Experimental Study of Geyser Boiling in High-temperature Sodium Heat Pipe at Inclined Angle Condition
-
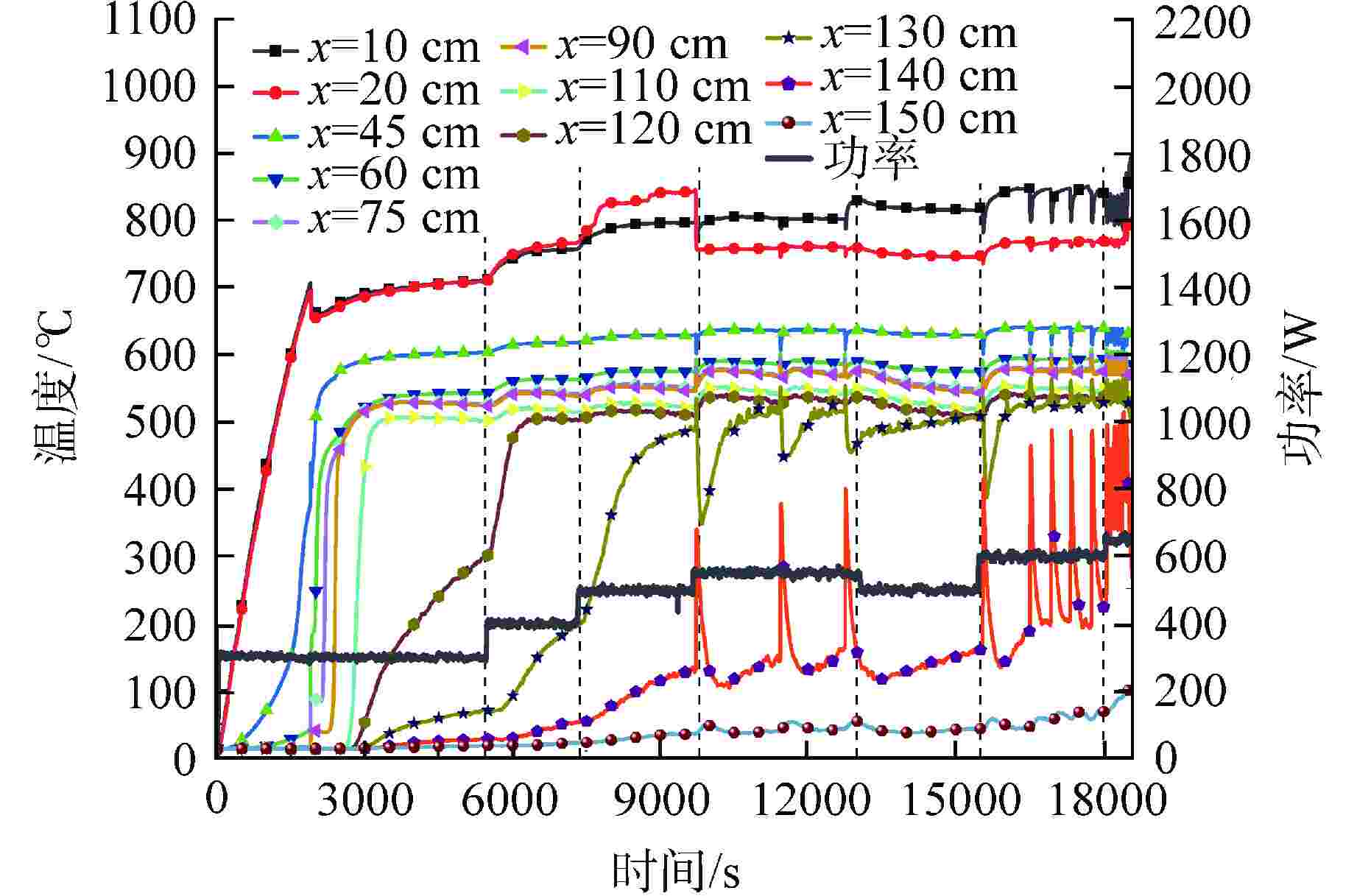
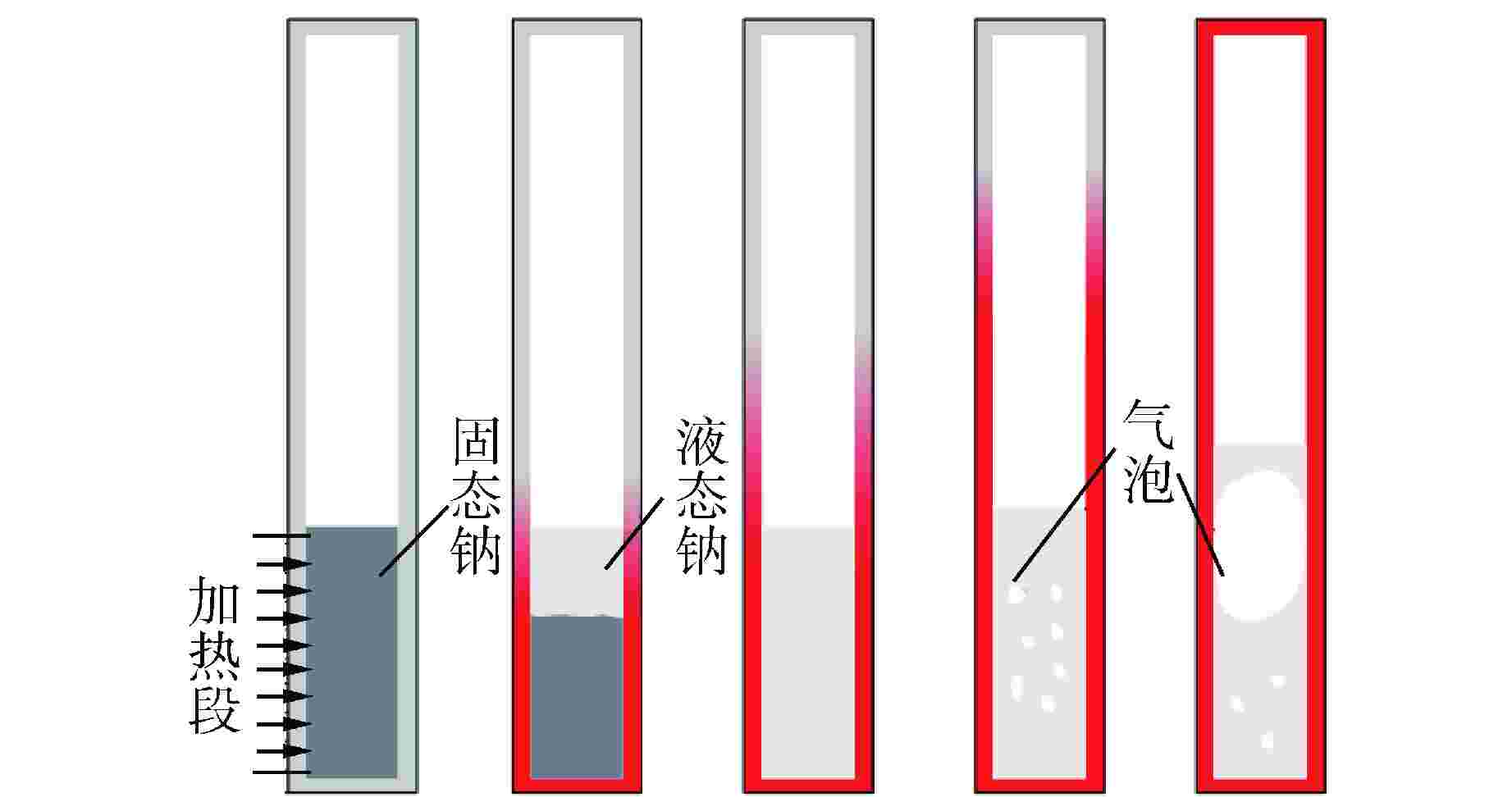
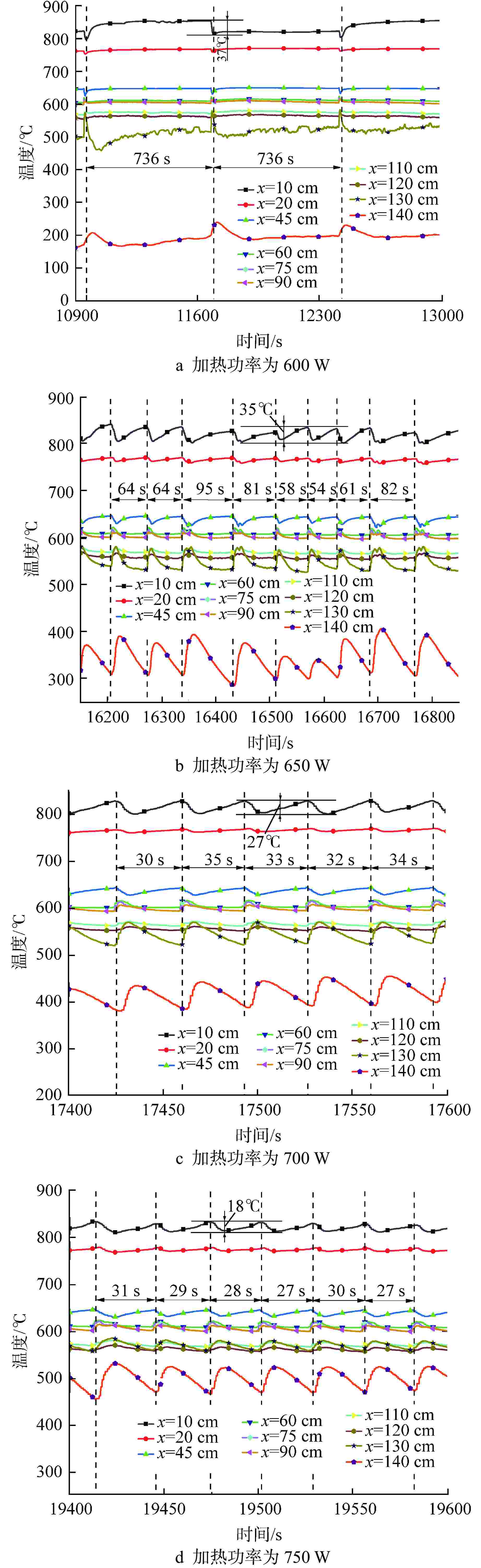
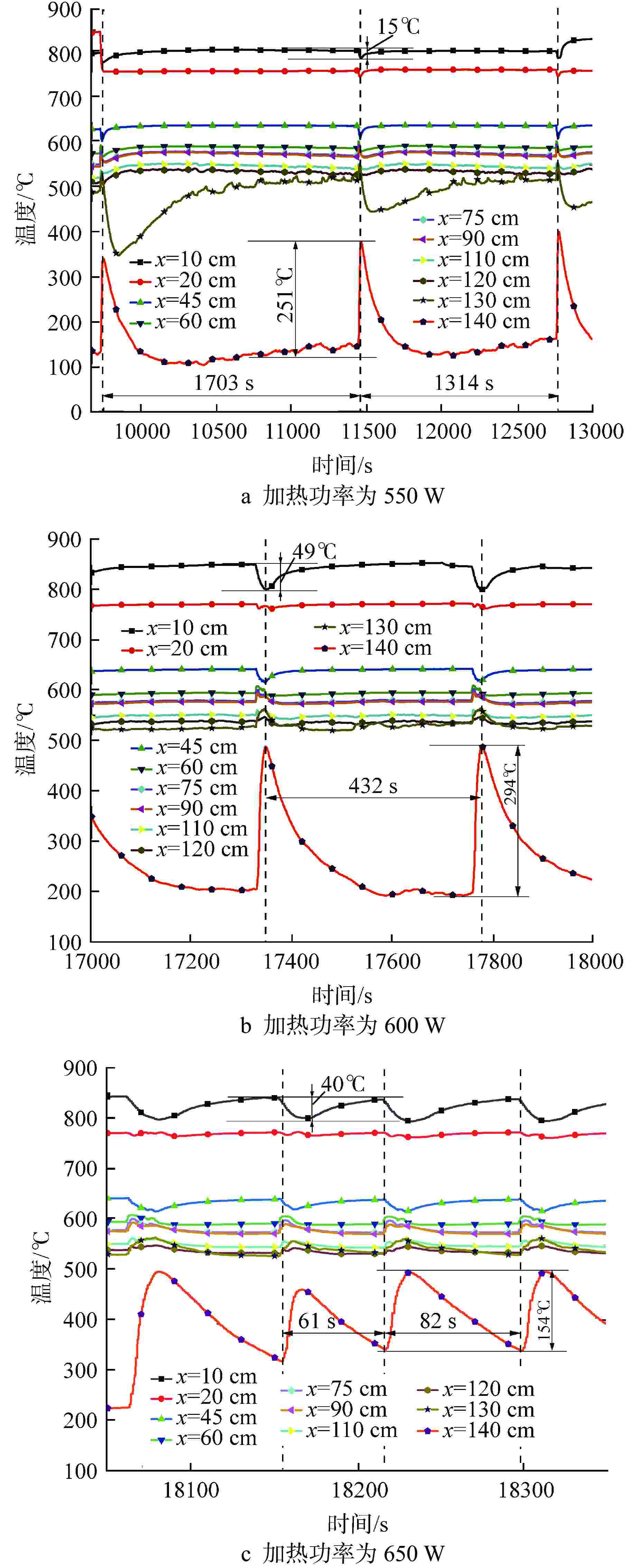
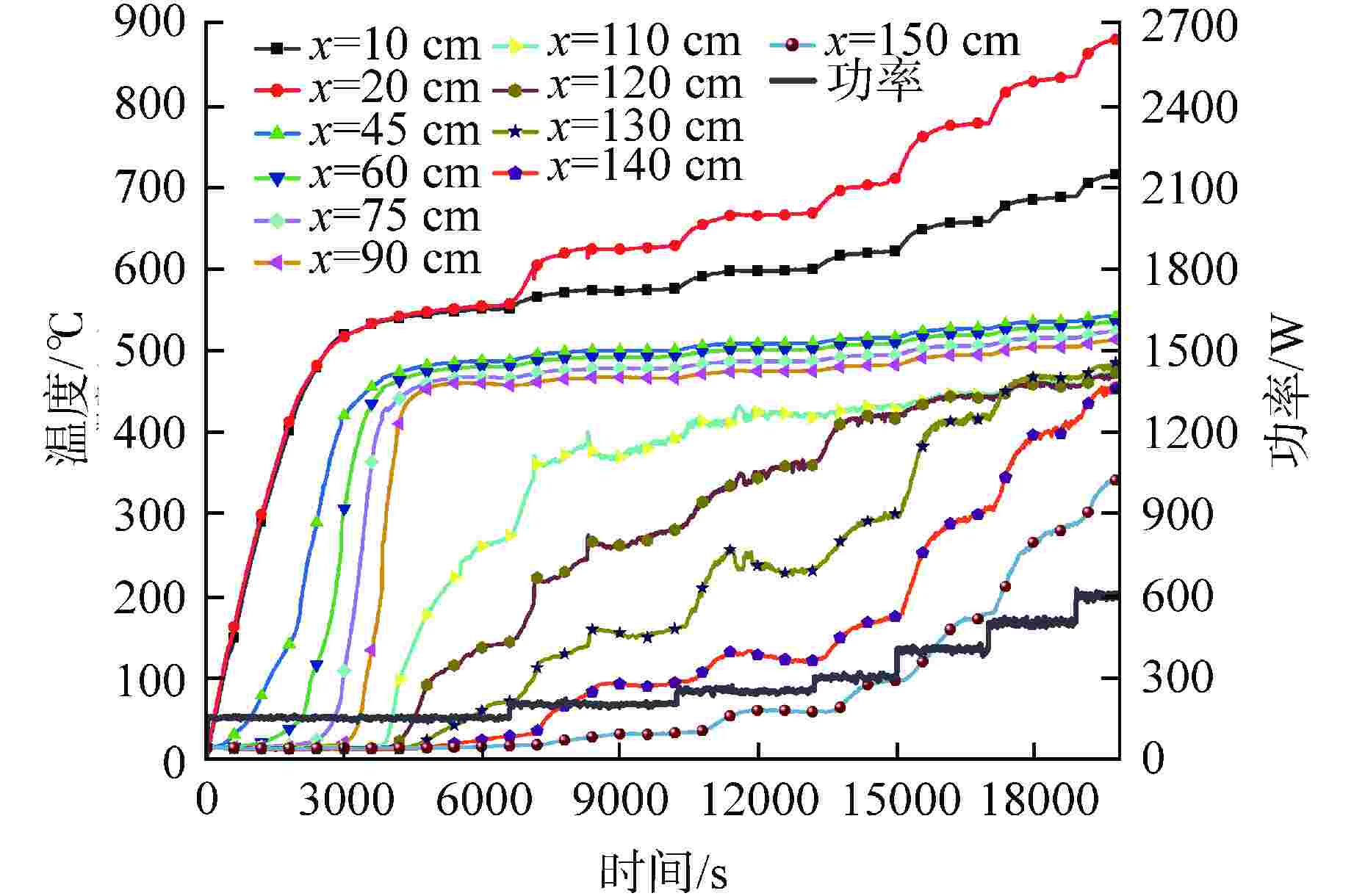
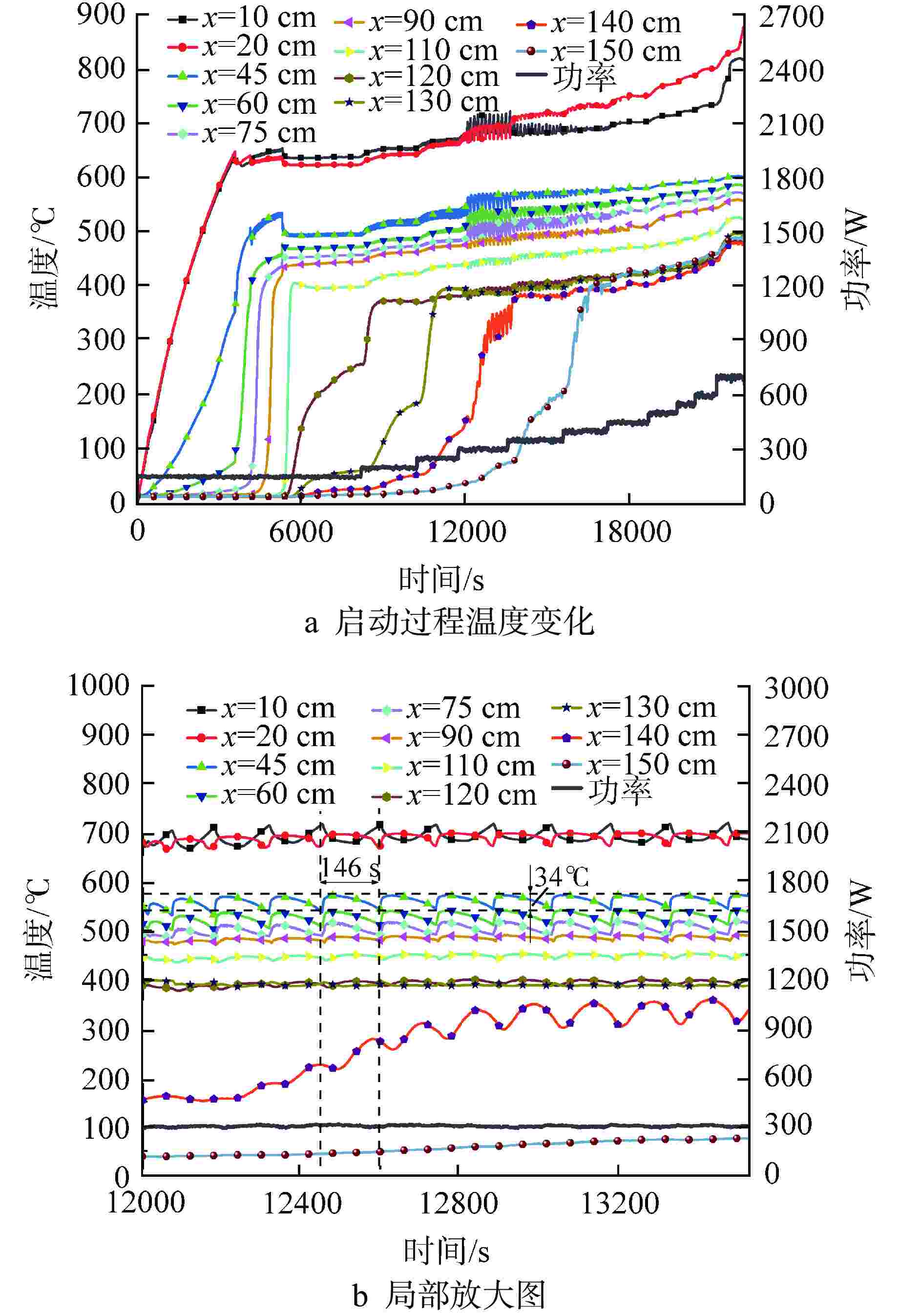
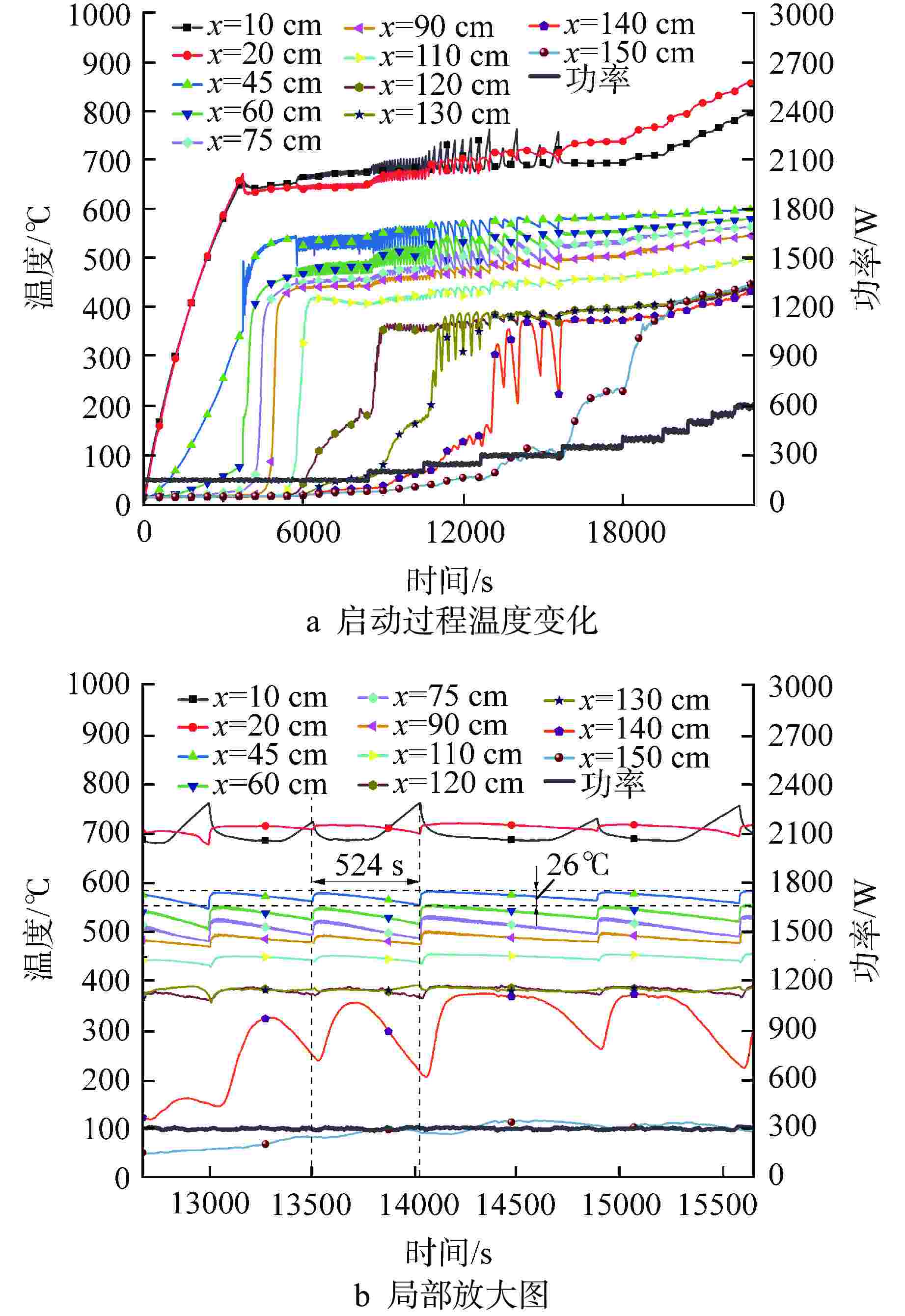
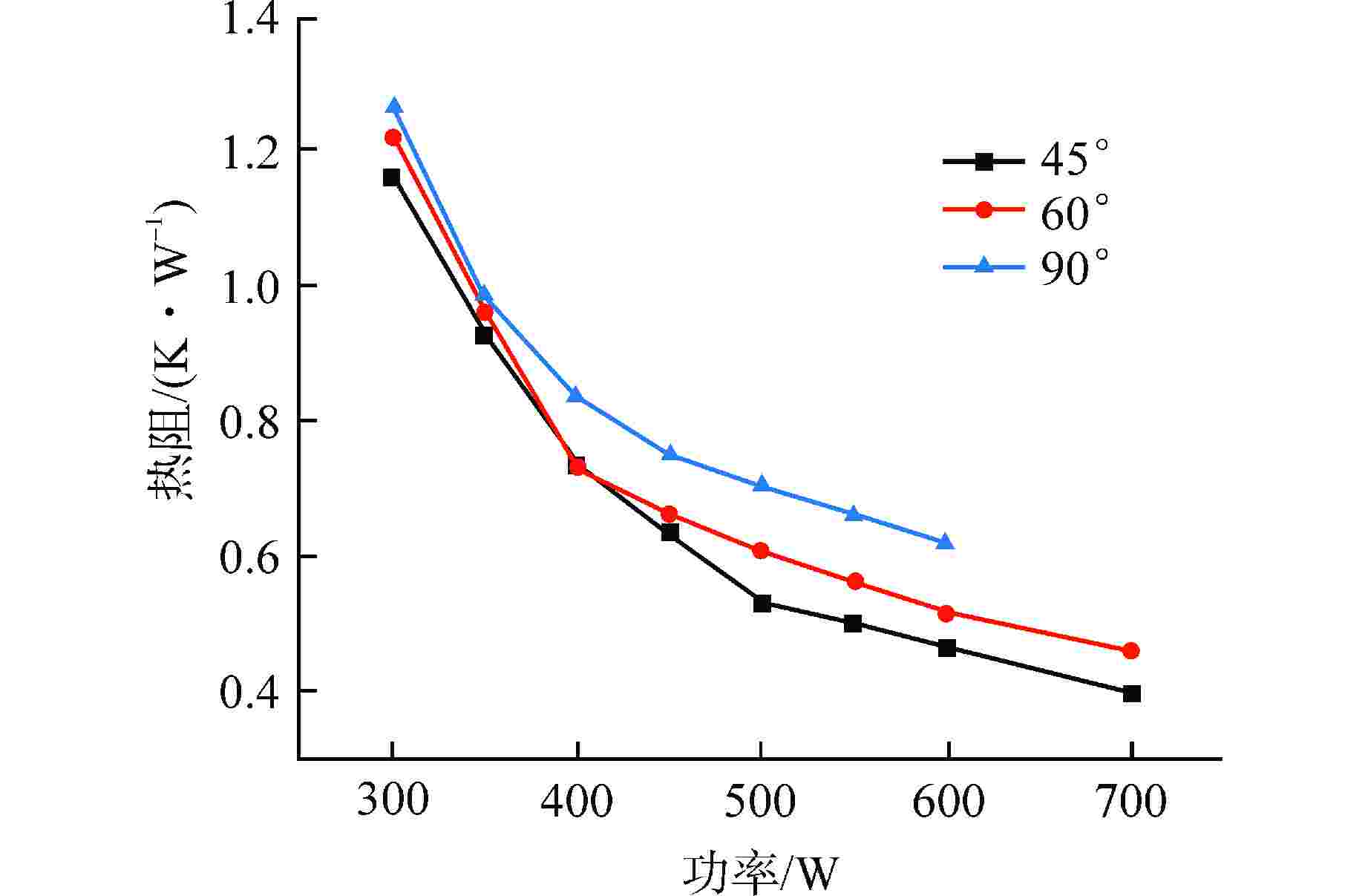
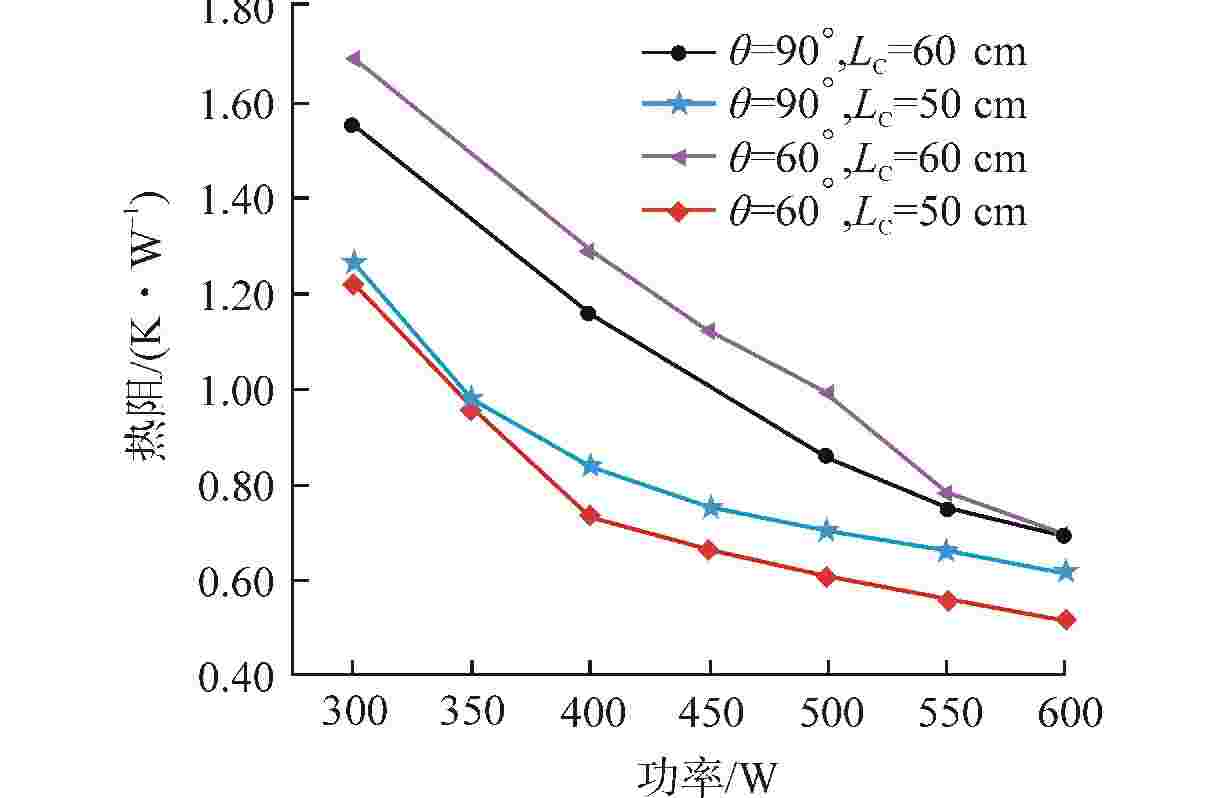
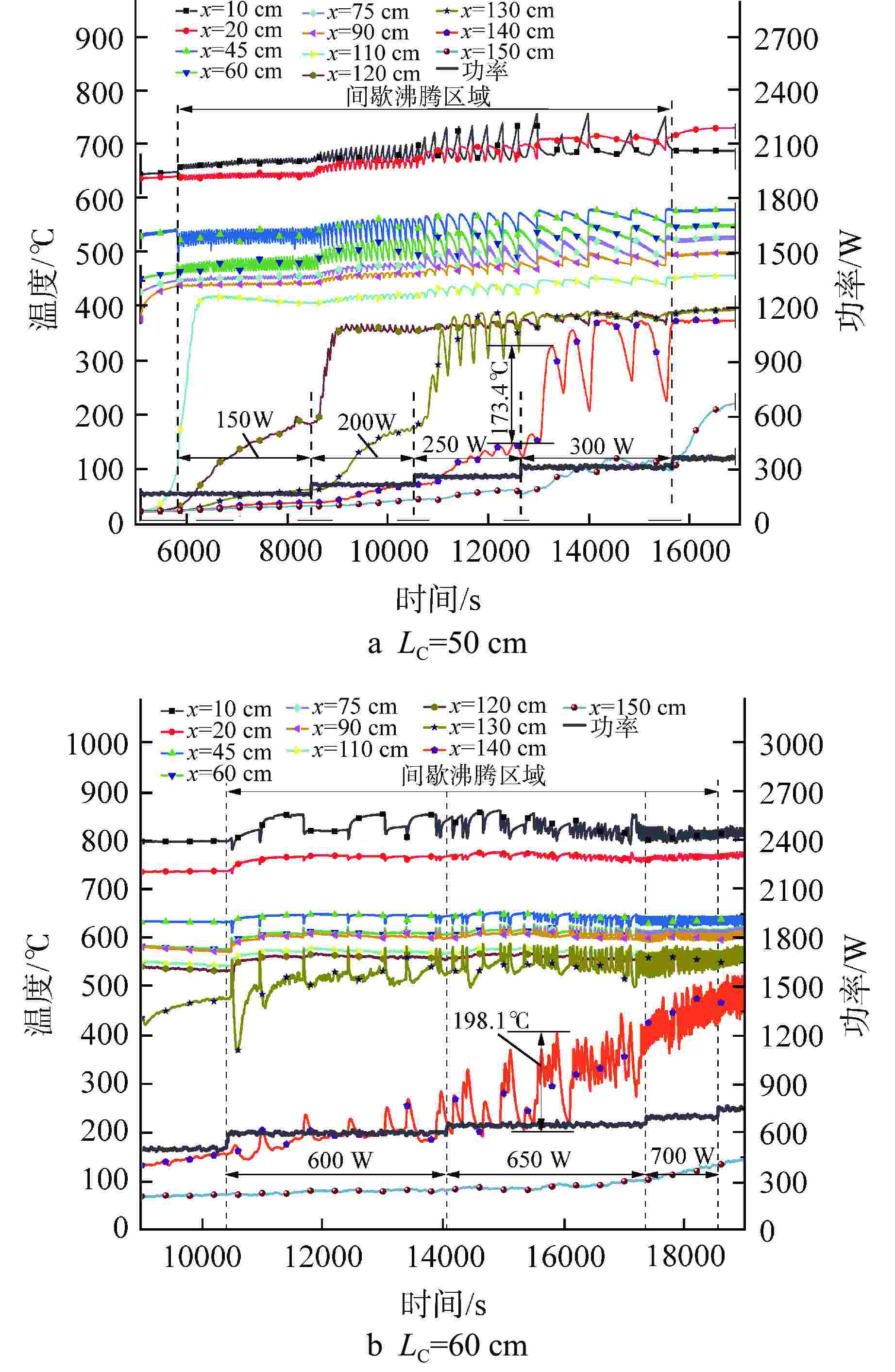
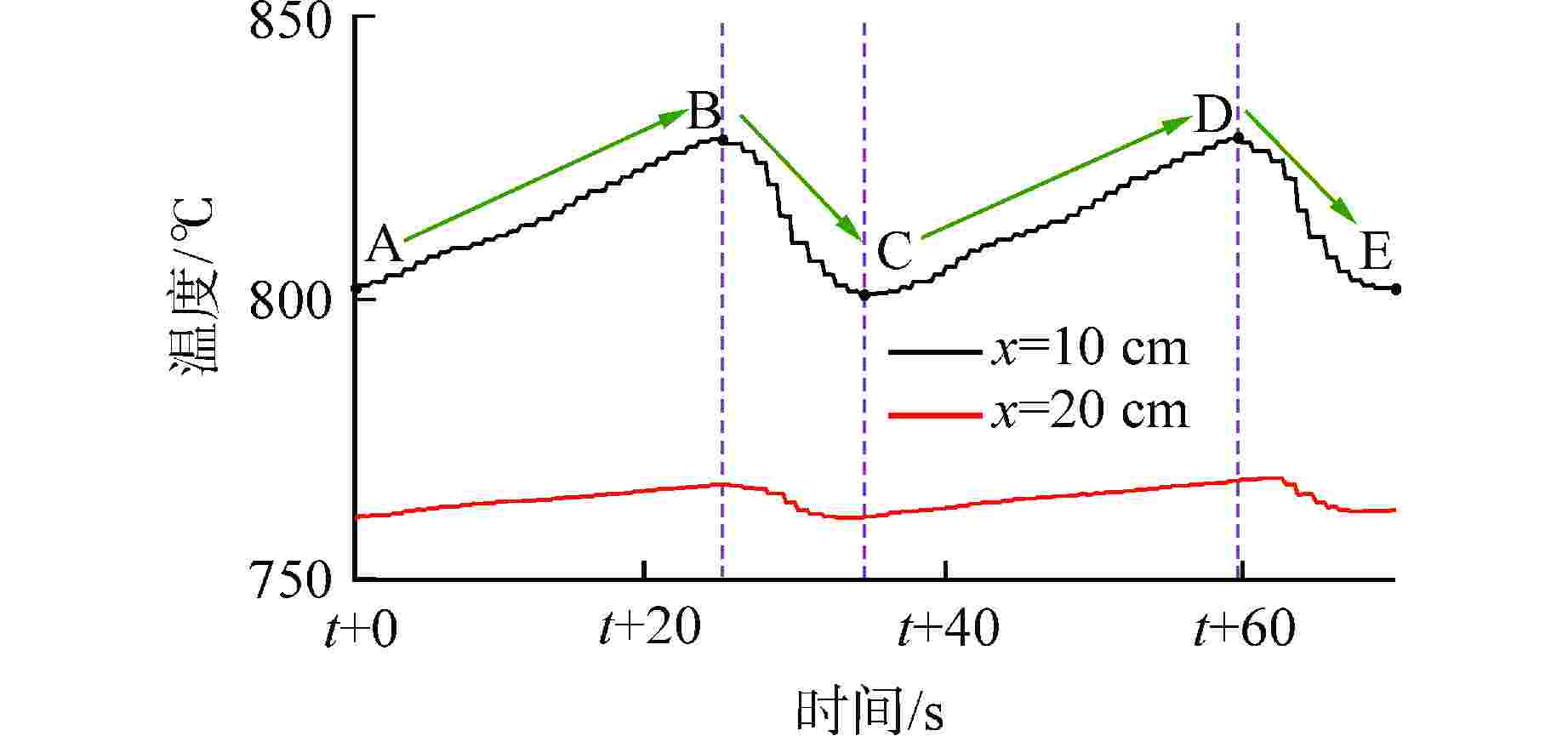
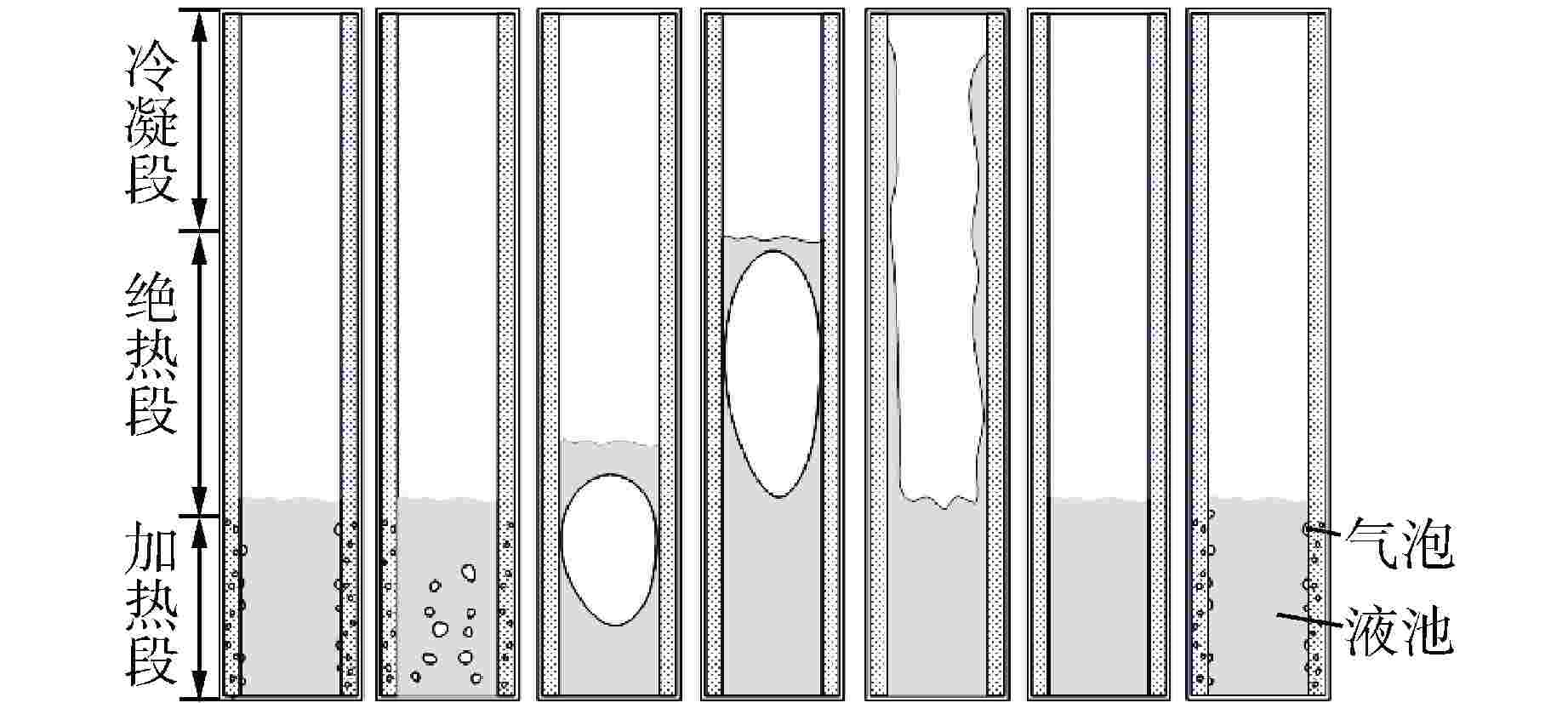
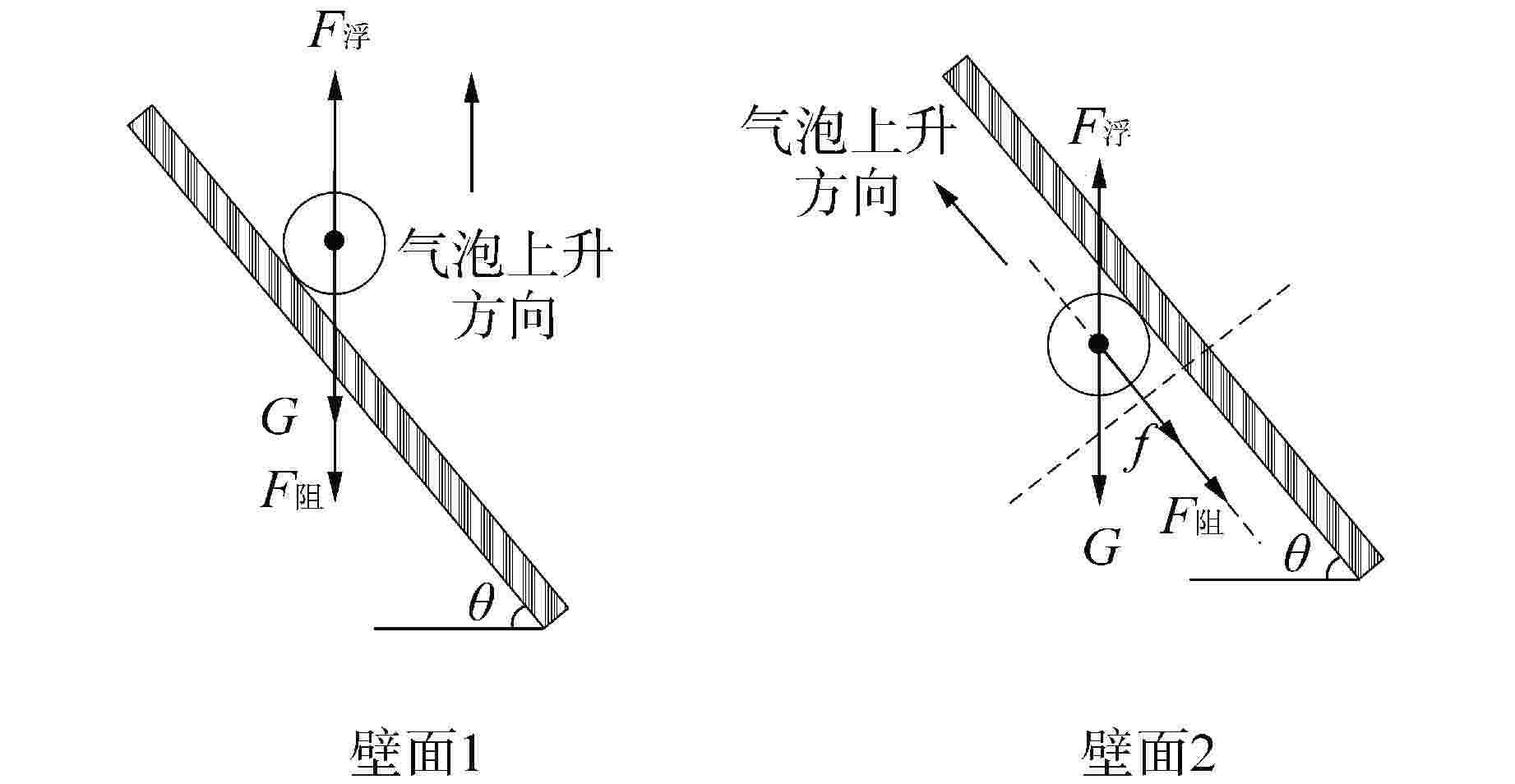
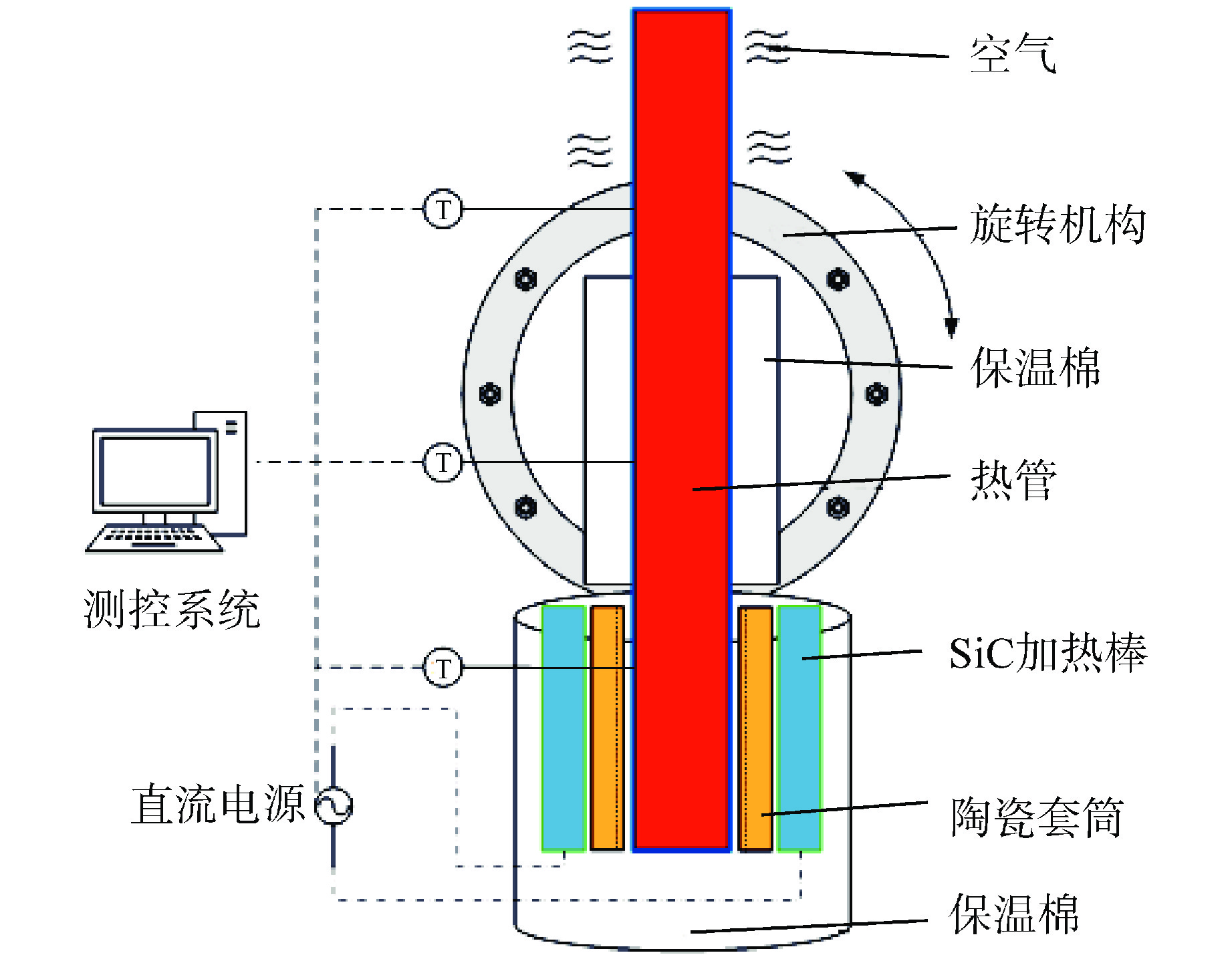
摘要: 为研究高温碱金属热管启动过程中的间歇沸腾现象,给热管反应堆安全运行提供可参考的操作条件,采用金属钠为热管工质,对热管启动过程的间歇沸腾的影响因素和作用机制开展了试验研究。研究结果表明,热管加热功率和倾角对间歇沸腾有重要影响,在90°倾角情况下,加热功率从600 W升至750 W,间歇沸腾周期变化范围为29~736 s,温度振幅范围为18~35℃;热管倾角为0°时不会发生间歇沸腾;间歇沸腾在中等加热功率条件下容易发生,随倾角的增大,间歇沸腾起始和截止的加热功率减小,倾角为45°、60°、90°工况下间歇沸腾起始和截止的加热功率分别为250、200、150 W和600、450、350 W。同一加热功率、不同倾角工况下间歇沸腾的周期差别较大,而温度振幅变化较小;冷凝段长度减小后间歇沸腾强度降低且发生间歇沸腾的功率区间提前;本研究结果为进一步探究碱金属热管间歇沸腾发生机理奠定了基础,对碱金属热管设计优化和热管反应堆安全运行提供了重要的数据和理论支持。Abstract: To study the geyser boiling phenomenon in the start-up process of high-temperature alkali metal heat pipe and provide reference operating conditions for the safe operation of the heat pipe reactor, sodium metal was used as the working medium to investigate the influence factors and mechanism of geyser boiling during the start-up process of the heat pipe. The results show that the heating power and inclination angle of the heat pipe have important effects on geyser boiling. Under the condition of 90° inclination angle, the heating power increases from 600 W to 750 W, the geyser boiling period varies from 736 s to 29 s, and the temperature amplitude ranges from 35℃ to 18℃. Geyser boiling is easy to occur under medium heating power conditions but will not happen when the inclination of the heat pipe is 0°. With the increase of inclination angle, the heating power of the start and stop of the geyser boiling decreases. When the inclination angle is 45°, 60°, 90° respectively, the geyser boiling starts at 250, 200, 150 W and stops at 600, 450, 350 W. The geyser boiling period varies at the same heating power from different inclination angles, but the temperature amplitude changes little. The geyser boiling intensity decreases and the power range of geyser boiling advances with the shortening of the condensing section. The results of this study laid a foundation for further research on the geyser boiling mechanism of alkali metal heat pipes, and provide important data and theoretical support for the design optimization of alkali metal heat pipes and the safe operation of heat pipe reactors.
-
Key words:
- Alkali metal heat pipe /
- Geyser boiling /
- Experimental investigation /
- Mechanism analysis
-
表 1 试验工况表
Table 1. Test Condition Table
序号 倾斜角度 加热功率/W 冷凝段长度/cm 冷凝段平均温度/℃ 辐射换热功率/W 自然对流换热功率/W 总散热功率/W 1 0° 150~600 60 500 550.87 215.75 766.62 2 45° 150~900 60 500 550.87 116.46 667.33 3 60° 300~650 60 500 550.87 115.69 666.56 4 90° 300~750 60 500 550.87 115.54 666.41 5 45° 150~900 50 500 459.10 101.81 560.91 6 60° 150~700 50 500 459.10 101.03 560.13 7 90° 150~600 50 500 459.10 100.89 559.99 -
[1] LIN T F, LIN W T, TSAY Y L, et al. Experimental investigation of geyser boiling in an annular two-phase closed thermosyphon[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1995, 38(2): 295-307. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(95)90019-5 [2] ALAMMAR A A, AL-DADAH R K, MAHMOUD S M. Effect of inclination angle and fill ratio on geyser boiling phenomena in a two-phase closed thermosiphon – Experimental investigation[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 156: 150-166. [3] EMAMI M R S, NOIE S H, KHOSHNOODI M, et al. Investigation of geyser boiling phenomenon in a two-phase closed thermosyphon[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2009, 30(5): 408-415. [4] KHAZAEE I, HOSSEINI R, NOIE S H. Experimental investigation of effective parameters and correlation of geyser boiling in a two-phase closed thermosyphon[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2010, 30(5): 406-412. [5] MANTELLI M B H, UHLMANN T W, CISTERNA L H R. Experimental study of a sodium two phase thermosyphon[Z]//9th World Conference on Experimental Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics. Iguazu Falls, 2017. [6] MANOJ R, KUMAR M C, RAO R N, et al. Performance evaluation of sodium heat pipe through parameteric studies[J]. Frontiers in Heat Pipes, 2013, 3(4). DOI: 10.5098/fhp.v3.4.3003. [7] CISTERNA L H R, CARDOSO M C K, FRONZA E L, et al. Operation regimes and heat transfer coefficients in sodium two-phase thermosyphons[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 152: 119555. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119555 [8] GUO H, GUO Q, YAN X K, et al. Experimental investigation on heat transfer performance of high-temperature thermosyphon charged with sodium-potassium alloy[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 139: 402-408. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.04.139 [9] WANG C L, ZHANG L R, LIU X, et al. Experimental study on startup performance of high temperature potassium heat pipe at different inclination angles and input powers for nuclear reactor application[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2020, 136: 107051. [10] MA Y G, YU H X, HUANG S F, et al. Effect of inclination angle on the startup of a frozen sodium heat pipe[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 201: 117625. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117625 [11] VLIET G C. Natural convection local heat transfer on constant-heat-flux inclined surfaces[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1969, 91(4): 511-516. [12] HUNNEWELL T S, WALTON K L, SHARMA S, et al. Total hemispherical emissivity of SS 316L with simulated very high temperature reactor surface conditions[J]. Nuclear Technology, 2017, 198(3): 293-305. doi: 10.1080/00295450.2017.1311120 [13] STANCULESCU A. The role of nuclear power and nuclear propulsion in the peaceful exploration of space[M]. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2005: 119. [14] 孙浩,王成龙,刘逍,等. 水下航行器微型核电源堆芯设计[J]. 原子能科学技术,2018, 52(4): 646-651. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2017.youxian.0465 [15] MCCLURE P R, REID R S, DIXON D D. Advantages and applications of megawatt-sized heat-pipe reactors[R]. La Grange Park: American Nuclear Society, 2012. -





 下载:
下载: