Research on Nuclear Signal Generator Based on Signal Characteristics of Pulsed Neutron Detector
-
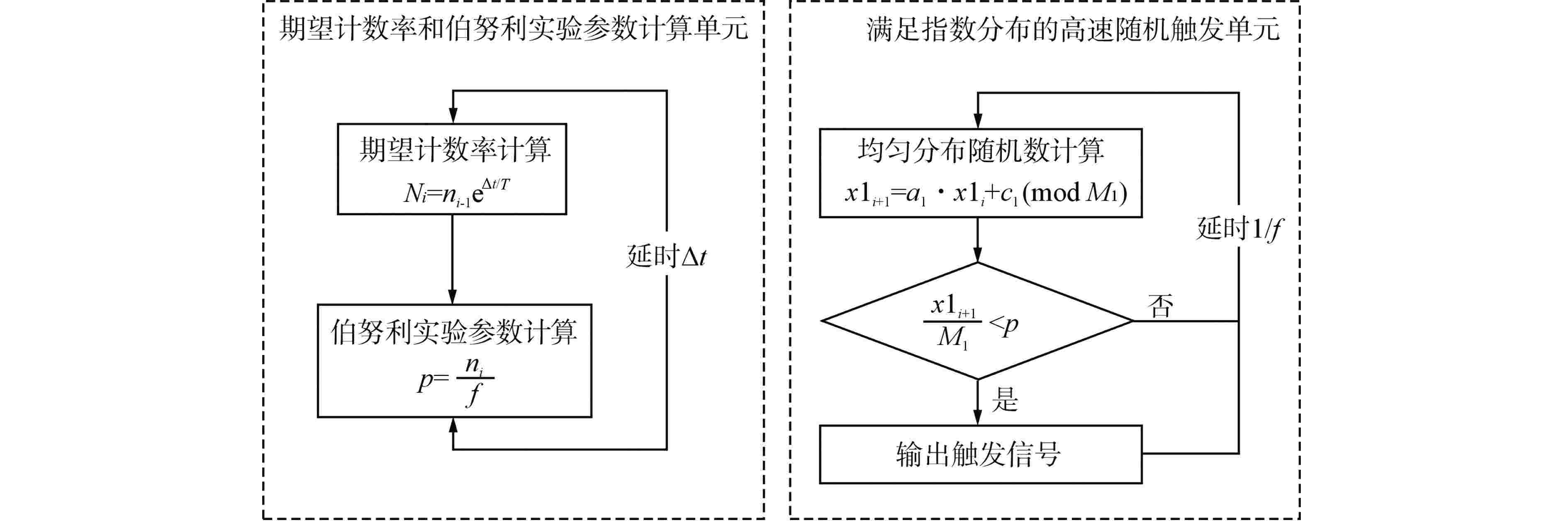
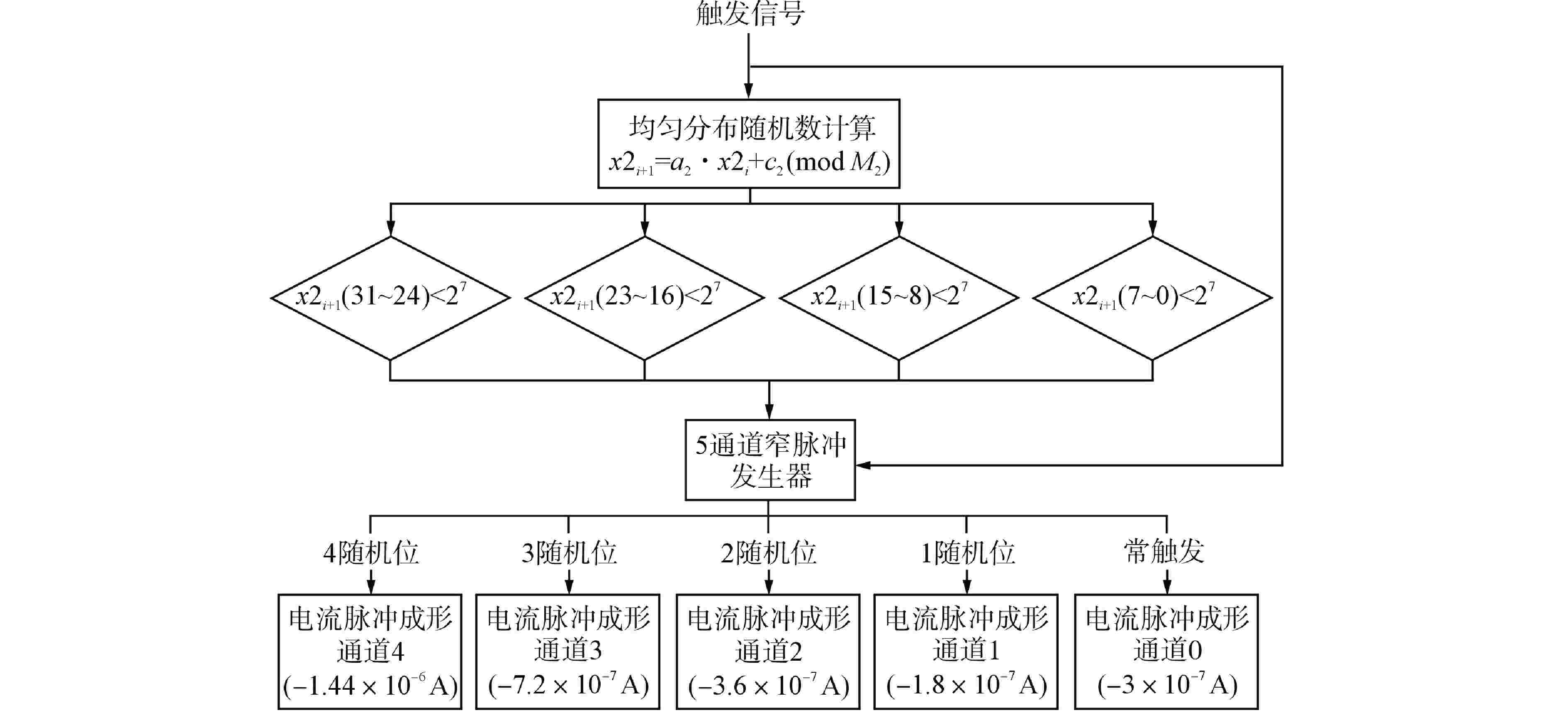
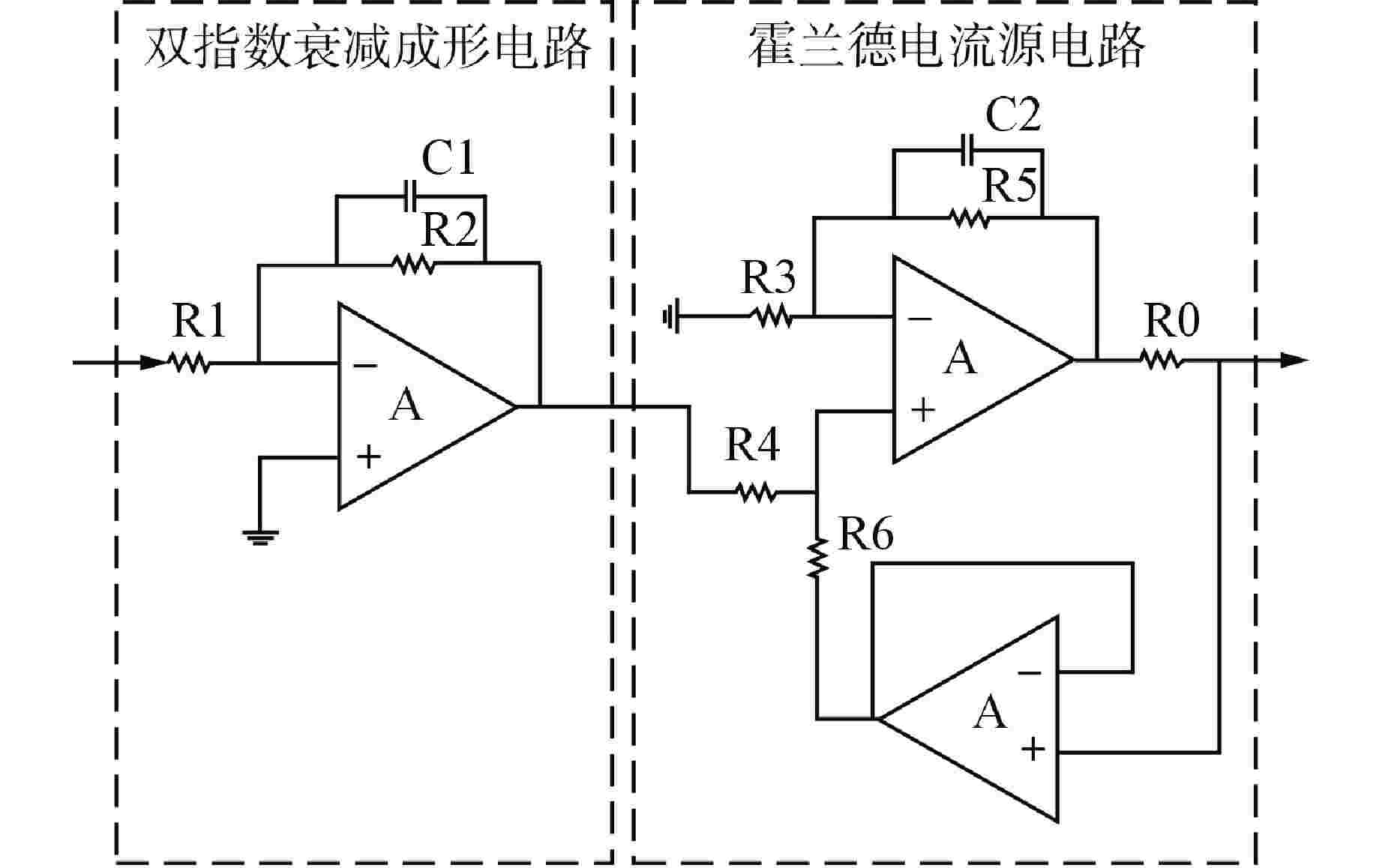
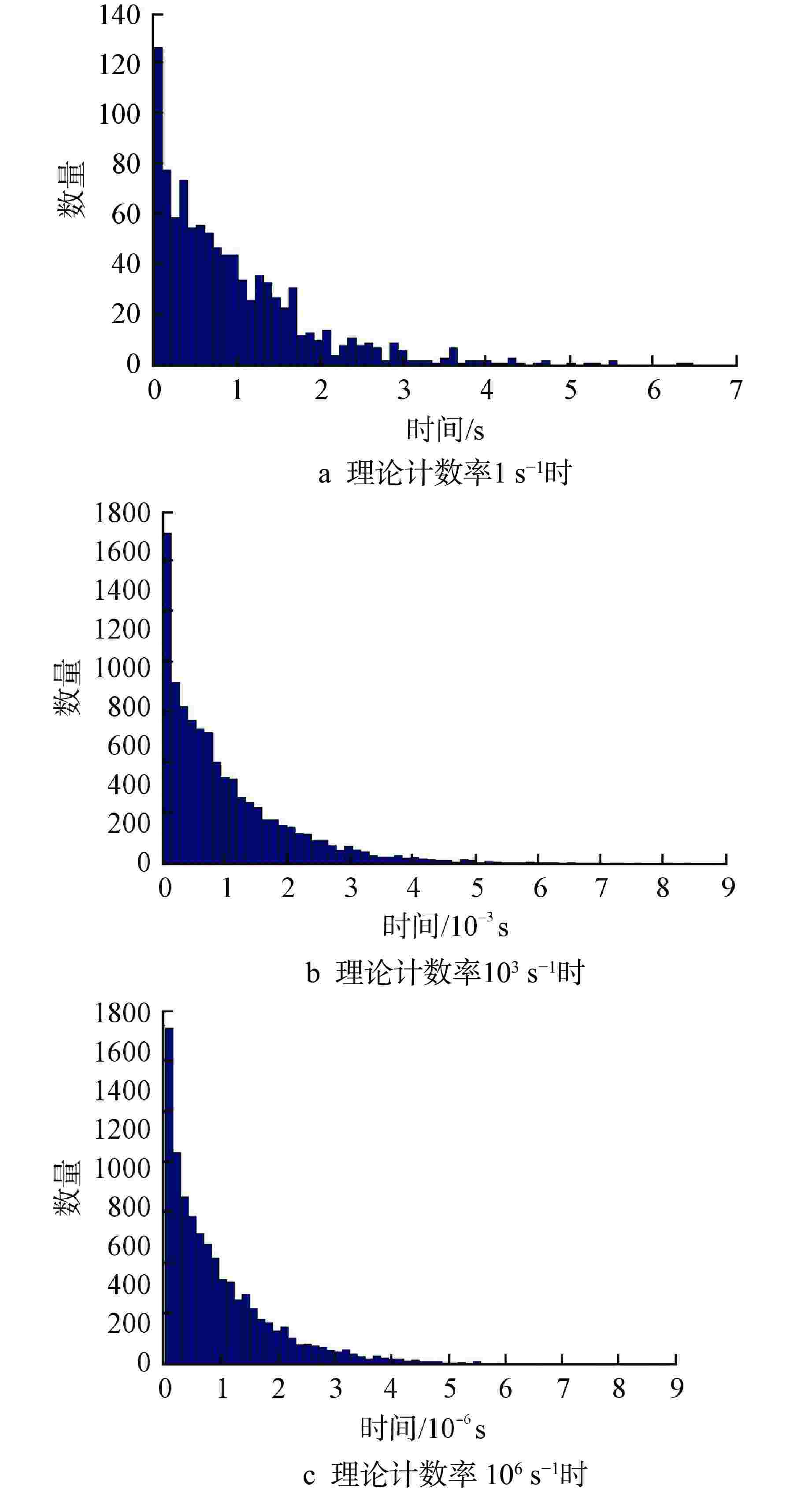
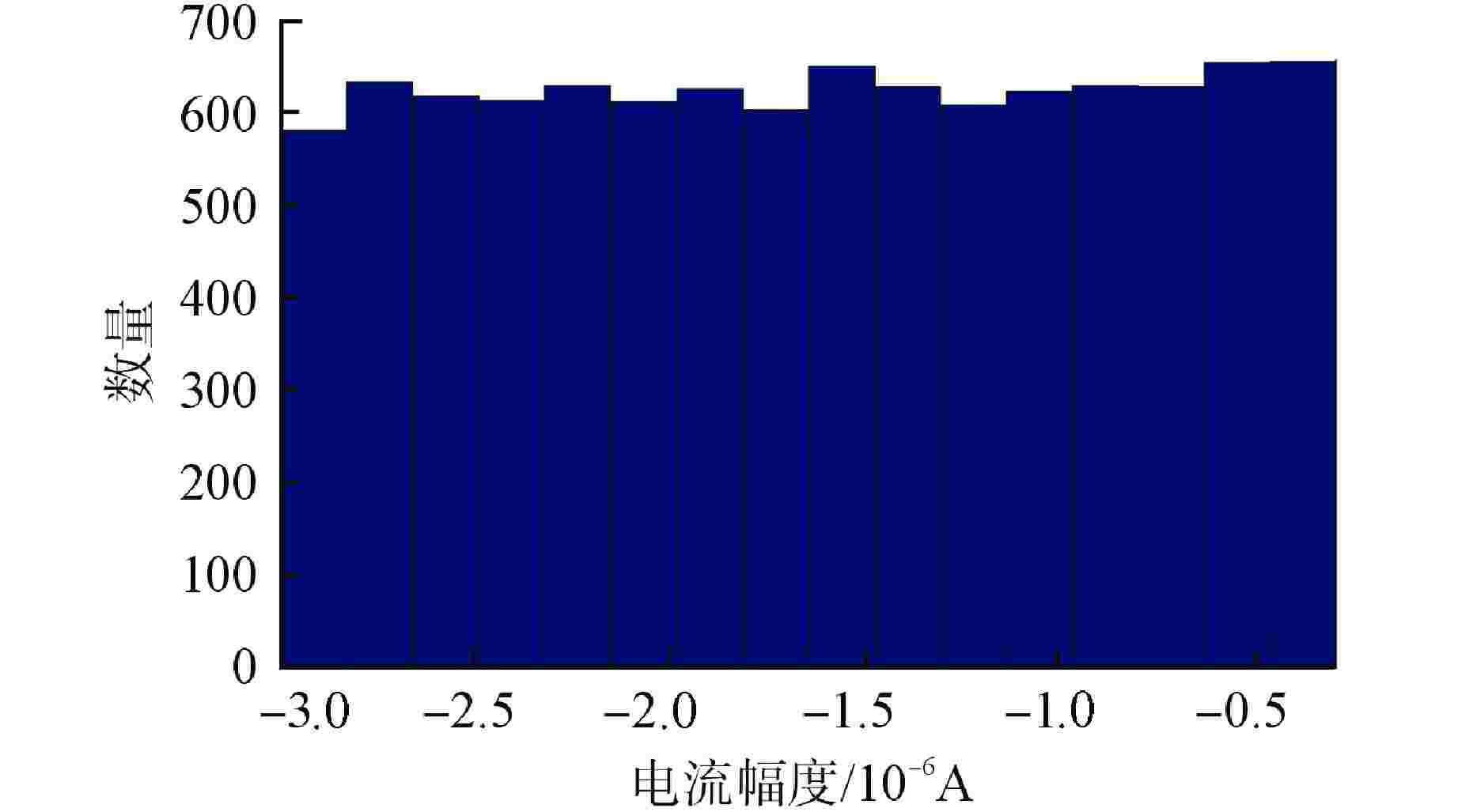
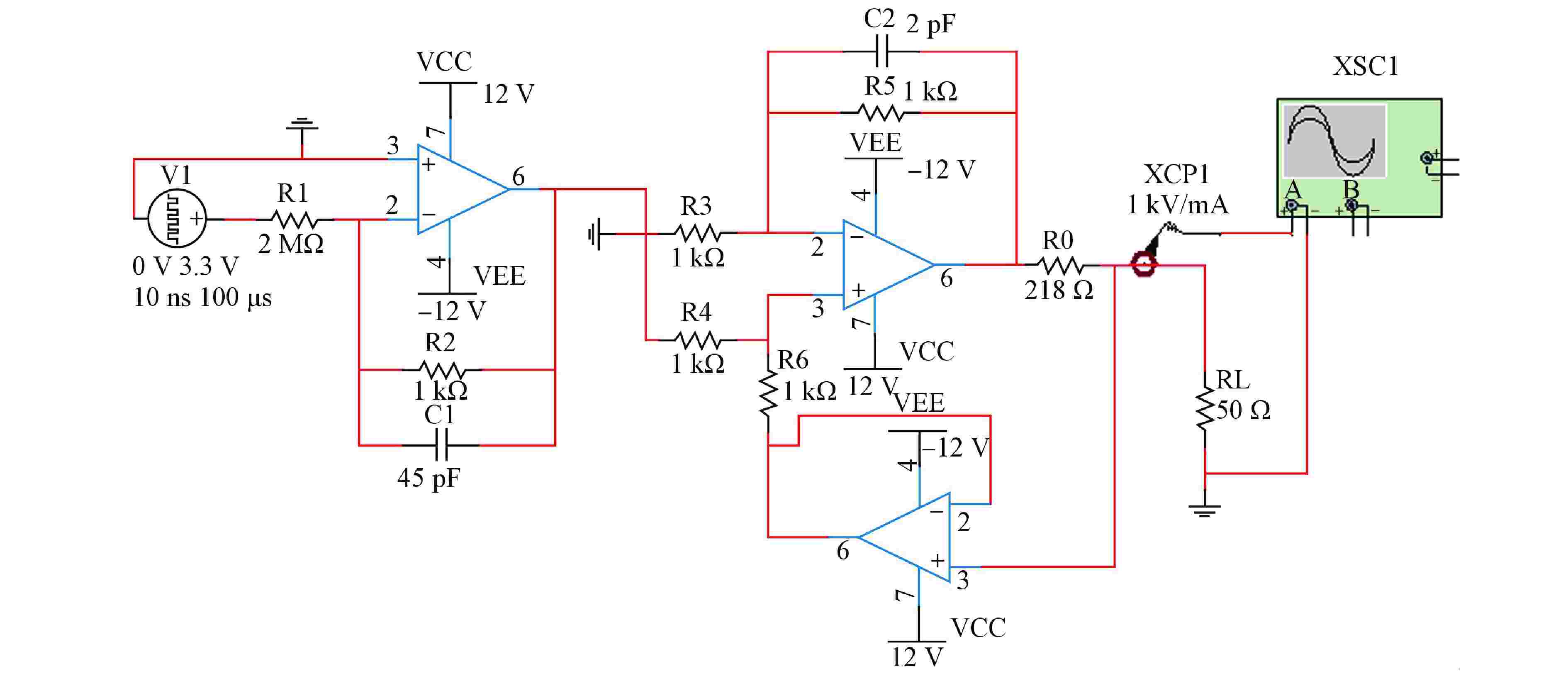
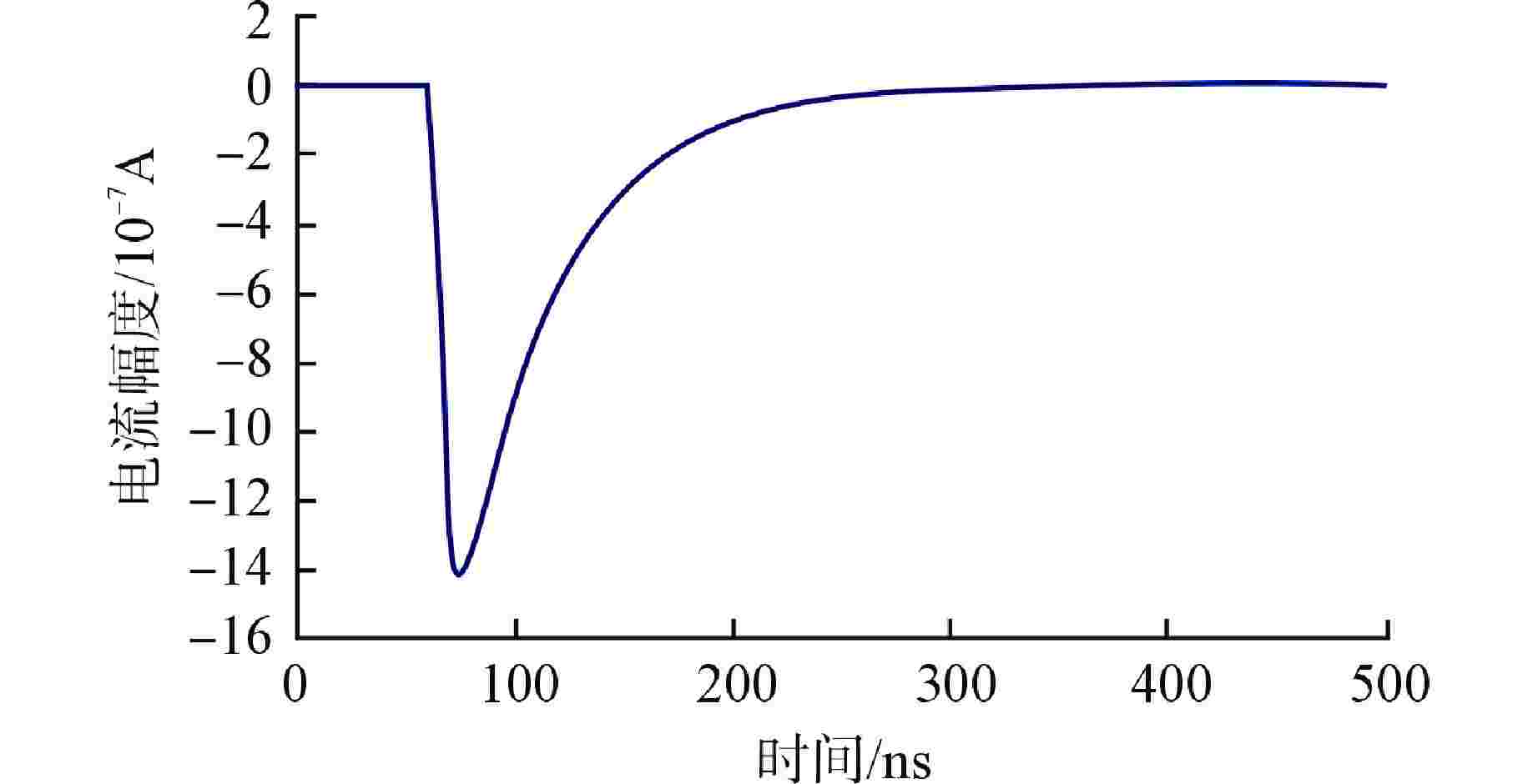
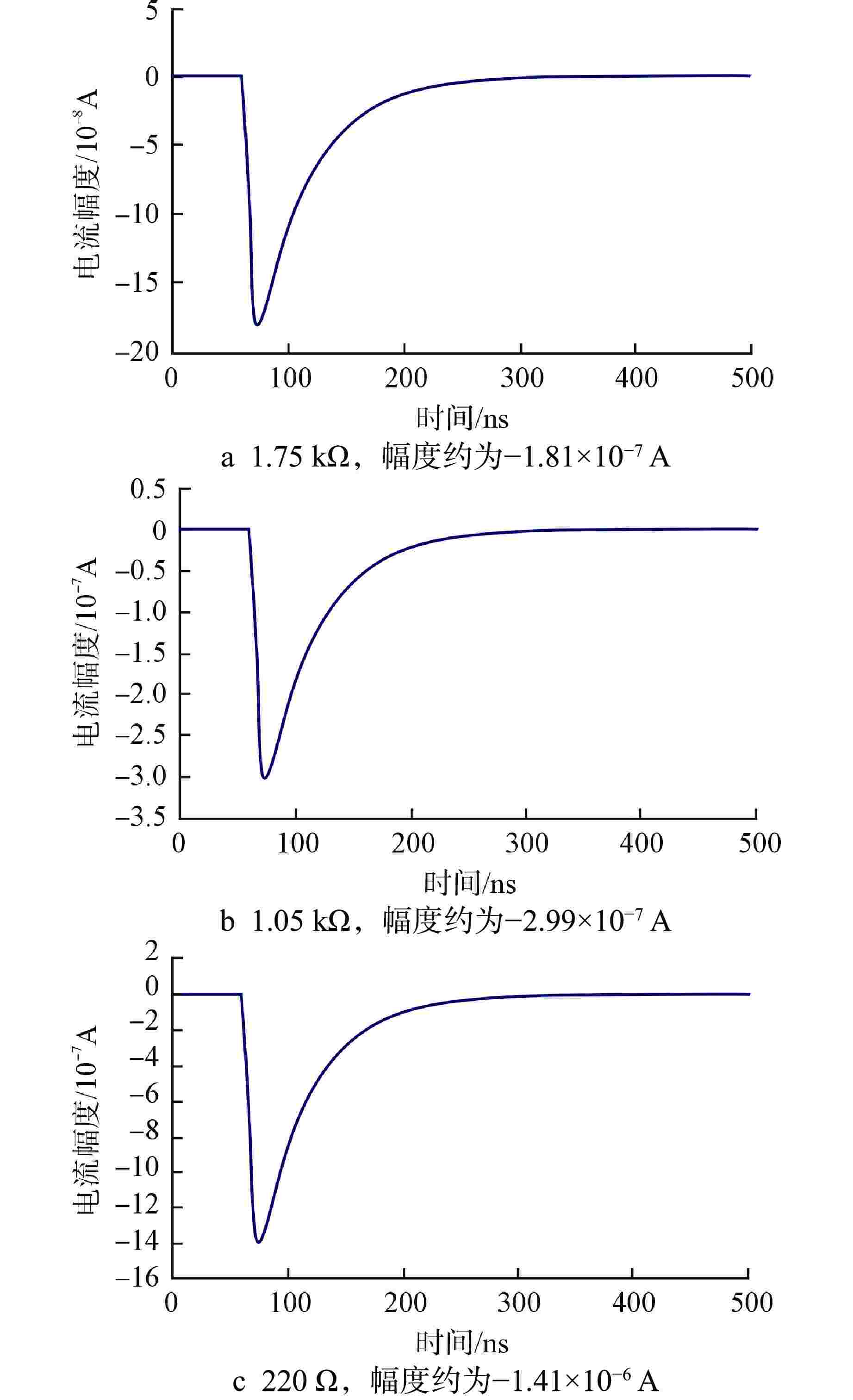
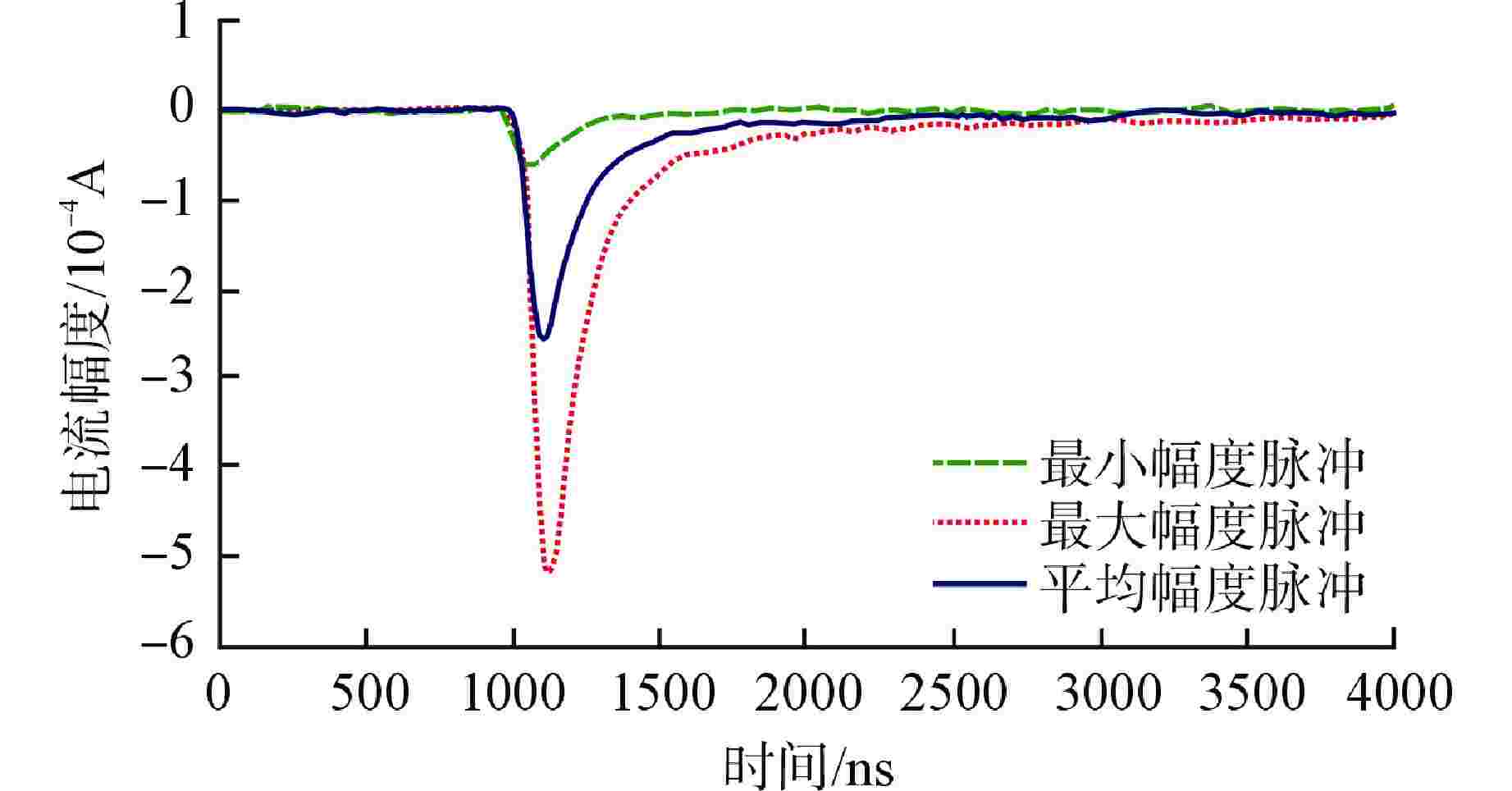
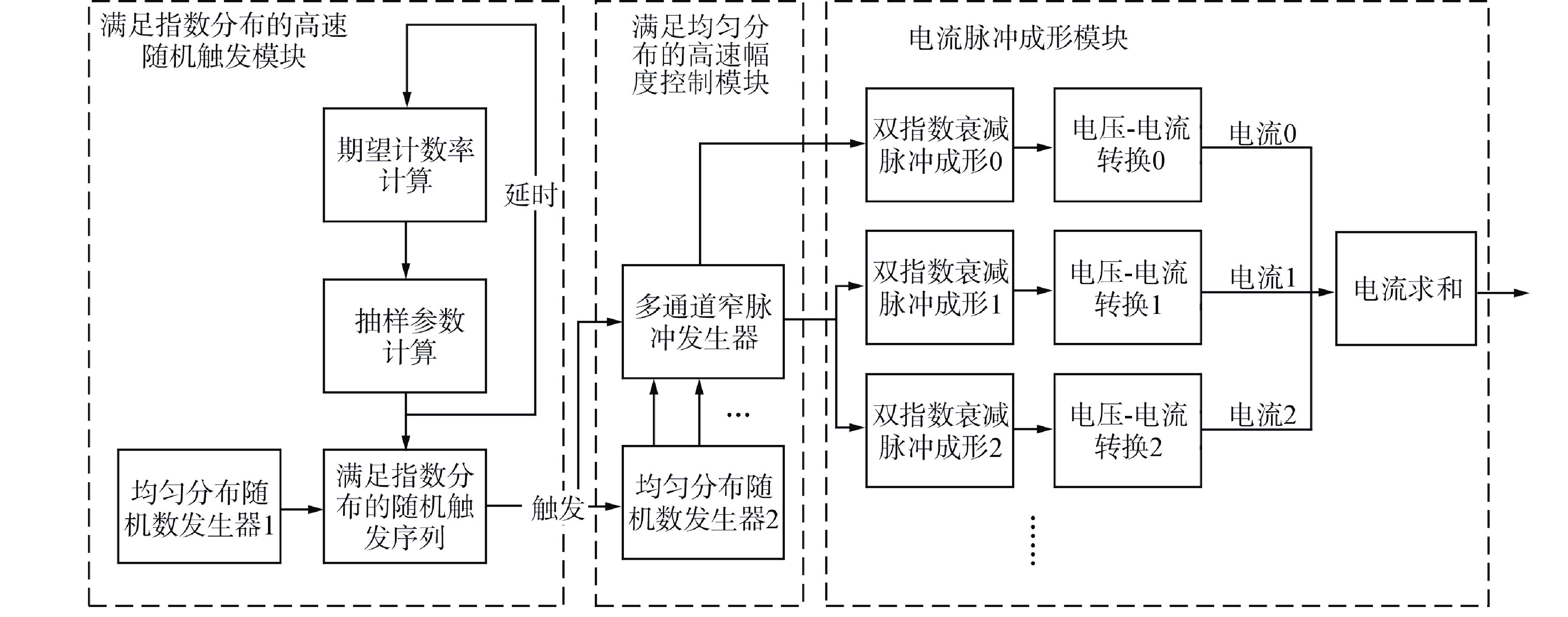
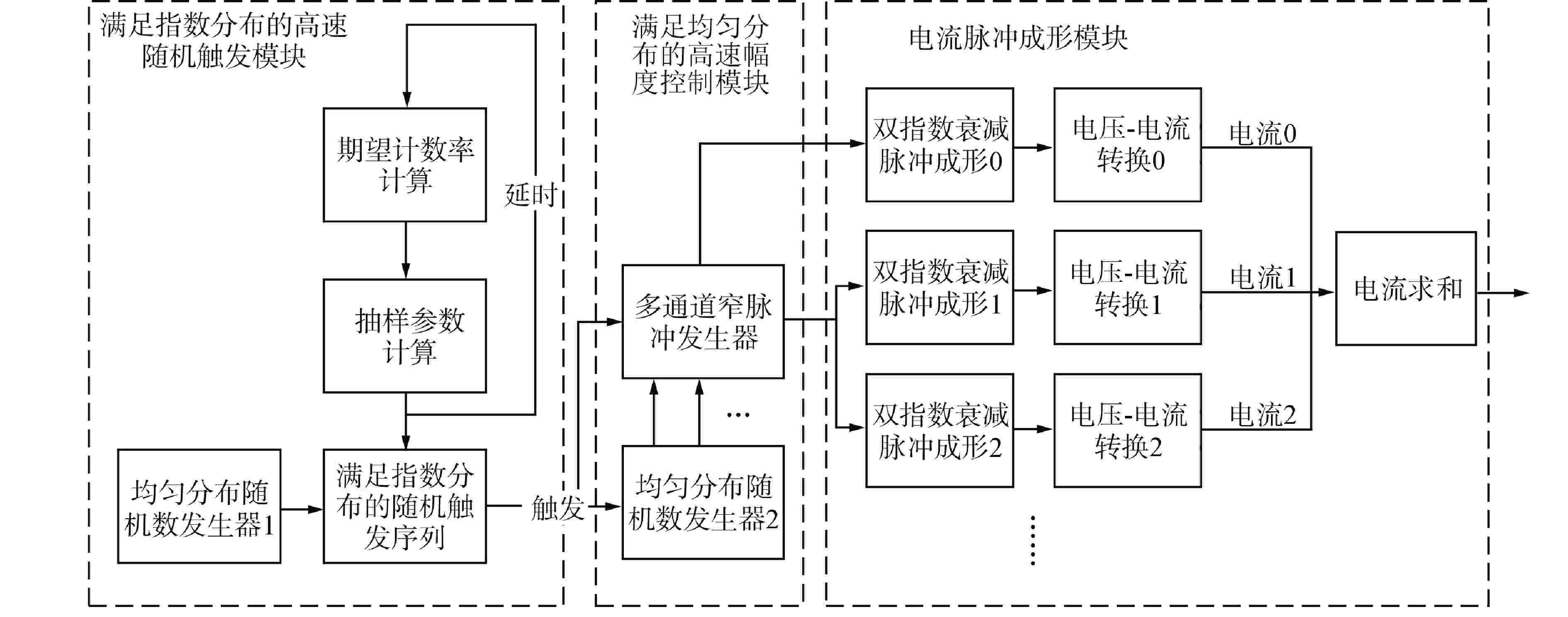
摘要: 脉冲型中子探测器将中子注量率转化为随机微弱电流脉冲信号,由于该信号的特殊性,核测量设备一般需要借助堆上试验验证实际探测性能。由于通过堆上试验的研究方式花费较大且时间受限,本文以涂硼正比计数管这类典型的脉冲型中子探测器为对象,研究了一种脉冲型中子探测器信号模型及其核信号发生器实现方案。通过仿真验证了各关键部分特性,验证结果表明:所提出的核信号发生器方案可以产生满足指数分布的时间间隔序列,单脉冲形状与探测器信号相似,幅度可按均匀分布随机变化。Abstract: Pulsed neutron detector converts neutron fluence rate into random weak current pulse signal. Due to the particularity of this signal, nuclear measurement equipment generally requires reactor tests to verify the actual detection performance. Because of the research method by reactor test costs a lot and has time limit, this paper, based on a typical pulsed neutron detector such as boron-coated proportional counting tube, studies a pulsed detector signal model and its nuclear signal generator implementation scheme. The characteristics of each key part are verified through simulation. The verification results show that: the proposed nuclear signal generator scheme can generate a sequence of time intervals satisfying the exponential distribution, the single current pulse shape is similar to the detector and the amplitude can vary randomly in a uniform distribution.
-
Key words:
- Pulsed neutron detector /
- Nuclear signal generator /
- Random signal
-
表 1 随机数产生方法对比表
Table 1. Comparison of Random Number Generation Methods
性能及参数 乘同余方法 乘加同余方法 电路噪声放大方法 混沌电路方法 振荡器采样方法 容量 $ {2^{s - 2}} $ $ {2^s} $ 理论无上限 理论无上限 理论无上限 稳定性 好,不受环境因素影响 好,不受环境因素影响 差,受环境因素、器件噪声特性影响 差,电路的不准确性限制了模数转换分辨率,也降低了系统,产生随机序列的能力 差,由于噪声导致的相位抖动范围很小,会使得随机序列质量下降 可重现性 好 好 差 差 差 生成速度 受电路运算速度影响,理论可做到10 ns的产生速度 受电路运算速度影响,理论可做到10 ns的产生速度 受电路带宽影响,整体带宽应超过100 MHz,理论上可以做到10 ns的产生速度 受电路带宽影响,整体带宽应超过100 MHz,理论上可以做到10 ns的产生速度 受电路带宽影响,整体带宽应超过100 MHz,理论上可以做到10 ns的产生速度 上标s为计算机中二进制数的最大可能有效位数 -
[1] 毛从光,郭晓强,周辉,等. 高空核电磁脉冲模拟波形的双指数函数拟合法[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2004, 16(3): 336-340. [2] KNOLL G F. Radiation detection and measurement[M]. 4th ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2010: 864. [3] 朱宏亮,刘艳阳,高志宇,等. 半实物仿真堆上试验脉冲信号发生器设计与实现[J]. 核电子学与探测技术,2018, 38(4): 563-567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2018.04.023 [4] 许淑艳. 蒙特卡罗方法在实验核物理中的应用[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社,2006: 306. [5] 过雅南,金大鹏,乔巧,等. 随机脉冲发生器[J]. 核电子学与探测技术,2007, 27(2): 167-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2007.02.001 [6] 韩慧,薛志华,刘松秋,等. 基于模拟贝努里试验的随机脉冲发生器的实现[J]. 核电子学与探测技术,2004, 24(4): 417-420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2004.04.025 [7] 韩春,蔡俊. 基于FPGA的高速伪随机序列发生器设计[J]. 电子测量技术,2013, 36(7): 55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2013.07.013 [8] 童诗白,华成英. 模拟电子技术基础[M]. 第五版. 北京: 高等教育出版社,2015: 525. [9] 胡晓东,董辰辉. MATLAB从入门到精通[M]. 第二版. 北京: 人民邮电出版社,2018: 462. [10] 黄智伟,黄国玉,王丽君. 基于NI Multisim的电子电路计算机仿真设计与分析[M]. 第三版. 电子工业出版社,2017: 288. -





 下载:
下载: