Simulation Research on Additional Mass of PWR Fuel Assembly
-
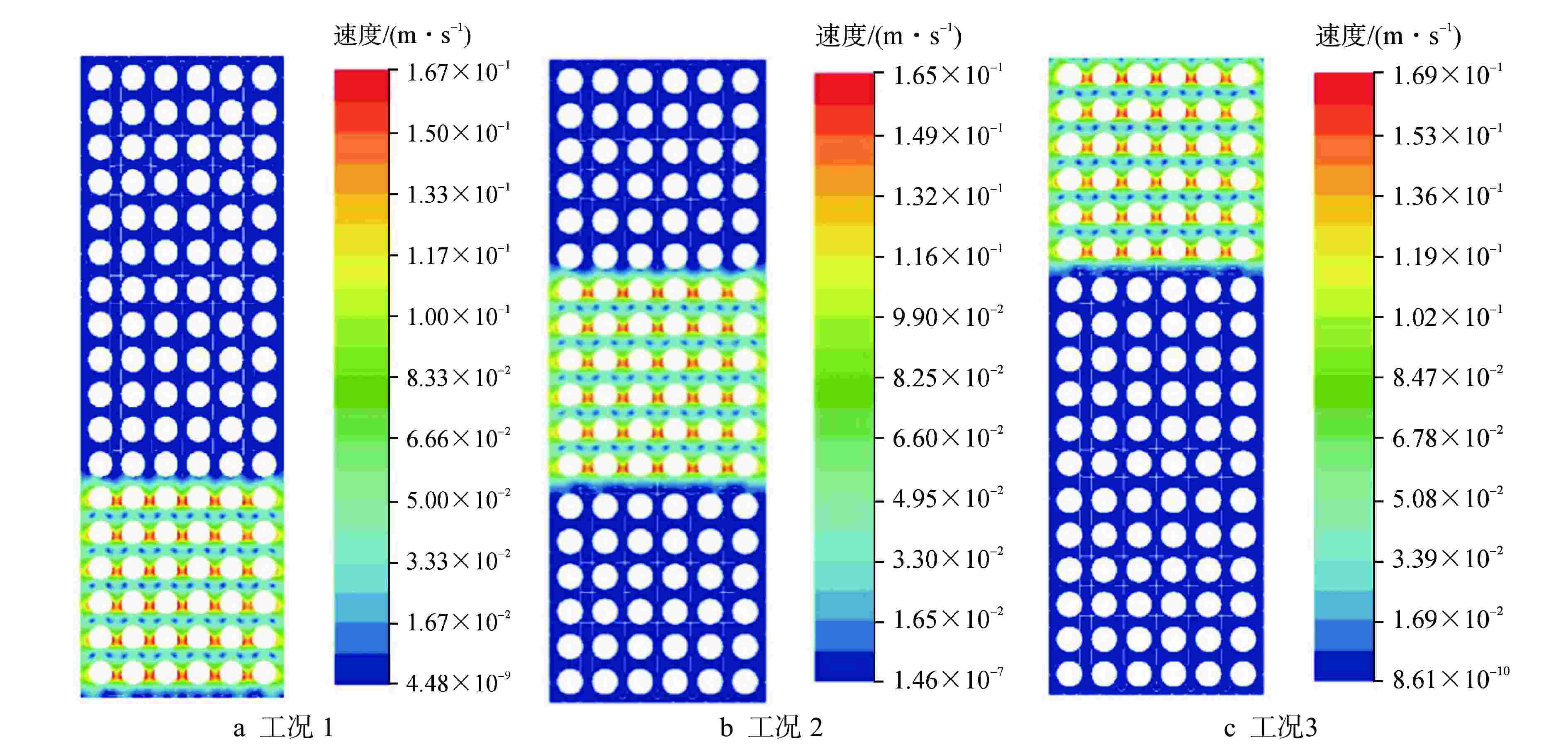
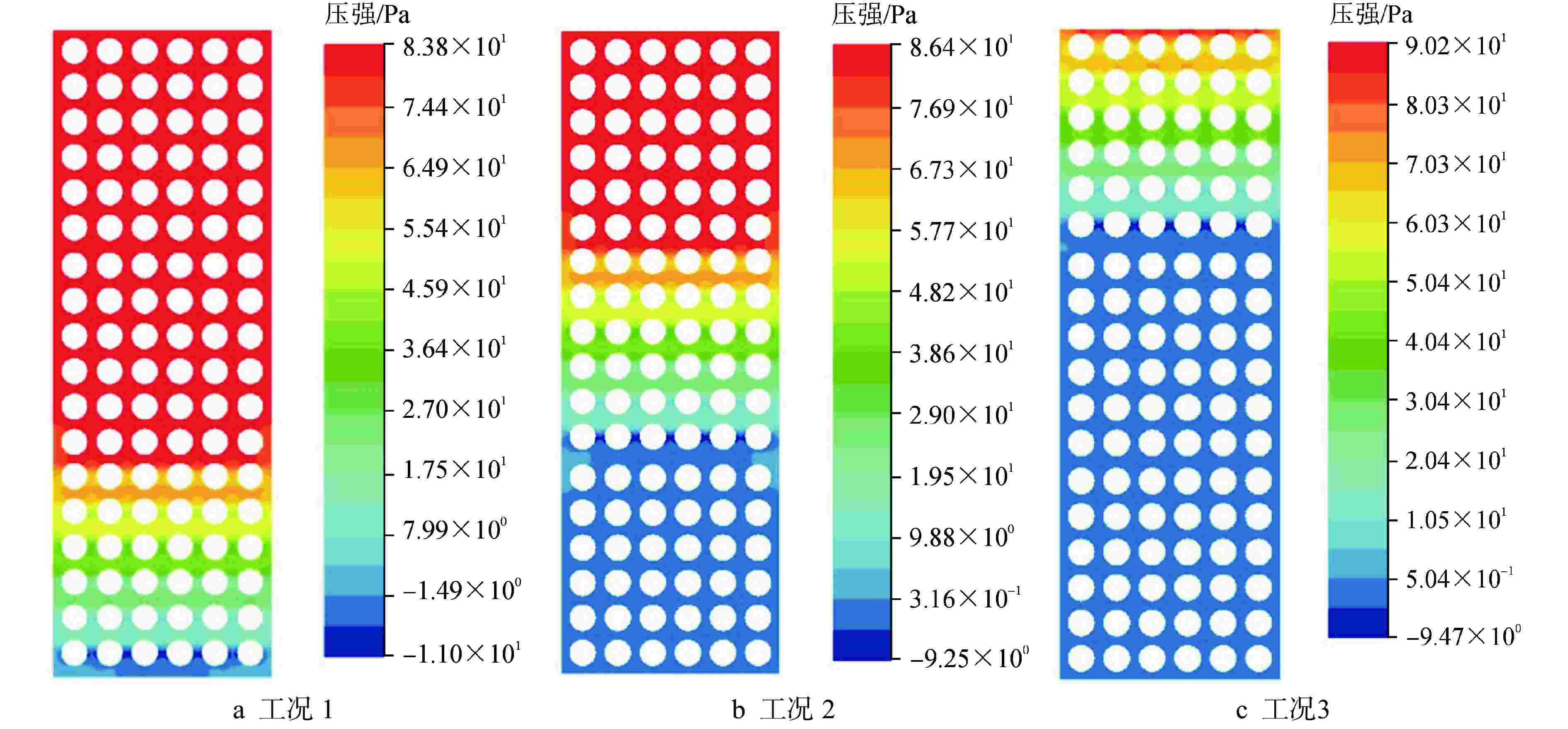
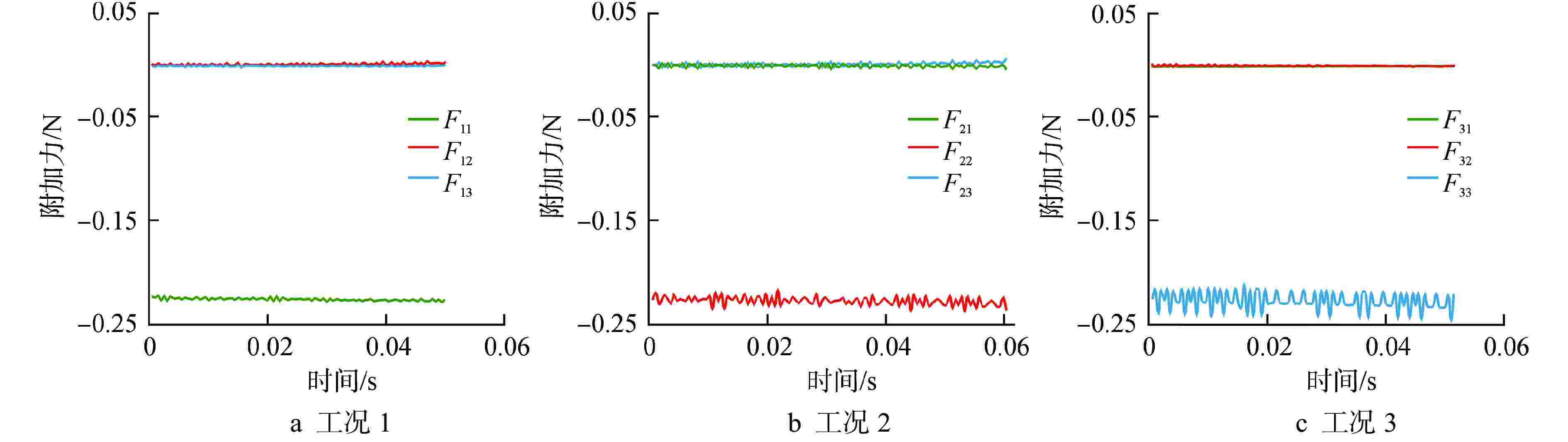
摘要: 为了准确探究反应堆冷却剂与燃料组件间存在流固耦合行为对燃料组件振动特性的影响,本文采用计算流体动力学(CFD)软件 Fluent平台,运用其中的动态网格技术,以压水堆燃料组件为研究对象,通过建立燃料组件模拟棒束、堆芯围板以及冷却剂模型,实现燃料组件与堆芯围板分别单独运动工况的燃料组件附加质量计算。结果显示:燃料组件运动工况下,燃料组件附加质量系数均值为 2.4712;围板运动工况下,燃料组件附加质量系数均值为–3.4713,均与文献值偏差小于5%。叠加附加质量后,燃料组件振动频率计算值与水中振动试验测试结果偏差小于 5%,验证了分析方法的合理性。本研究建立的仿真计算方法能够用于压水堆燃料组件附加质量计算。Abstract: In order to accurately explore the influence of fluid-structure interaction behavior between reactor coolant and fuel assembly on the vibration characteristics of fuel assembly, this paper takes the pressurized water reactor (PWR) fuel assembly as the research object, applies the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software FLUENT platform and the dynamic mesh technology thereof and calculates the additional mass of fuel assembly under separate motion conditions of fuel assembly and core baffle by establishing the fuel assembly simulation rod bundle, core baffle and coolant model. The results show that the mean value of the fuel assembly's additional mass coefficient is 2.4712 under the fuel assembly motion condition and –3.4713 under the baffle motion condition, both with a deviation of less than 5% from the literature value. After superimposing of additional masses, the deviation between the calculated value of the fuel assembly vibration frequency and the underwater vibration test result is less than 5%, which verifies the rationality of the analysis method. The simulation calculation method established in this study can be used to calculate the additional mass of PWR fuel assembly.
-
表 1 模型几何参数 mm
Table 1. Geometric Parameters of Model
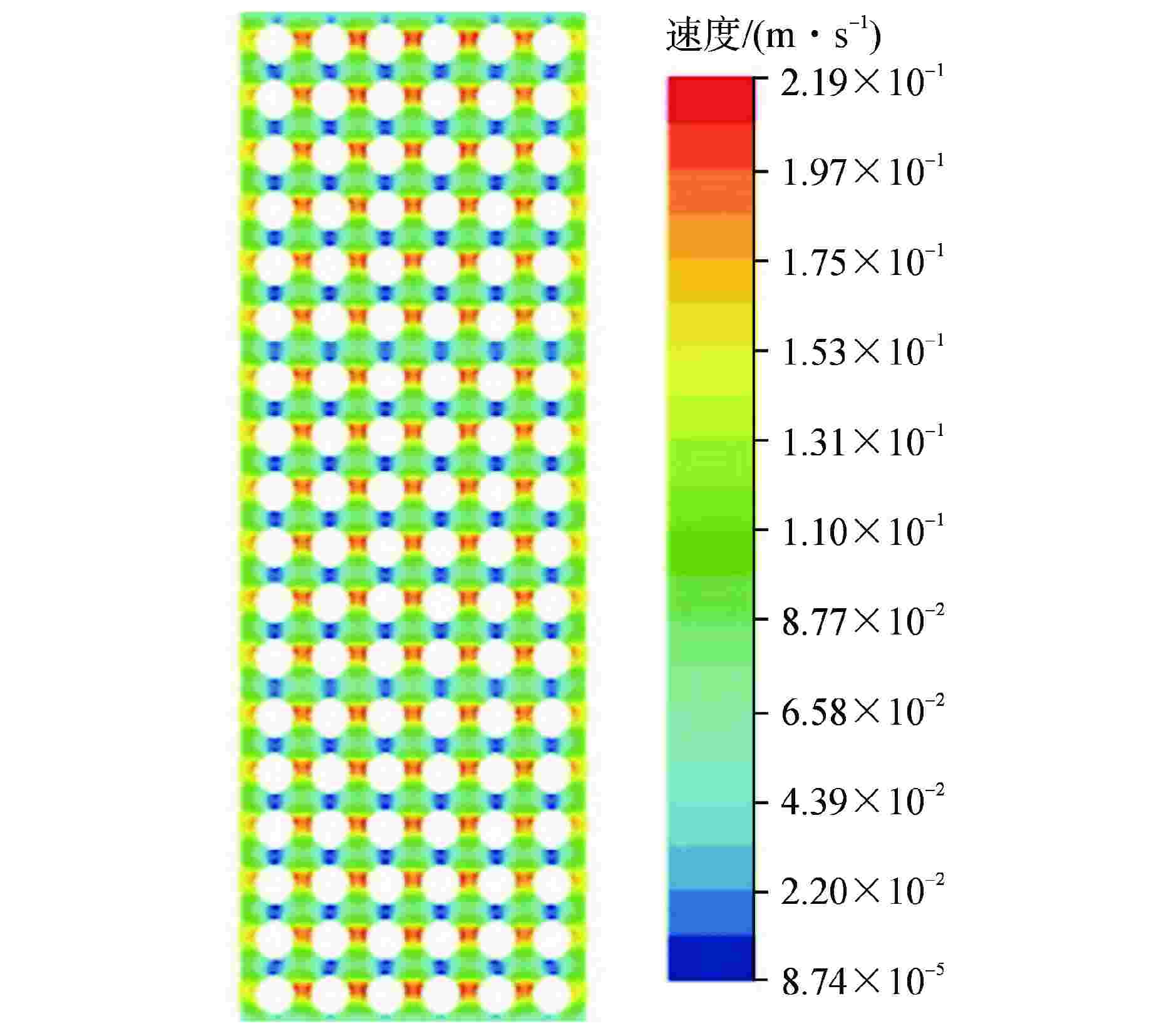
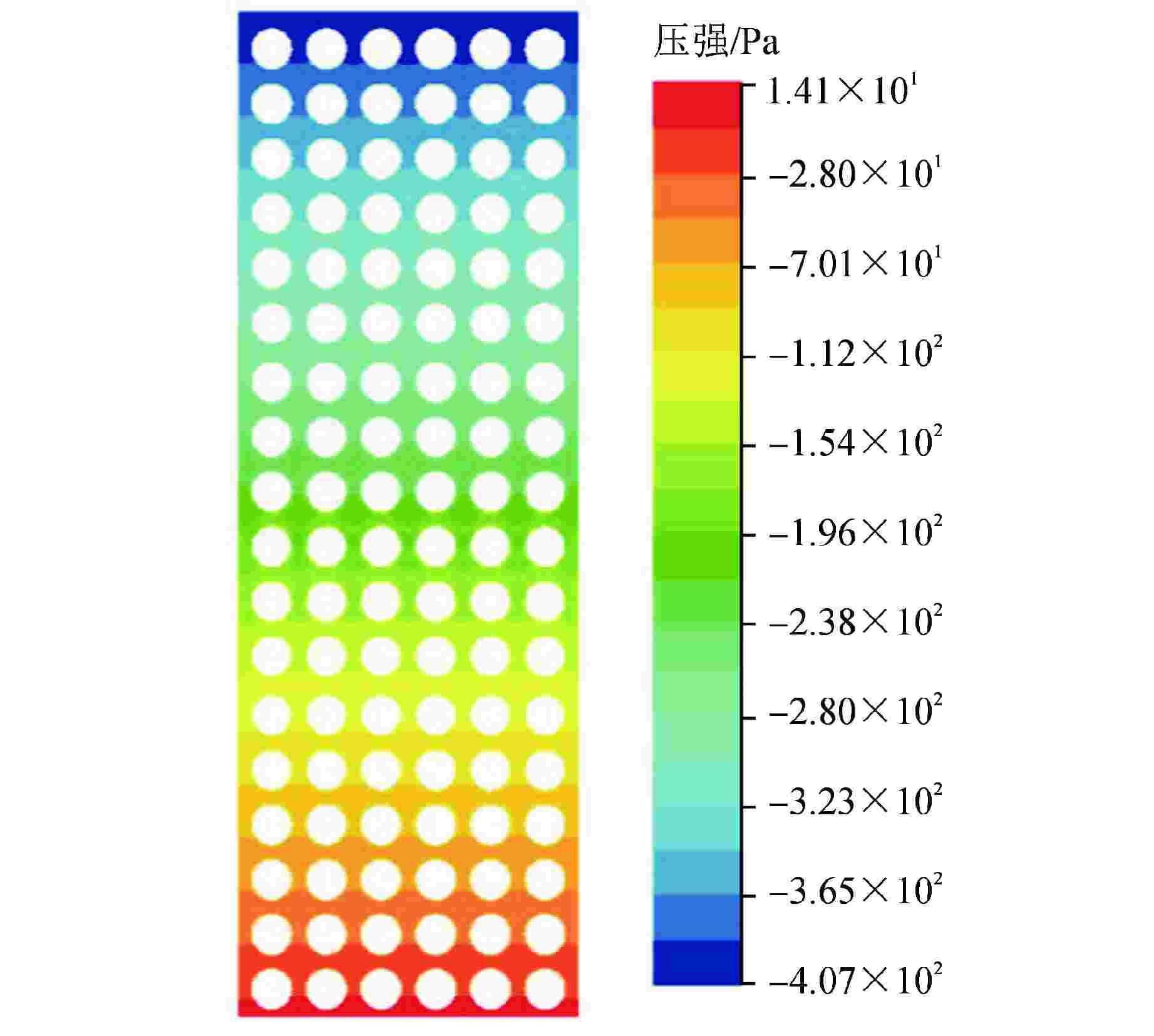
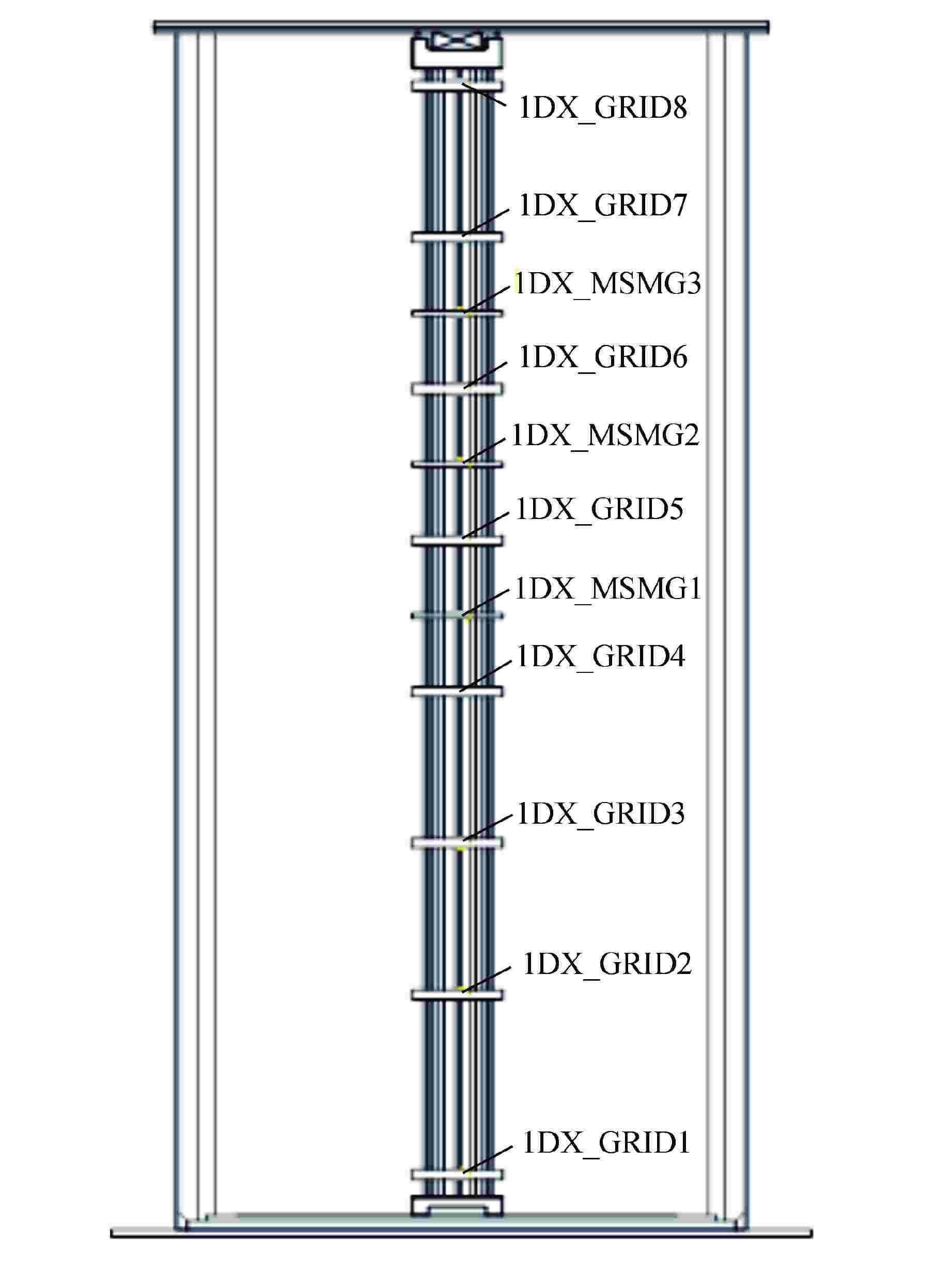
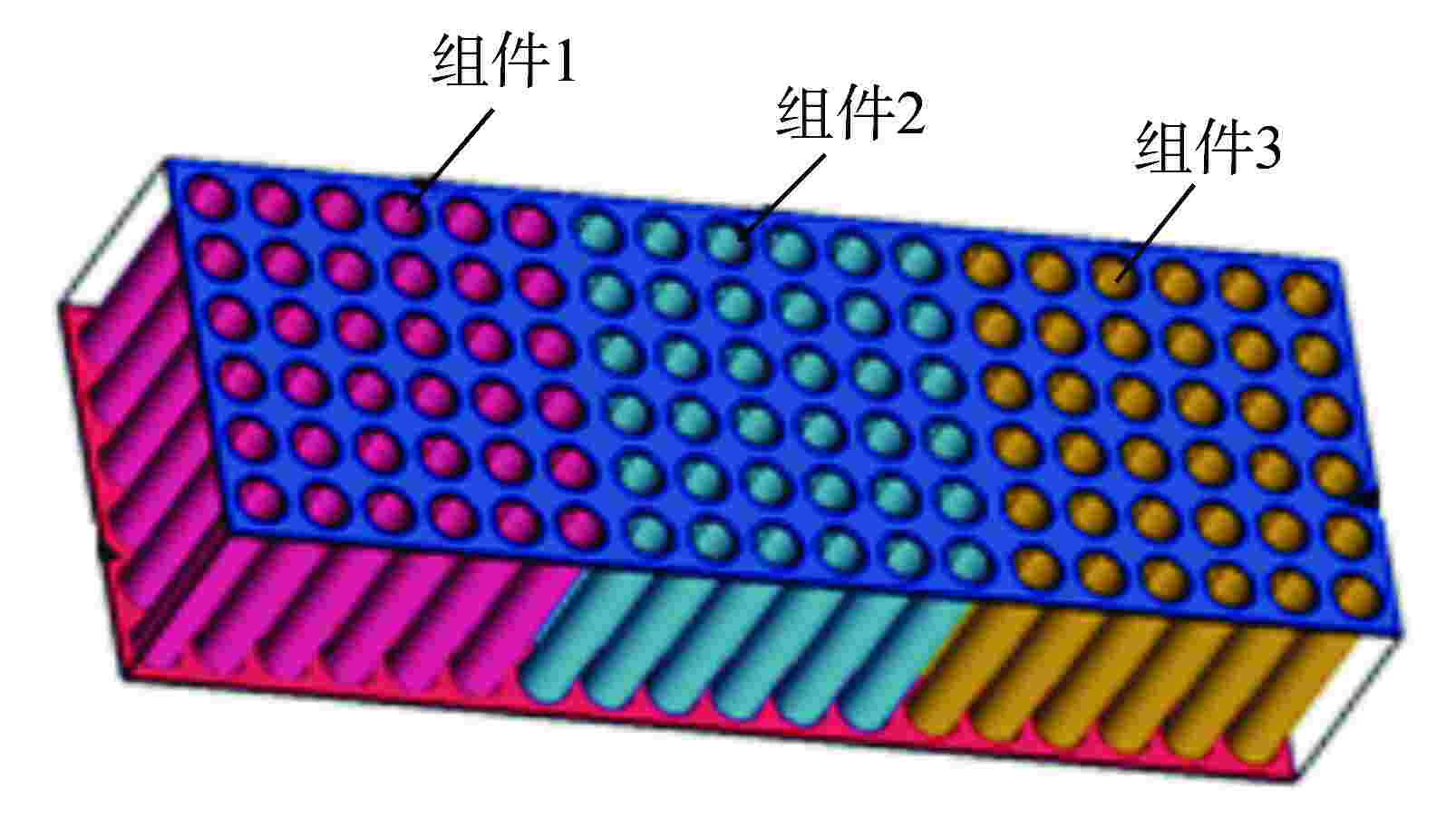
参数名 参数值 格架宽度 214.1 围板宽度 3243 相邻组件的中心距 216.1 燃料棒外径 9.5 组件内部燃料棒棒间距 12.6 边缘组件燃料棒表面与围板间距 3.08 相邻组件燃料棒表面间距 4.75 表 2 4种典型分析工况
Table 2. Four Typical Analysis Conditions
工况序号 状态 运动加速度/(m·s−2) 组件1 组件2 组件3 围板 1 反应堆热态运行 1 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 3 0 0 1 0 4 0 0 0 1 -
[1] Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Standard review plan. 4.2 fuel system design: NUREG-0800[S]. NRC, 2007: 29-32. [2] 国家能源局. 压水堆燃料组件及相关组件抗震设计规范: NB/T 20566—2019[S]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 2020: 4. [3] 崔尔杰. 流固耦合力学研究与应用进展[C]//钱学森科学贡献暨学术思想研讨会论文集. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2001: 146. [4] KARAMCHETI K. Principles of ideal-fluid aerodynamics[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1966: 382-389. [5] 于肖宇,张继革,顾卫国,等. 薄壁圆筒结构附加质量的实验研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑,2010, 25(5): 655-659. [6] 马烨,单雪雄. 数值计算复杂外形物体附加质量的新方法[J]. 计算机仿真,2007, 24(5): 75-78,113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2007.05.022 [7] 王万惠,陆道纲. 快堆燃料组件抗震分析流体附加质量计算方法研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2008, 42(S1): 602-608. [8] FRITZ R J. The effect of liquids on the dynamic motions of immersed solids[J]. Journal of Engineering for Industry, 1972, 94(1): 167-173. doi: 10.1115/1.3428107 [9] 齐欢欢,姜乃斌,吴万军,等. 反应堆冷却剂系统动力分析流体附加质量研究[J]. 机械工程师,2018(8): 34-36,39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2333.2018.08.011 [10] RIGAUDEAU J. 压水堆燃料组件和其它浸入水中结构在地震响应中的水力耦合[J]. 肖忠,译. 国外核动力,2004(4): 36-45. [11] 谢永诚,姚伟达,姜南燕. 燃料组件在地震和失水工况下的结构动力反应分析[J]. 核动力工程,2002, 23(S2): 139-147. [12] 齐欢欢,吴万军,沈平川,等. 基于ANSYS的燃料组件事故动力分析程序[J]. 核动力工程,2018, 39(3): 40-44. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2018.03.0040 -





 下载:
下载: