化ELM的滚动轴承性能退化趋势预测[J]. 振动与冲击,2020, 39(19): 187-194. [6] 程小林,郑兴,李旭伟. 基于概率后缀树的股票时间序列预测方法研究[J]. 四川大学学报:自然科学版,2018, 55(1): 61-66. [7] LIU Y K, XIE F, XIE C L, et al. Prediction of time series of NPP operating parameters using dynamic model based on BP neural network[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 85: 566-575. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2015.06.009 [8] 陈涵瀛,高璞珍,谭思超,等. 基于极限学习机模型的流动不稳定性多热工参量联合预测方法[J]. 原子能科学技术,2015, 49(12): 2164-2169. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2015.49.12.2164 [9] LIU J, SERAOUI R, VITELLI V, et al. Nuclear power plant components condition monitoring by probabilistic support vector machine[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2013, 56: 23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2013.01.005 [10] 武云云,刘建香,崔宏星,等. 探讨ARIMA模型在核电站外围环境放射性水平预测中的应用[J]. 现代预防医学,2014, 41(11): 1941-1944. [11] 张思原,卢忝余,曾辉,等. 基于LSTM的核电传感器多特征融合多步状态预测[J]. 核动力工程,2021, 42(4): 208-213. [12] 张黎明,蔡琦,宋梅村. 基于RBF神经网络的NPP运行状态趋势预测[J]. 原子能科学技术,2013, 47(11): 2103-2107. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2013.47.11.2103 [13] 刘永阔,谢春丽,于竹君,等. 基于GM(1,1)模型与灰色马尔可夫GM(1,1)模型的核动力装置趋势预测方法研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2011, 45(9): 1075-1079. [14] 孙轶轩,邵春福,计寻,等. 基于ARIMA与信息粒化SVR组合模型的交通事故时序预测[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版,2014, 54(3): 348-353, 359. [15] 陈振宇,刘金波,李晨,等. 基于LSTM与XGBoost组合模型的超短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电网技术,2020, 44(2): 614-620. [16] BOX G E P, JENKINS G M, REINSEL G C. Time series analysis: forecasting and control[M]. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2013: 131-137. [17] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 -





 下载:
下载: