Study on New Burnable Poison Material Combinations Based on Long-life Pressurized Water Reactor
-
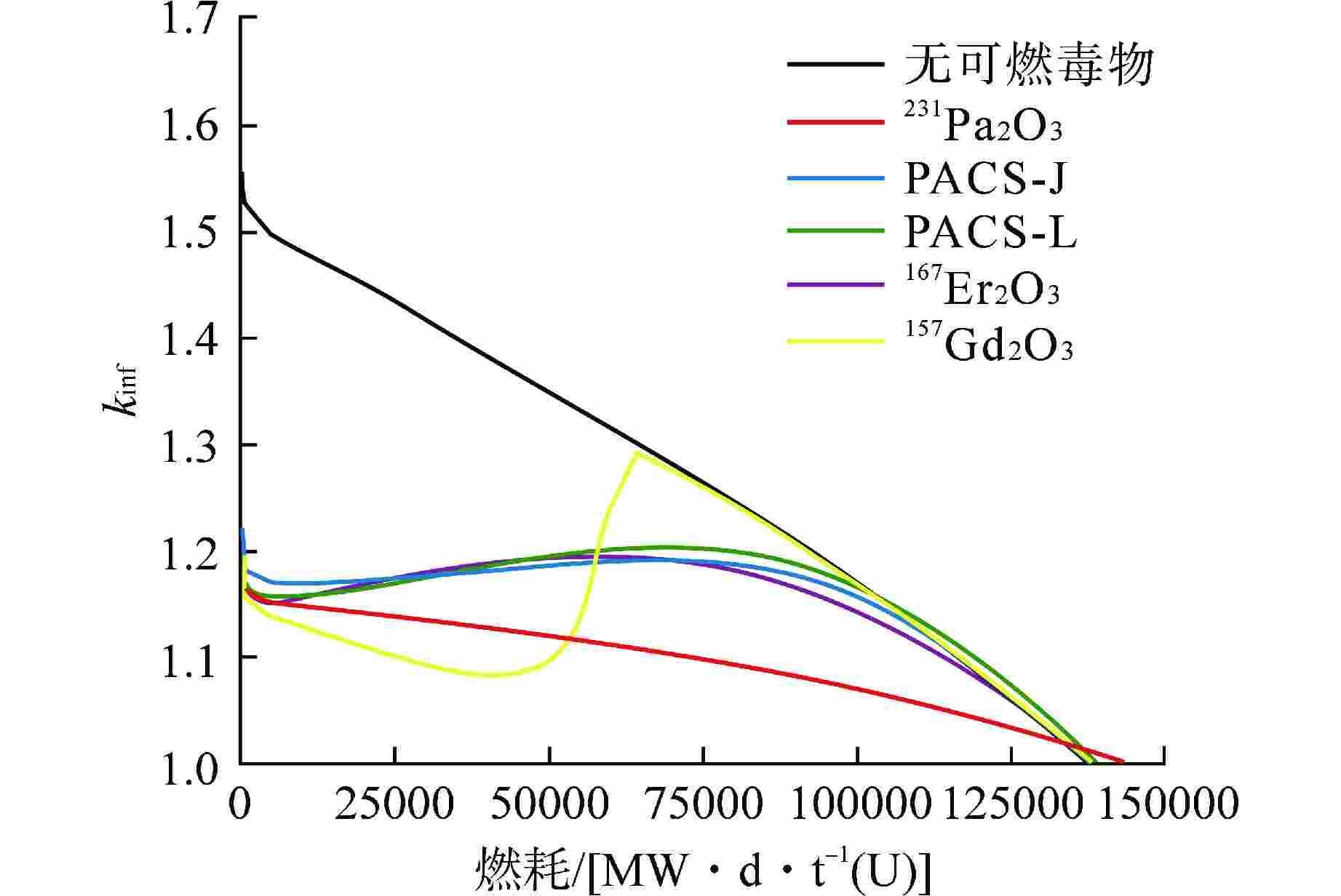
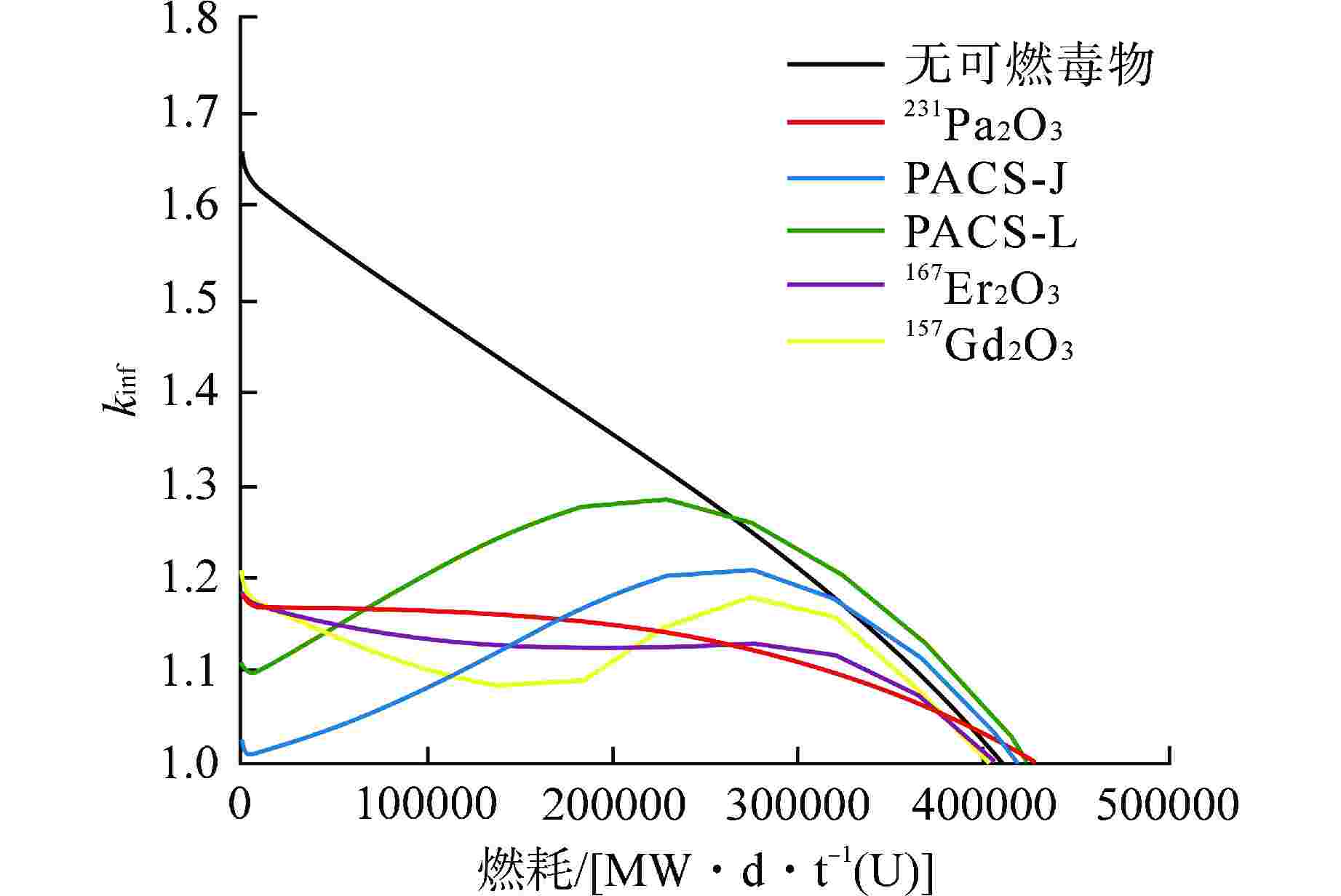
摘要: 长寿期压水堆采用单一可燃毒物组件的设计不是最优选择。为满足长寿期压水堆中可燃毒物对反应性控制的综合需求,本文针对具有较好中子学性能的新型可燃毒物231Pa2O3、PACS-J、PACS-L、167Er2O3和157Gd2O3进行组合研究。结果表明,采用“快燃耗”与“慢燃耗”可燃毒物进行组合的组件可以达到更优的结果。其中对于“低富集度”下的燃料组件,可以选用231Pa2O3与PACS-J、PACS-L与167Er2O3的组合方案;对于“高富集度”下的燃料组件,可以选用231Pa2O3与PACS-J、157Gd2O3和167Er2O3的组合方案。因此,本文通过对“快燃耗”与“慢燃耗”可燃毒物组合设计,可实现对长寿期压水堆初始剩余反应性控制、反应性平缓释放及增加燃耗深度的要求。Abstract: Long-life pressurized water reactors using a single burnable poison assembly design is not the optimal choice. In order to meet the comprehensive requirements of burnable poisons for reactivity control in long-life pressurized water reactors, this paper conducts a combined study on new burnable poisons with good neutronics characteristics: 231Pa2O3, PACS-J, PACS-L, 167Er2O3, and 157Gd2O3. The results show that the combination of "fast burnup" and "slow burnup" burnable poisons can achieve better results. For fuel assemblies with "low enrichment", the combination of 231Pa2O3 with PACS-J, PACS-L with 167Er2O3 can be selected; for fuel assemblies with "high enrichment", the combination of 231Pa2O3 with PACS-J, 157Gd2O3 with 167Er2O3 can be selected. Therefore, this paper realizes the initial excess reactivity control, smooth release of reactivity, and increased burnup level of long-life pressurized water reactors through the combined design of "fast burnup" and "slow burnup" burnable poisons.
-
Key words:
- New burnable poison /
- Combination of burnable poisons /
- Fast burnup /
- Slow burnup
-
表 1 聚碳硼烷-硅氧烷-乙炔基组成[11]
Table 1. Poly-Acetylenic-Carborane-Siloxane Composition
可燃毒物 密度/(g·cm−3) 不同元素的原子数 C H B O Si PACS-J 1.0 14 34 10 2 4 PACS-L 0.9 44 84 10 5 12 表 2 18%燃料富集度较优可燃毒物组合结果
Table 2. Results of the Optimal Burnable Poison Combination with 18% Fuel Enrichment
可然毒物组合 相较于无可燃毒物
组件的燃耗深度变化/
[MW·d·t−1(U)]相较于含单一“快燃耗”
可燃毒物组件的反应
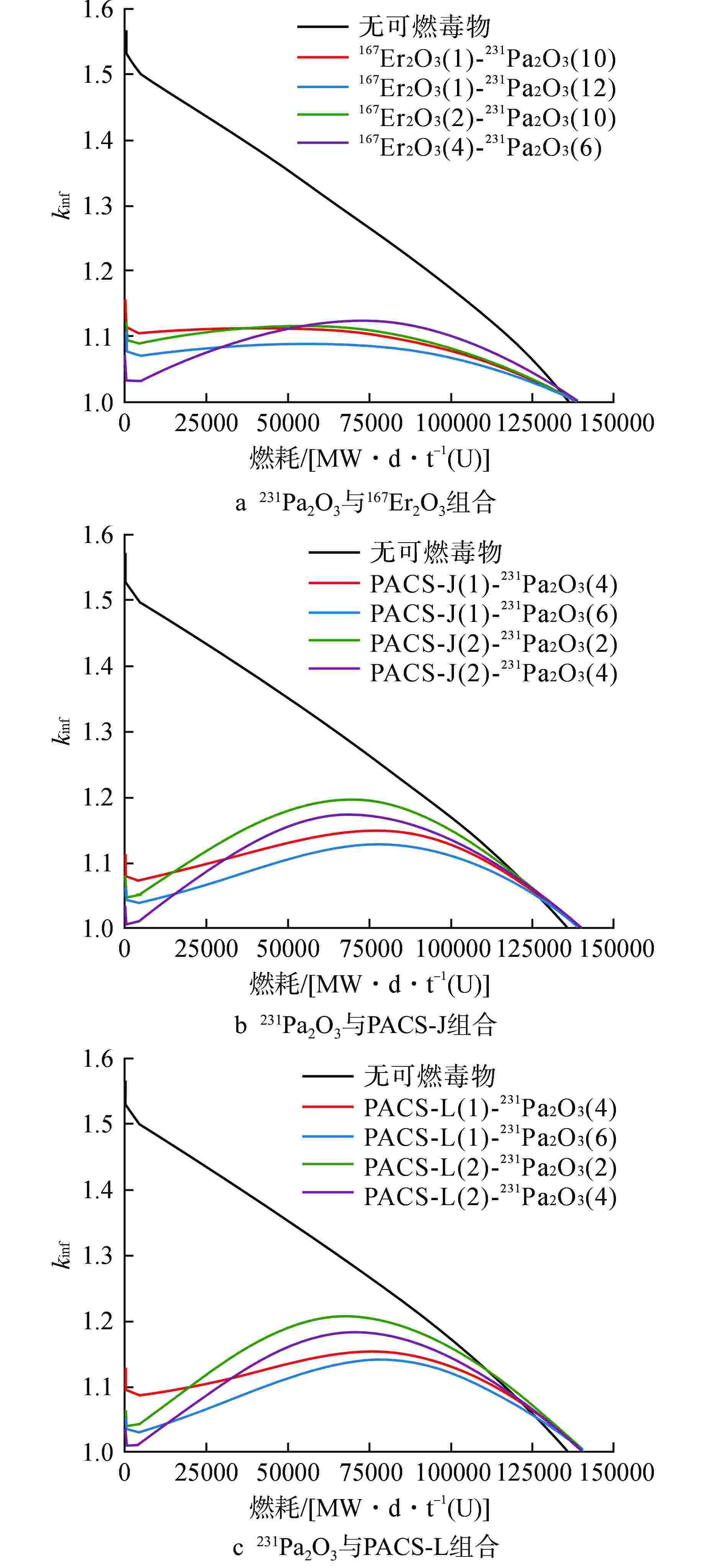
性波动变化167Er2O3(1)-231Pa2O3(12) +5500 −0.07 PACS-J(1)-231Pa2O3 (6) +7790 −0.06 PACS-L(1)-231Pa2O3(6) +5040 −0.11 表 3 60%燃料富集度较优可燃毒物组合结果
Table 3. Results of the Optimal Burnable Poison Combination with 60% Fuel Enrichment
可然毒物组合 相较于无可燃毒物
组件的燃耗深度变化/
[MW·d·t−1 (U)]相较于含单一“快燃耗”
可燃毒物组件的
反应性波动变化167Er2O3(1)-231Pa2O3(12) +18336 −0.1 157Gd2O3(1)-231Pa2O3(10) −4581 −0.04 PACS-J(1)-231Pa2O3(10) +13752 −0.09 -
[1] GALPERIN A, SEGEV M, RADKOWSKY A. Substitution of the soluble boron reactivity control system of a pressurized water reactor by gadolinium burnable poisons[J]. Nuclear Technology, 1986, 75(2): 127-133. doi: 10.13182/NT86-A33855 [2] ALAM S B, ALMUTAIRI B, RIDWAN T, et al. Neutronic investigation of alternative & composite burnable poisons for the soluble-boron-free and long life civil marine small modular reactor cores[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 19591. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55823-2 [3] VAN DER MERWE L, HAH C J. Reactivity balance for a soluble boron-free small modular reactor[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2018, 50(5): 648-653. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2018.01.019 [4] 强胜龙,秦冬,柴晓明,等. PWR堆芯中弥散型可燃毒物的燃耗特性研究[J]. 核动力工程,2014, 35(2): 1-4. [5] XU S K, YU T, XIE J S, et al. Selection of burnable poison in plate fuel assembly for small modular marine reactors[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2022, 54(4): 1526-1533. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2021.10.018 [6] 肖鹏,王健,刘仕倡,等. 基于遗传算法的可燃毒物设计优化方法研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2021, 55(8): 1456-1463. [7] 于涛,刘金聚,谢金森,等. 锕系可燃毒物板状燃料组件燃耗特性研究[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(3): 1-7. [8] CANBAKAN A, HÉBERT A. Accuracy of a 2-level scheme based on a subgroup method for pressurized water reactor fuel assembly models[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2015, 81: 164-173. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2015.03.034 [9] XU S K, YU T, XIE J S, et al. Burnable poison selection and neutronics analysis of plate fuel assemblies[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2021, 9: 729552. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2021.729552 [10] 李满仓,于颖锐,肖鹏,等. 富集同位素用于长循环堆芯可燃毒物的中子学分析[J]. 核动力工程,2019, 40(S2): 74-77. [11] 徐士坤,于涛,谢金森,等. 长寿期压水堆板状燃料组件可燃毒物选型研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2022, 56(1): 113-120. [12] 徐士坤,于涛,谢金森,等. 长寿期板状压水堆组件可燃毒物装载形式选型研究[J]. 核动力工程,2021, 42(6): 5-11. [13] CACUCI D G. Handbook of nuclear engineering: vol. 1: nuclear engineering fundamentals; vol. 2: reactor design; vol. 3: reactor analysis; vol. 4: reactors of generations III and IV; vol. 5: fuel cycles, decommissioning, waste disposal and safeguards[M]. New York: Springer, 2010: 2928. -





 下载:
下载: