Study on Control Strategy of Natural Circulation Lead-cooled Fast Reactor Coupled with S-CO2 Brayton Cycle
-
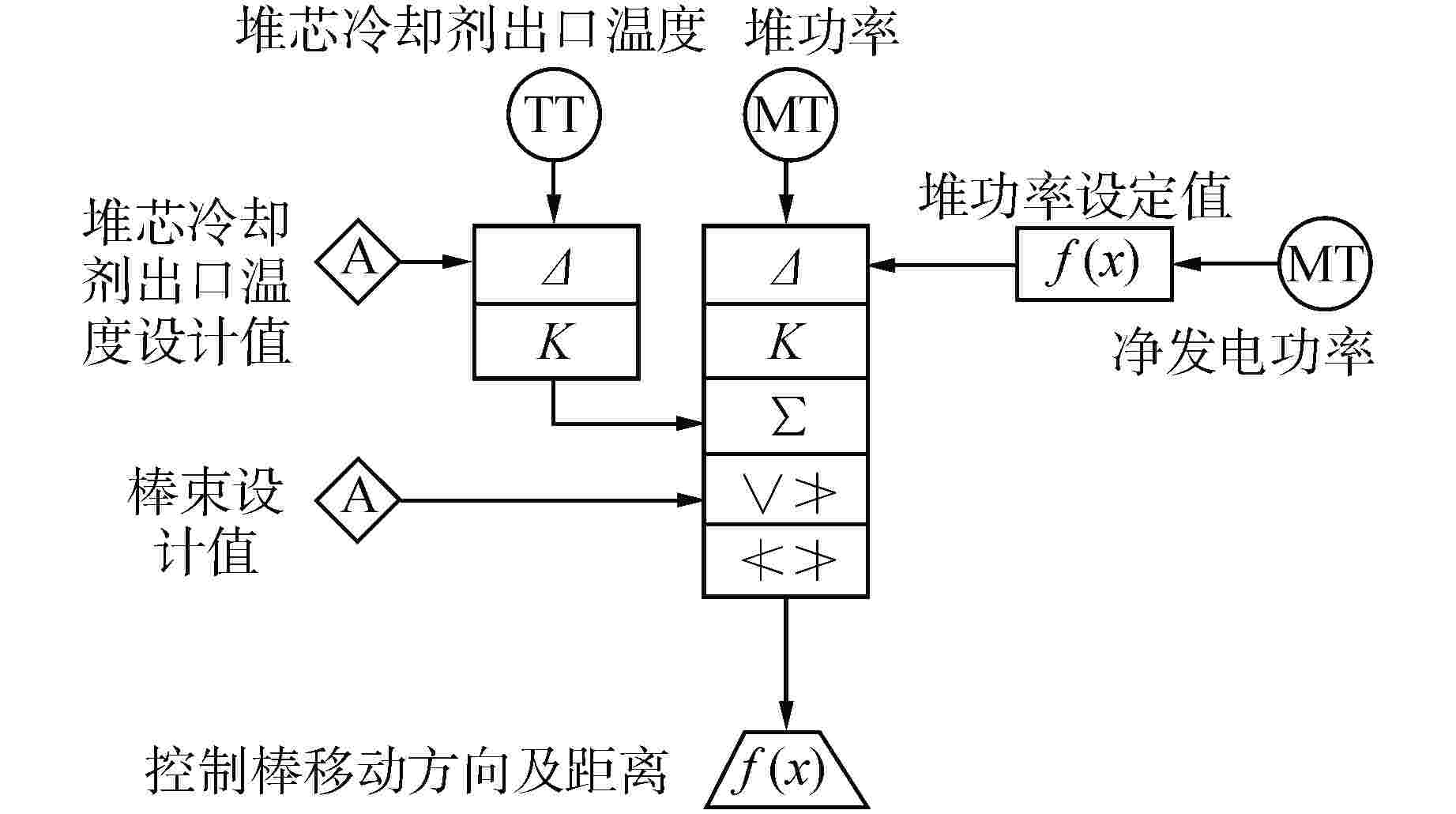
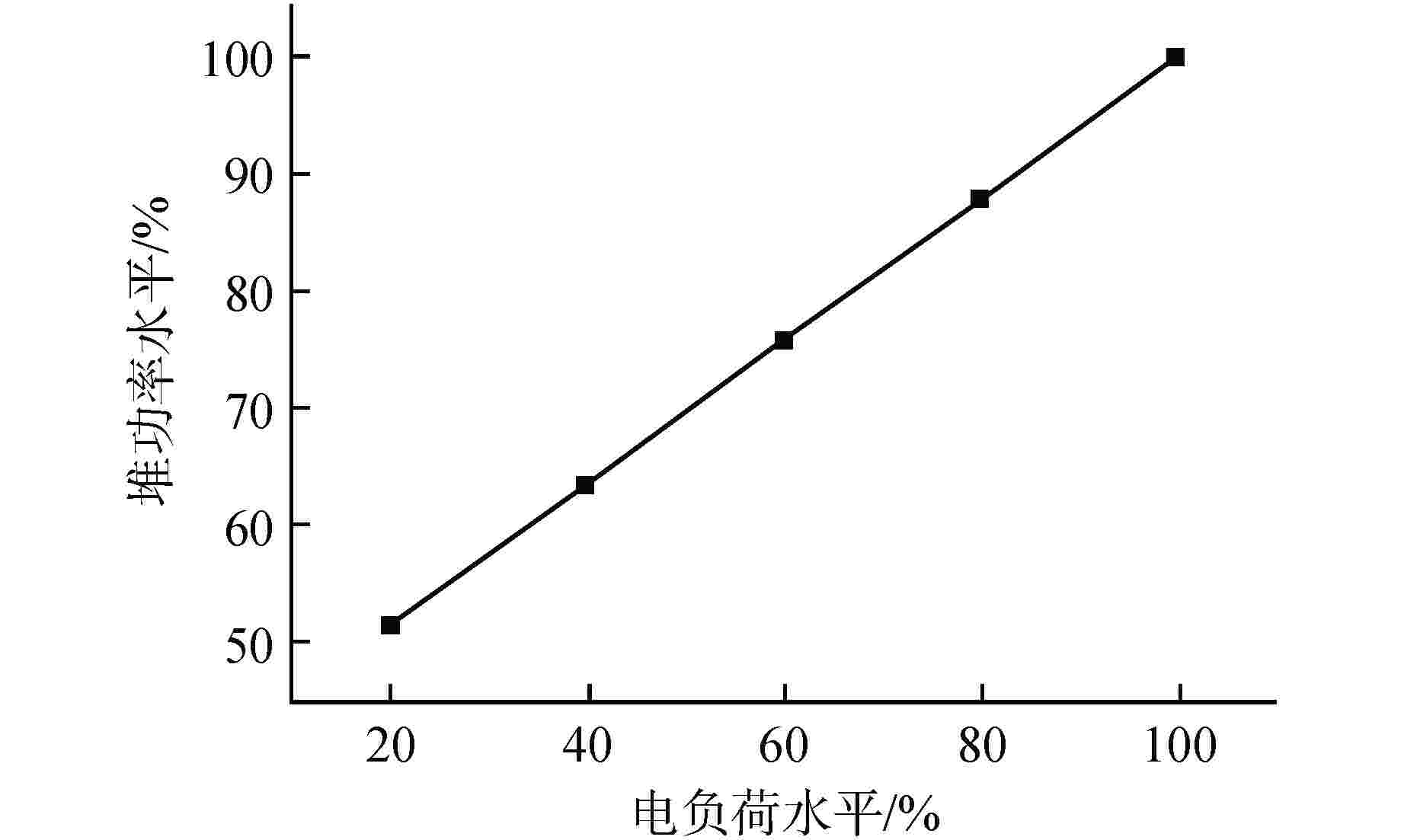
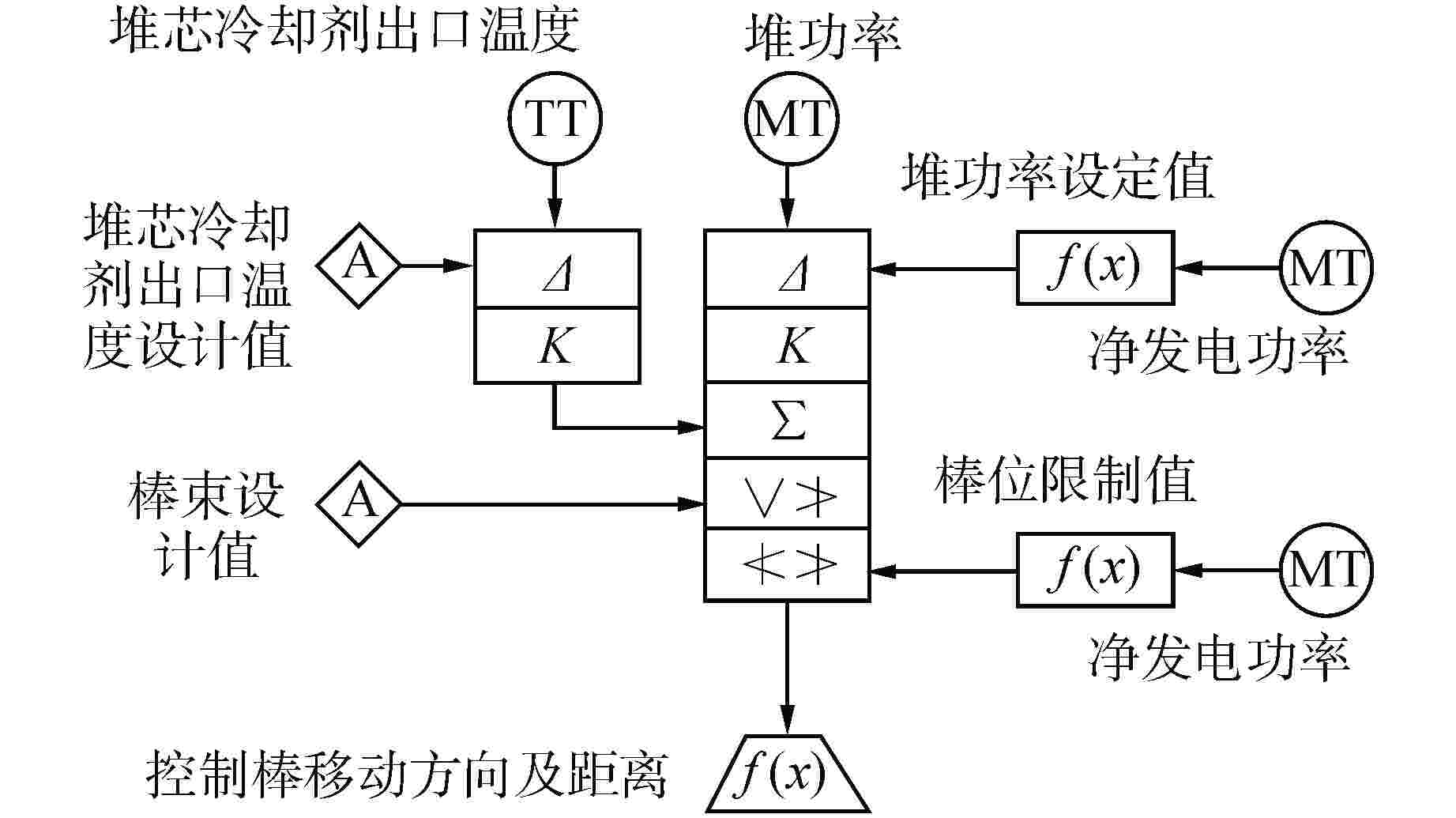
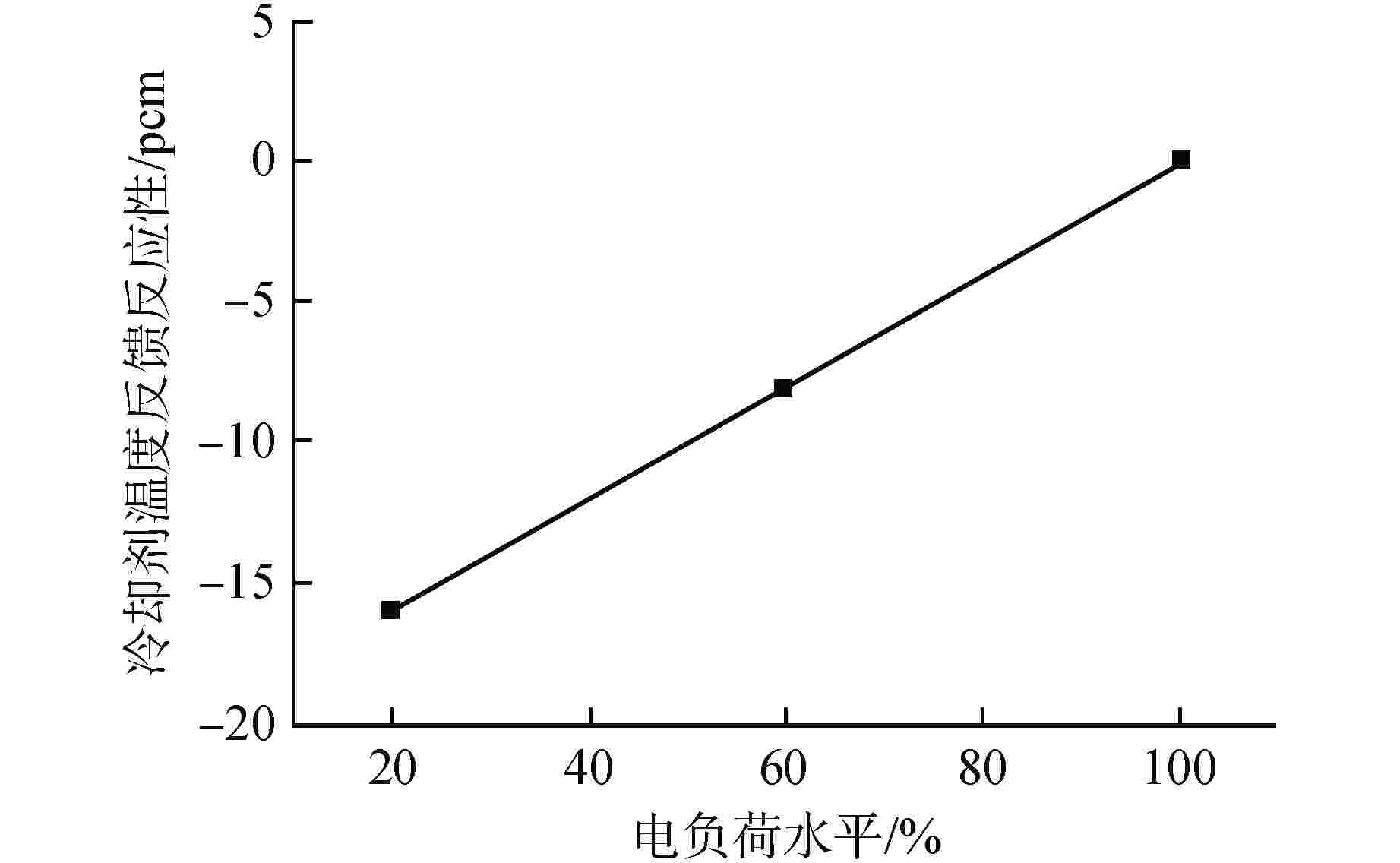
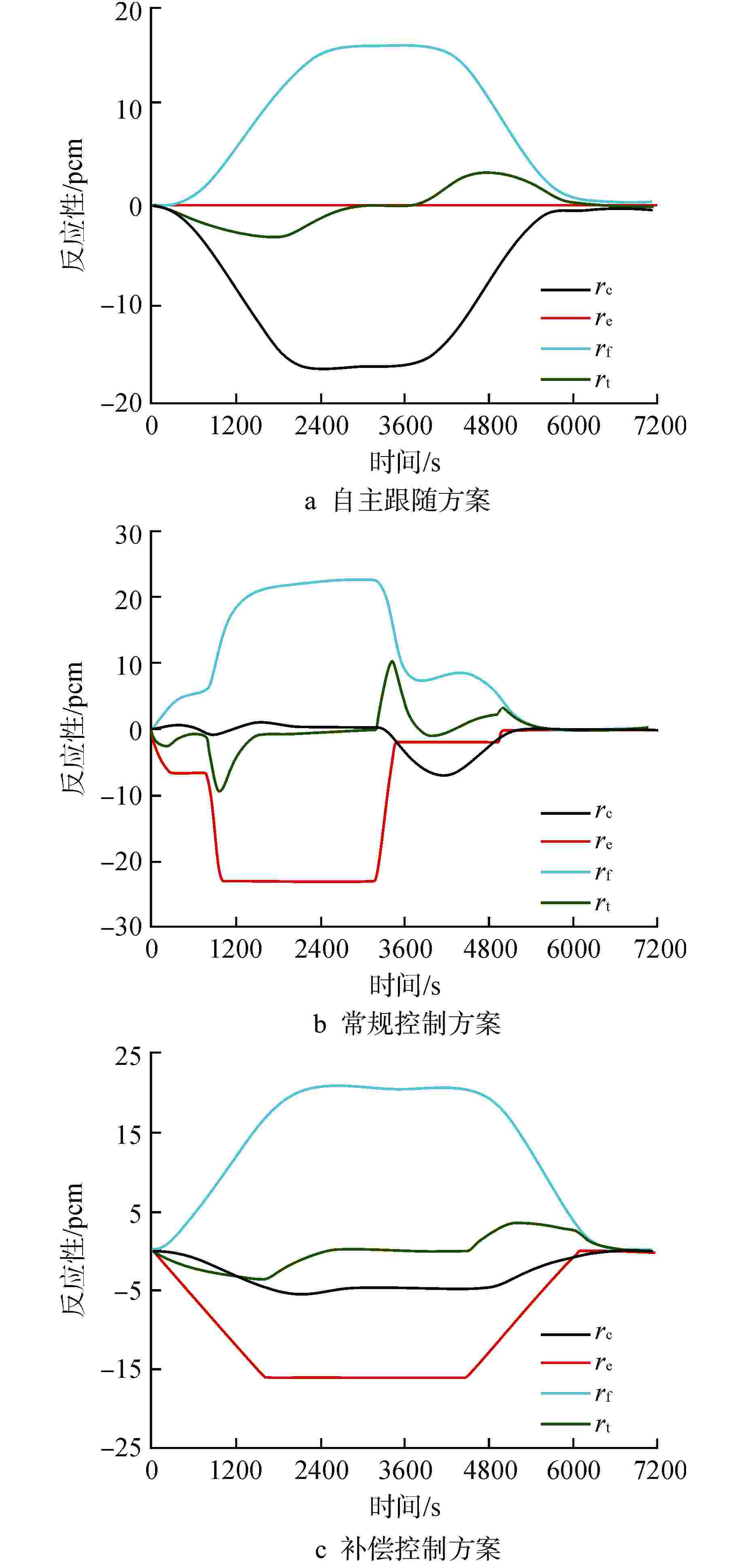
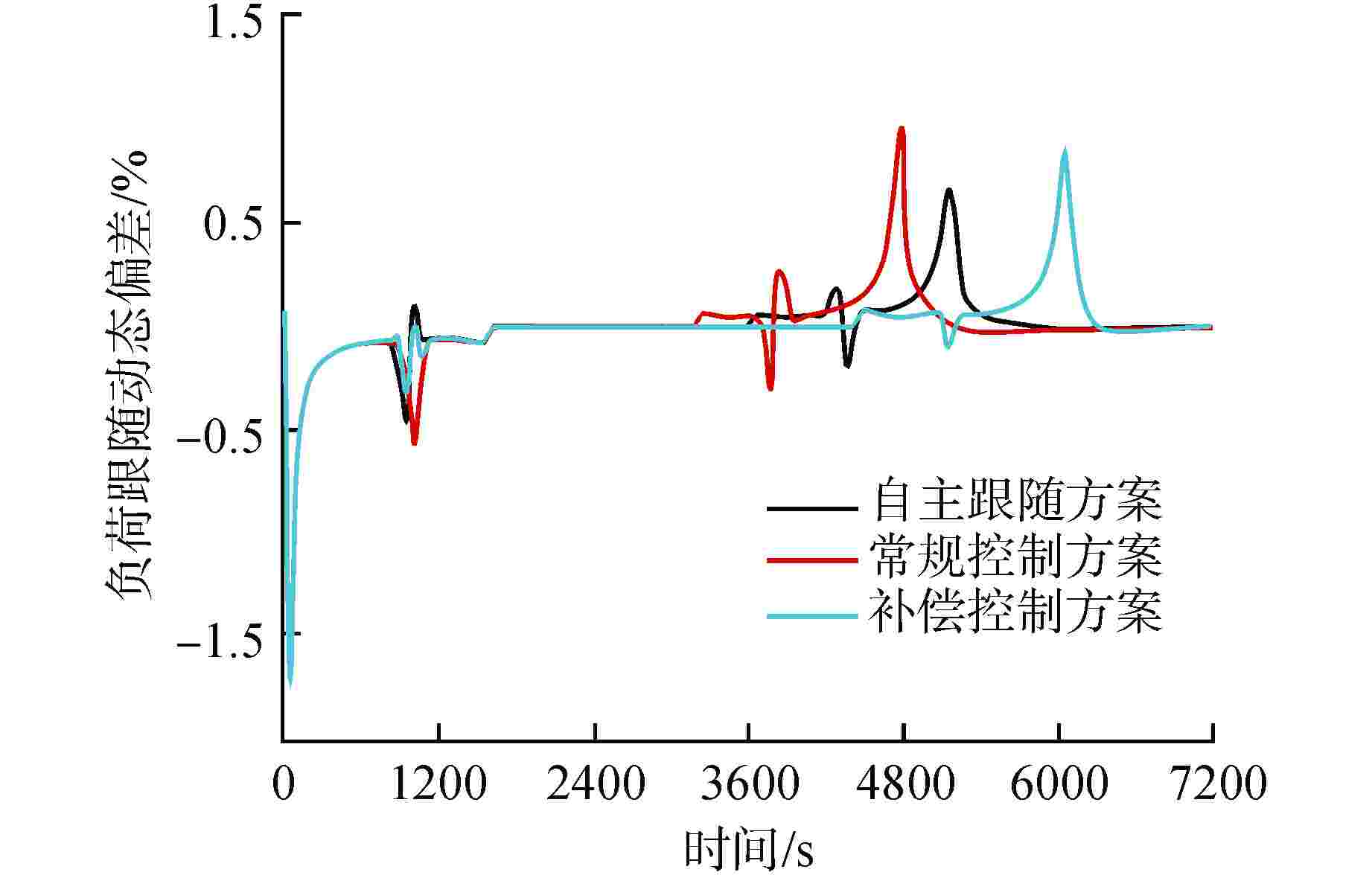
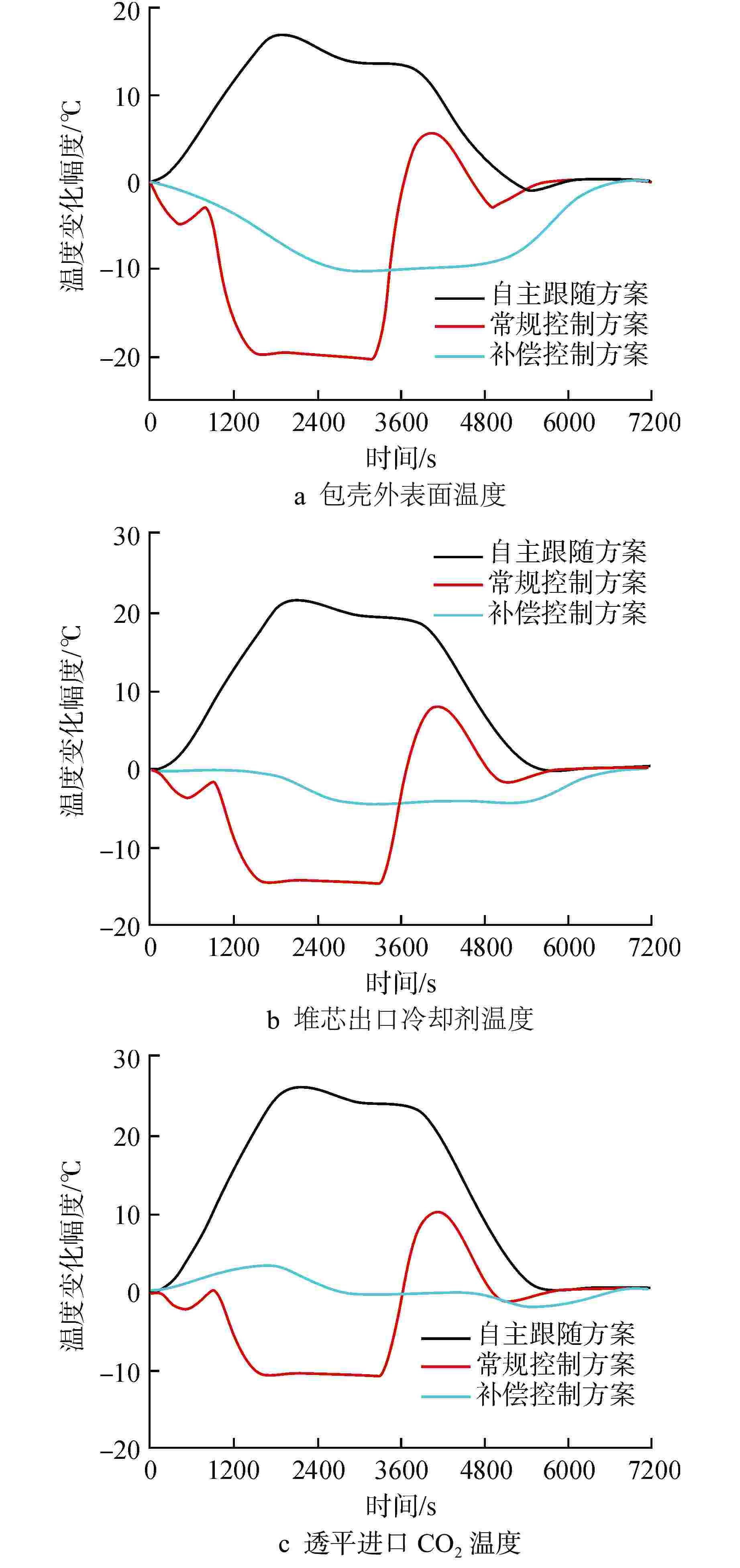
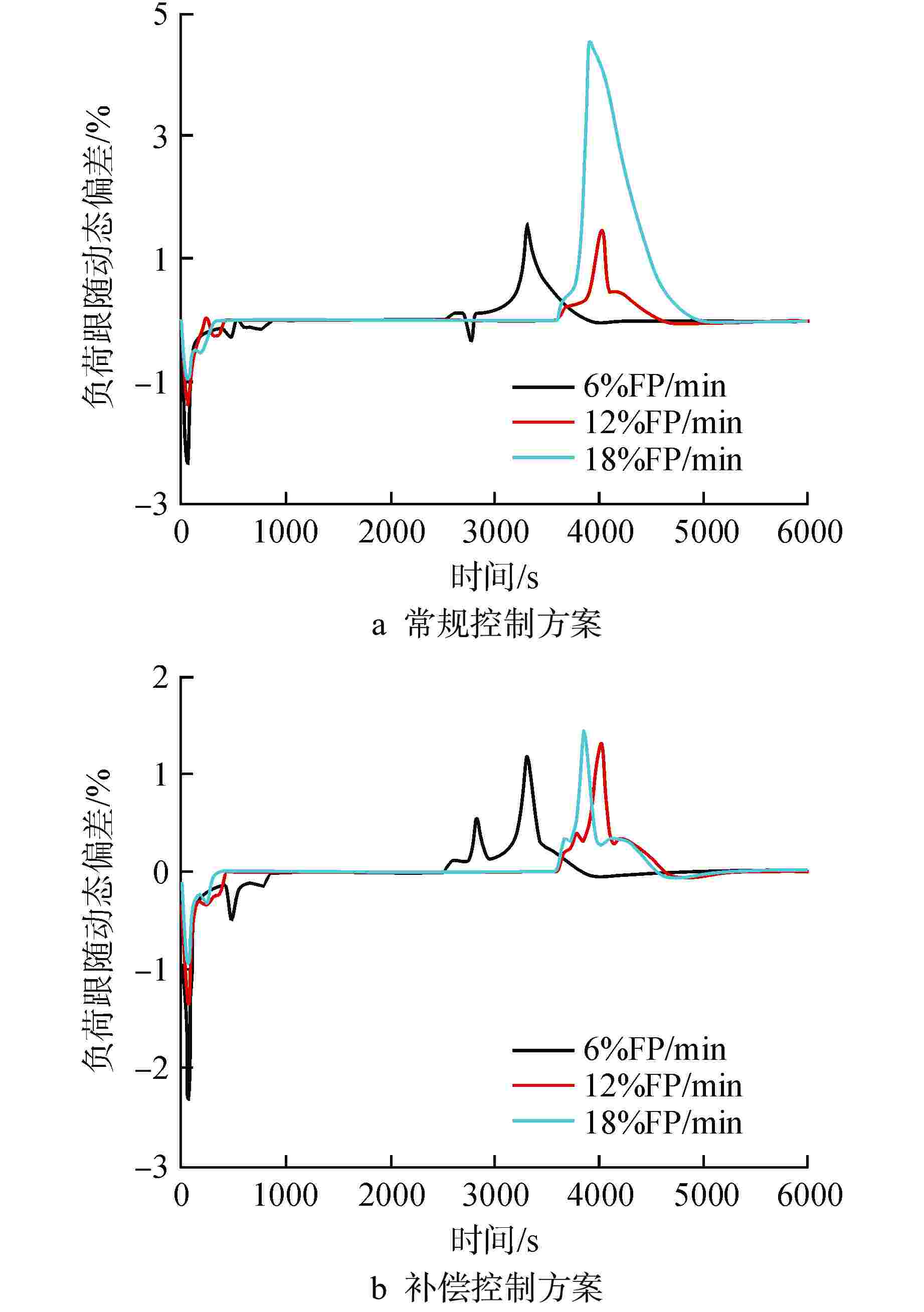
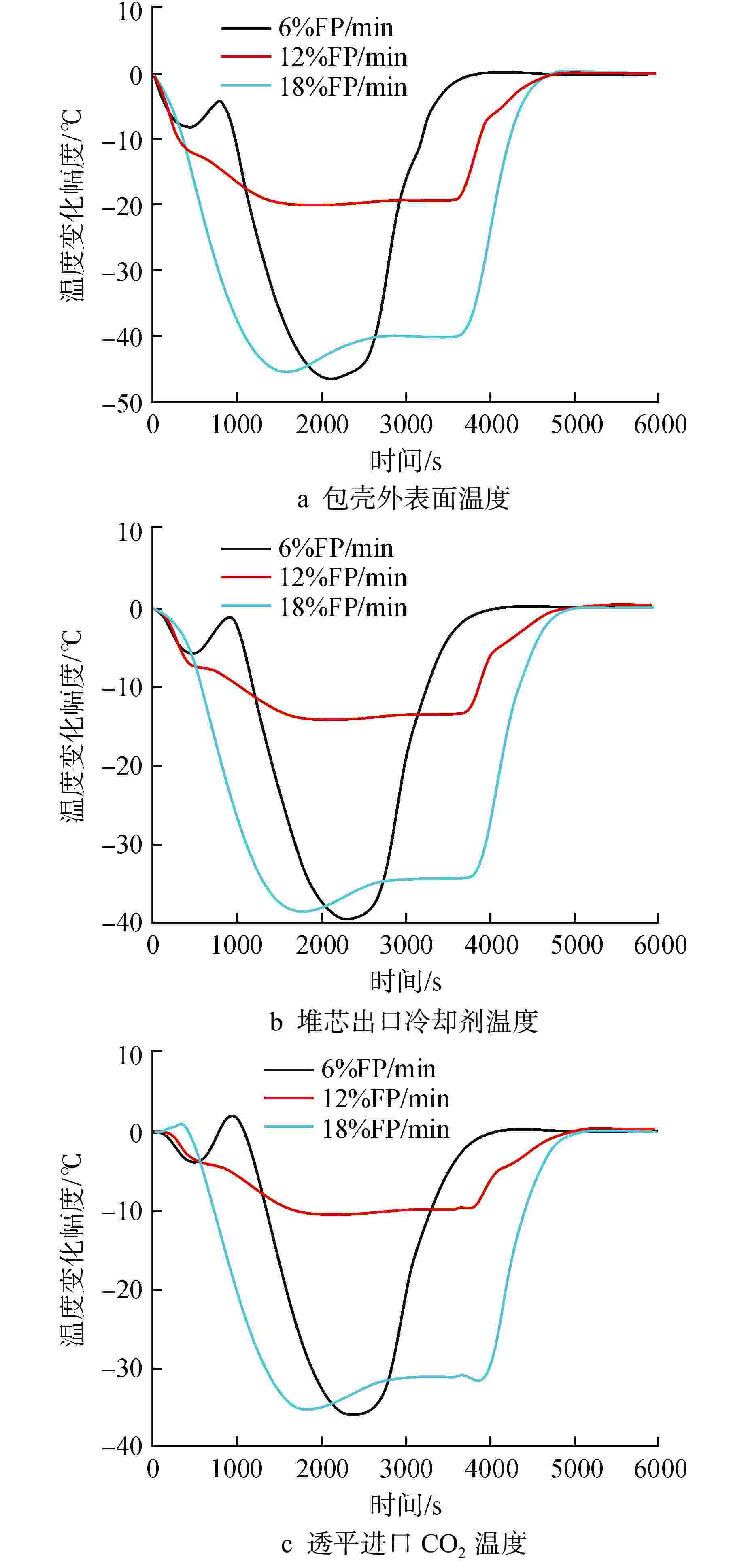
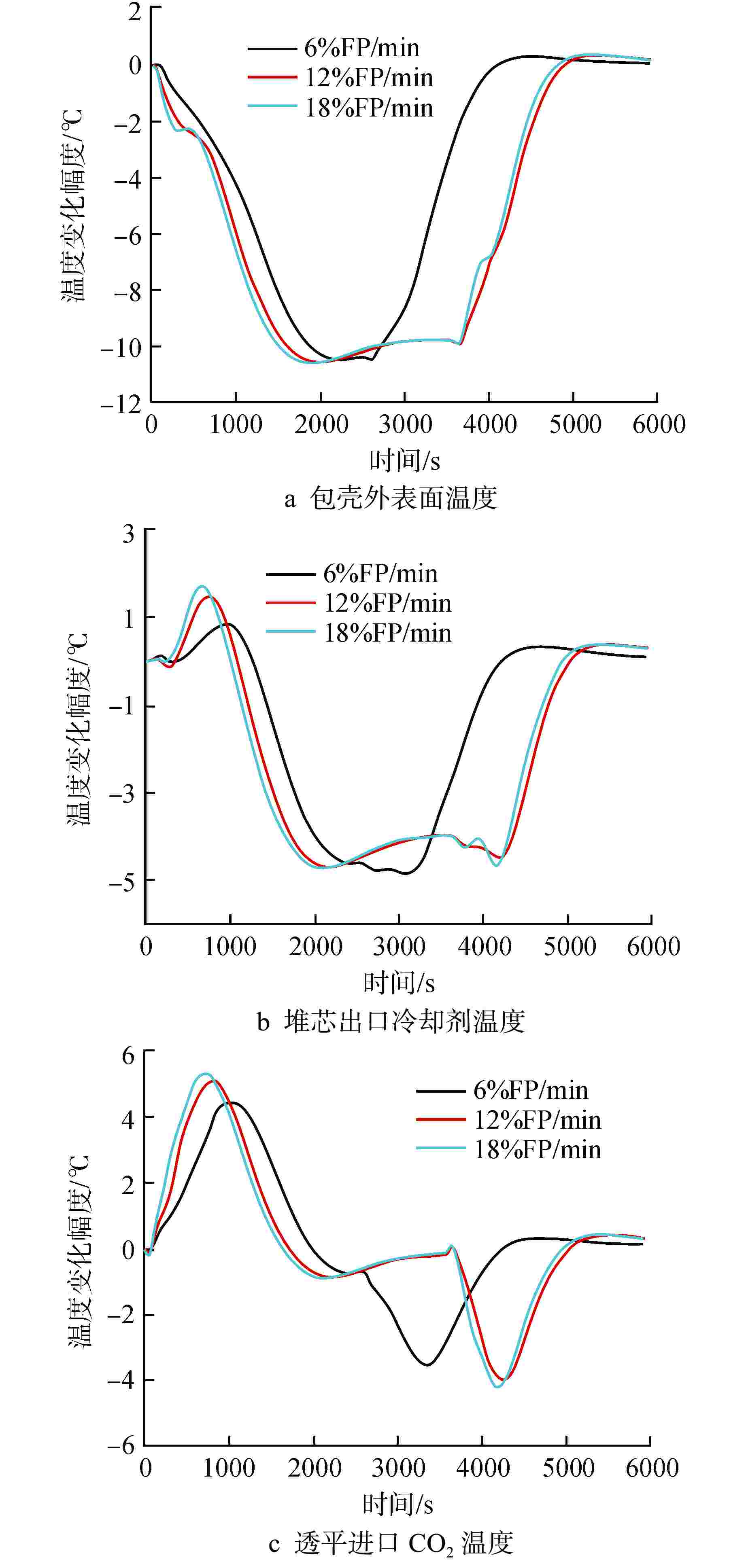
摘要: 自然循环铅冷快堆与超临界二氧化碳(S-CO2)布雷顿循环耦合发电系统是未来先进核能系统的发展方向。基于Apros软件搭建了该耦合发电系统的动态模型,并设计了2种反应堆控制方案,一种为参考压水堆堆芯功率控制系统的常规控制方案,另一种为添加控制棒棒位限制的补偿控制方案。研究结果表明,在3%FP/min(FP为满功率)的小变负荷速率下,2种控制方案下的负荷跟随动态偏差皆在−2%~1%之间,但对于堆芯出口冷却剂温度的稳定,补偿控制方案优于常规控制方案;在6%FP/min~18%FP/min的大变负荷速率下,常规控制方案下的堆芯出口温度变化幅度为−40~0℃,而补偿控制方案下的堆芯出口温度的变化幅度为−5~2℃。因此,补偿控制方案可作为自然循环铅冷快堆控制的有效手段。
-
关键词:
- 铅冷快堆 /
- 自然循环 /
- S-CO2布雷顿循环 /
- 反应堆控制
Abstract: The coupled power generation system of natural circulation lead cooled fast reactor with supercritical carbon dioxide (S-CO2) Brayton cycle is the development trend of advanced nuclear energy systems in the future. Based on the software Apros, a dynamic model of the coupled power generation system was built, and two reactor control schemes were designed, one of which was the conventional control scheme of the reference core power control system of pressurized water reactor, and the other was the compensation control scheme with rod position limit of control rods. The research results showed that under a small variable load rate of 3% FP/min (FP is short for full power), the dynamic deviation of load following under both control schemes was between −2% and 1%, however, for the stability of core outlet coolant temperature, the compensation control scheme was superior to the conventional control scheme; at a large variable load rate of 6%FP/min-18%FP/min, the variation range of core outlet temperature under conventional control was −40℃-0℃, while the variation range of the core outlet temperature under compensation control was −5℃-2℃. Therefore, the compensation control scheme can be used as an effective means for the control of natural circulation lead cooled fast reactor.-
Key words:
- Lead cooled fast reactor /
- Natural circulation /
- S-CO2 Brayton cycle /
- Reactor control
-
表 1 S-CO2布雷顿循环的多参数优化结果
Table 1. Multiple Parameter Optimization Results of S-CO2 Brayton Cycle
参数 总压比 分流比 循环最低温度/℃ 循环最高温度/℃ 高温回热器回热度 低温回热器回热度 循环最低压力/MPa 优化范围 2~3.3 0.4~0.9 35~45 440~465 0.8~0.95 0.8~0.95 8.5~10 优化结果 2.126 0.641 35.09 464.99 0.95 0.95 8.507 表 2 堆芯区域热工水力模拟结果验证
Table 2. Thermal Hydraulic Simulation Results of Core Area
位置 内部燃料区 中间燃料区 外部燃料区 控制棒区 温度文
献值/℃温度模
拟值/℃相对
误差/%温度文
献值/℃温度模
拟值/℃相对
误差/%温度文
献值/℃温度模
拟值/℃相对
误差/%温度文
献值/℃温度模
拟值/℃相对
误差/%1 667.87 681.92 2.10 717.57 721.62 0.56 653.73 642.06 1.79 642.13 684.68 6.63 2 487.2 489 0.37 498.67 498 0.13 479.21 482.7 0.73 478.99 484.6 1.17 3 479.65 481.3 0.34 490.73 489.4 0.27 472.82 475.5 0.57 472.07 476.4 0.92 位置1—芯块中心;位置2—包壳外表面;位置3—冷却剂;表2中相对误差为绝对值 表 3 耦合发电系统动态模型稳态验证结果
Table 3. Steady State Validation Results of Dynamic Model for Coupled Power Generation System
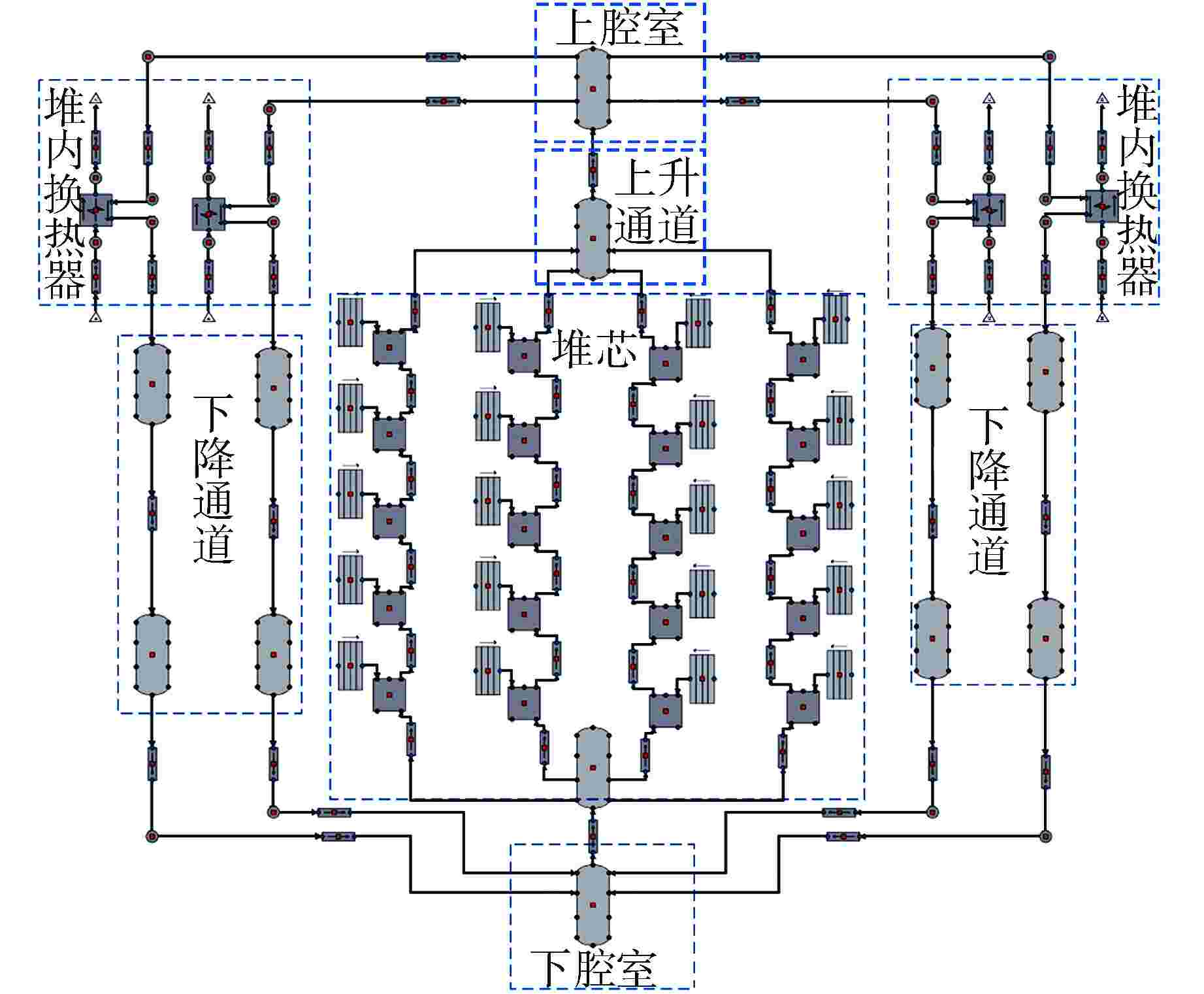
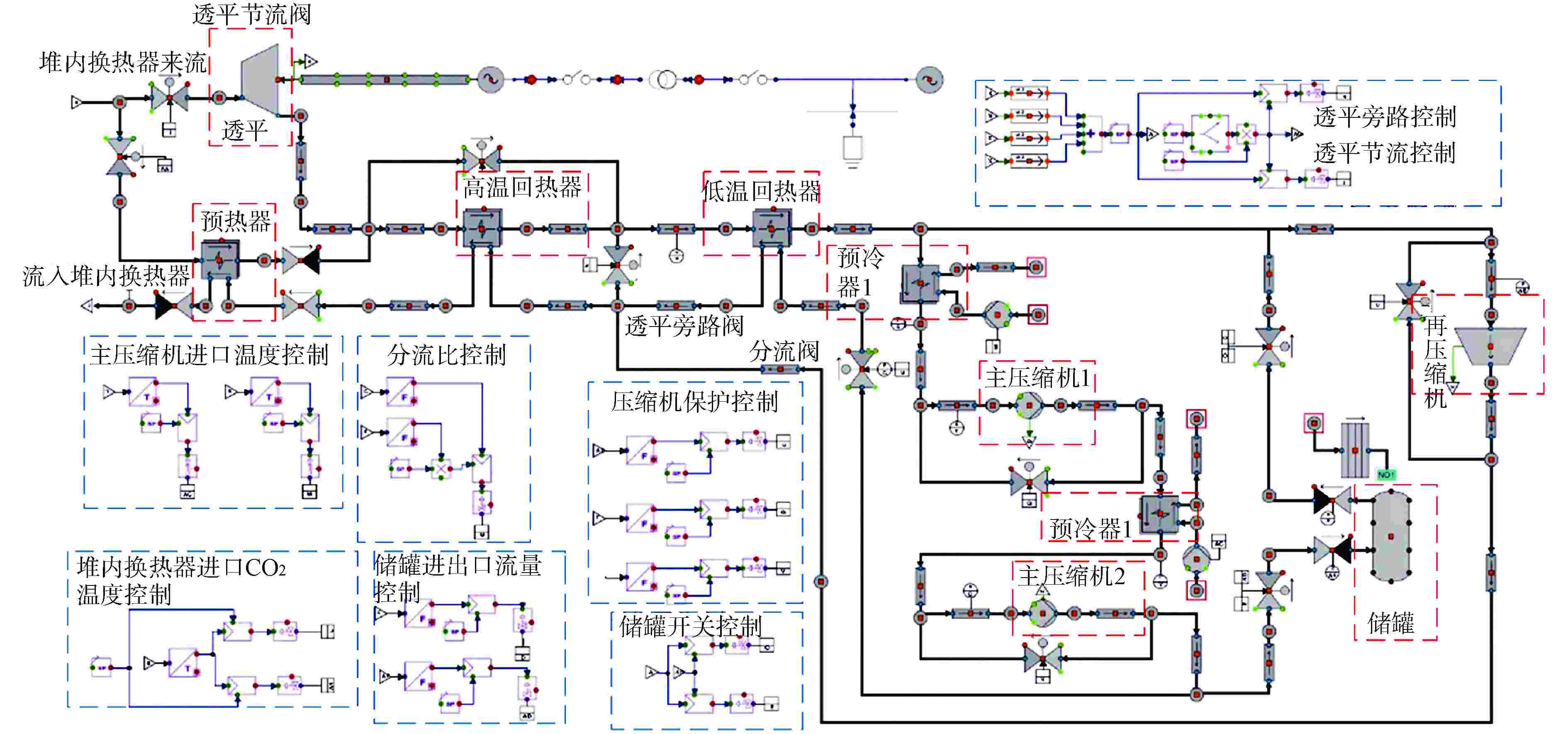
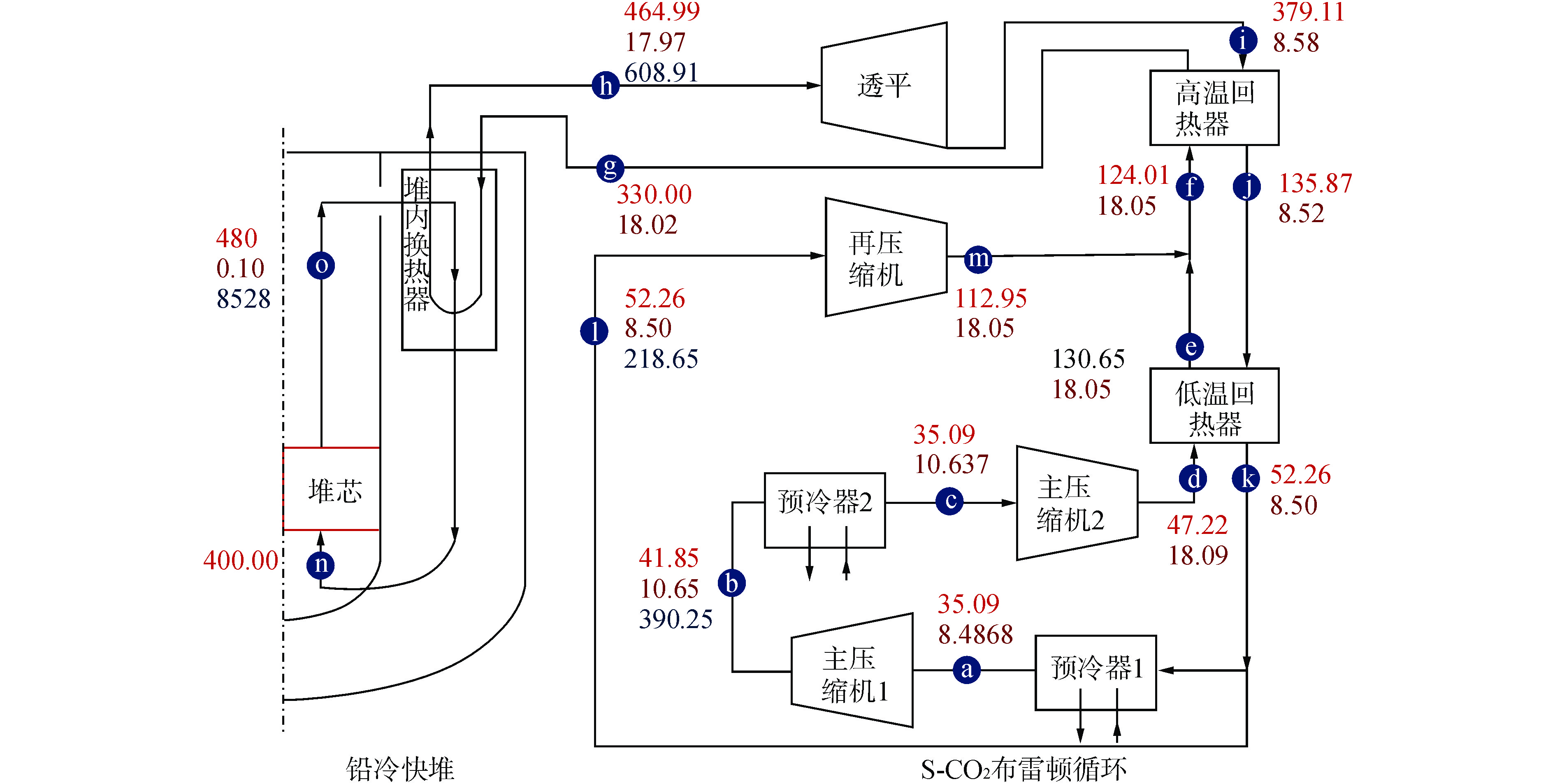
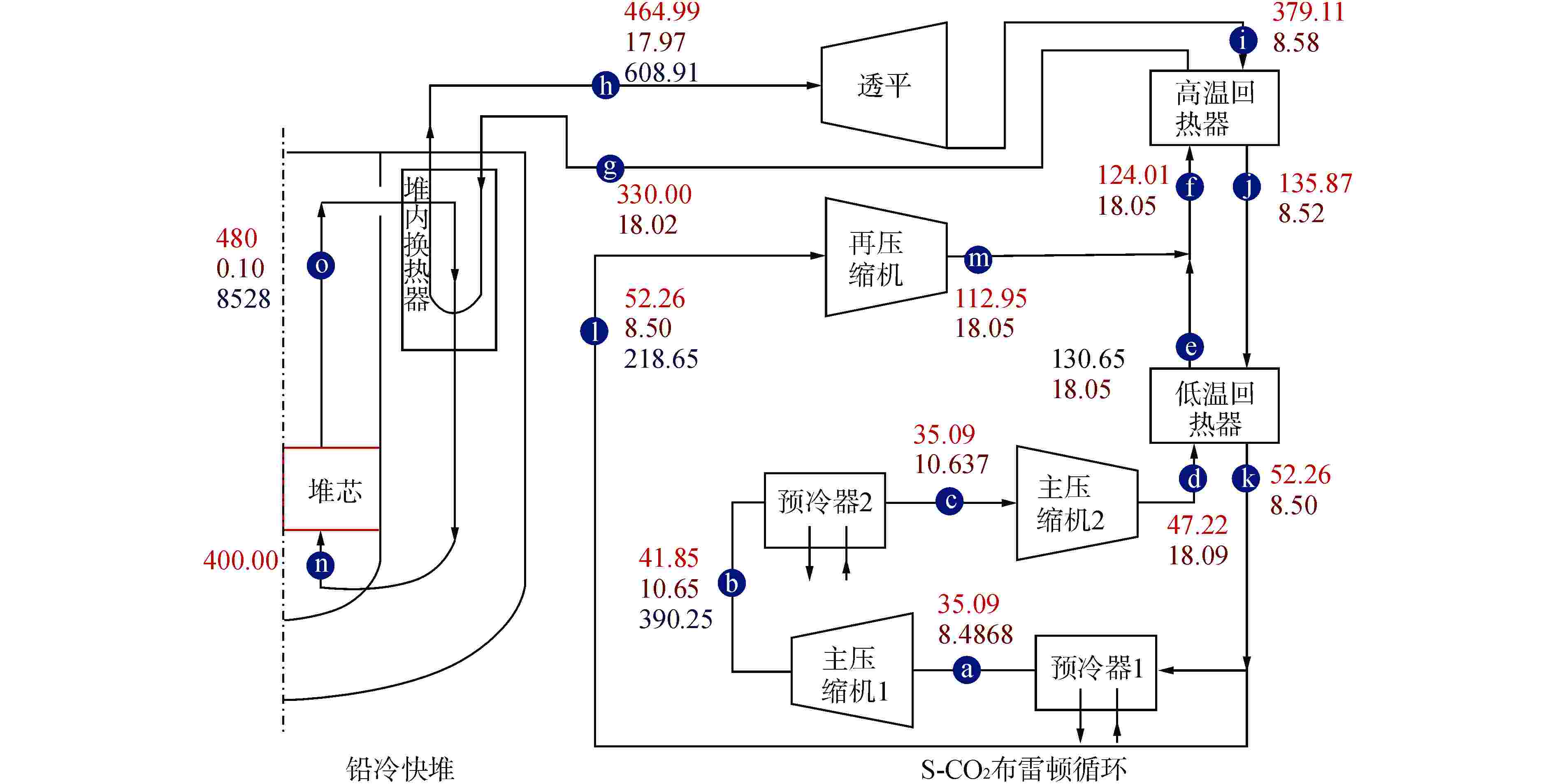
节点 温度设计值/℃ 温度模拟值/℃ 温度相对误差/% 压力设计值/MPa 压力模拟值/MPa 压力相对误差/% a 35.09 35.10 −0.03 8.48 8.34 −1.72 b 41.85 44.42 −6.14 10.65 10.71 0.48 c 35.09 35.10 −0.03 10.63 10.66 0.23 d 47.22 44.88 4.95 18.09 18.46 2.05 e 130.65 133.92 −2.50 18.05 18.05 −0.02 f 124.01 122.49 1.22 18.05 17.96 −0.52 g 330.00 330.00 0.00 18.02 17.93 −0.52 h 464.99 465.51 −0.11 17.97 17.88 −0.52 i 379.11 378.77 0.09 8.58 8.50 −0.98 J 135.87 134.13 1.28 8.52 8.44 −1.01 k 52.26 50.61 3.16 8.50 8.43 −0.96 l 52.26 50.61 3.16 8.50 8.43 −0.96 m 112.95 115.02 −1.83 18.05 17.96 −0.52 N 400.00 399.79 0.05 0.87 o 480.00 480.27 −0.06 0.10 0.10 0 节点标号与图1对应,4个流量值(冷却剂流量、透平进口流量、主压缩机进口流量、再压缩机进口流量)的模拟值与设计值相对误差分别为−0.03%、−0.47%、−0.47%、−0.47% -
[1] MOISSEYTSEV A, SIENICKI J J. Transient accident analysis of a supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle energy converter coupled to an autonomous lead-cooled fast reactor[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2008, 238(8): 2094-2105. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2007.11.012 [2] 赵鹏程. 小型自然循环铅冷快堆SNCLFR-100一回路主冷却系统热工安全分析[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017. [3] WU P, MA Y D, GAO C T, et al. A review of research and development of supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle technology in nuclear engineering applications[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2020, 368: 110767. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2020.110767 [4] PONCIROLI R, CAMMI A, DELLA BONA A, et al. Development of the ALFRED reactor full power mode control system[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2015, 85: 428-440. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2015.06.024 [5] MOISSEYTSEV A, SIENICKI J J. Development of a plant dynamics computer code for analysis of a supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle energy converter coupled to a natural circulation lead-cooled fast reactor: ANL-06/27 TRN: US0704255[R]. U.S.: Argonne National Lab, 2007. [6] YANG M H, SONG Y, WANG J Y, et al. Temperature control characteristics analysis of lead-cooled fast reactor with natural circulation[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2016, 90: 54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2015.11.029 [7] WAN J S, XIE J Y, WANG P F, et al. Control system design for the once-through steam generator of lead–bismuth cooled reactor based on classical control theory[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2022, 175: 109214. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2022.109214 [8] 张建民. 核反应堆控制[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2002: 172. [9] MA, Y G, MOROSUK T, LUO J, et al. Superstructure design and optimization on supercritical carbon dioxide cycle for application in concentrated solar power plant[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 206: 112290. [10] AL-MALIKI W A K, ALOBAID F, KEZ V, et al. Modelling and dynamic simulation of a parabolic trough power plant[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2016, 39: 123-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2016.01.002 [11] DYREBY J J. Modeling the supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle with recompression[D]. Madison: University of Wisconsin-Madison, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: