Experimental and CFD Simulation of the RPV Head Plenum
-
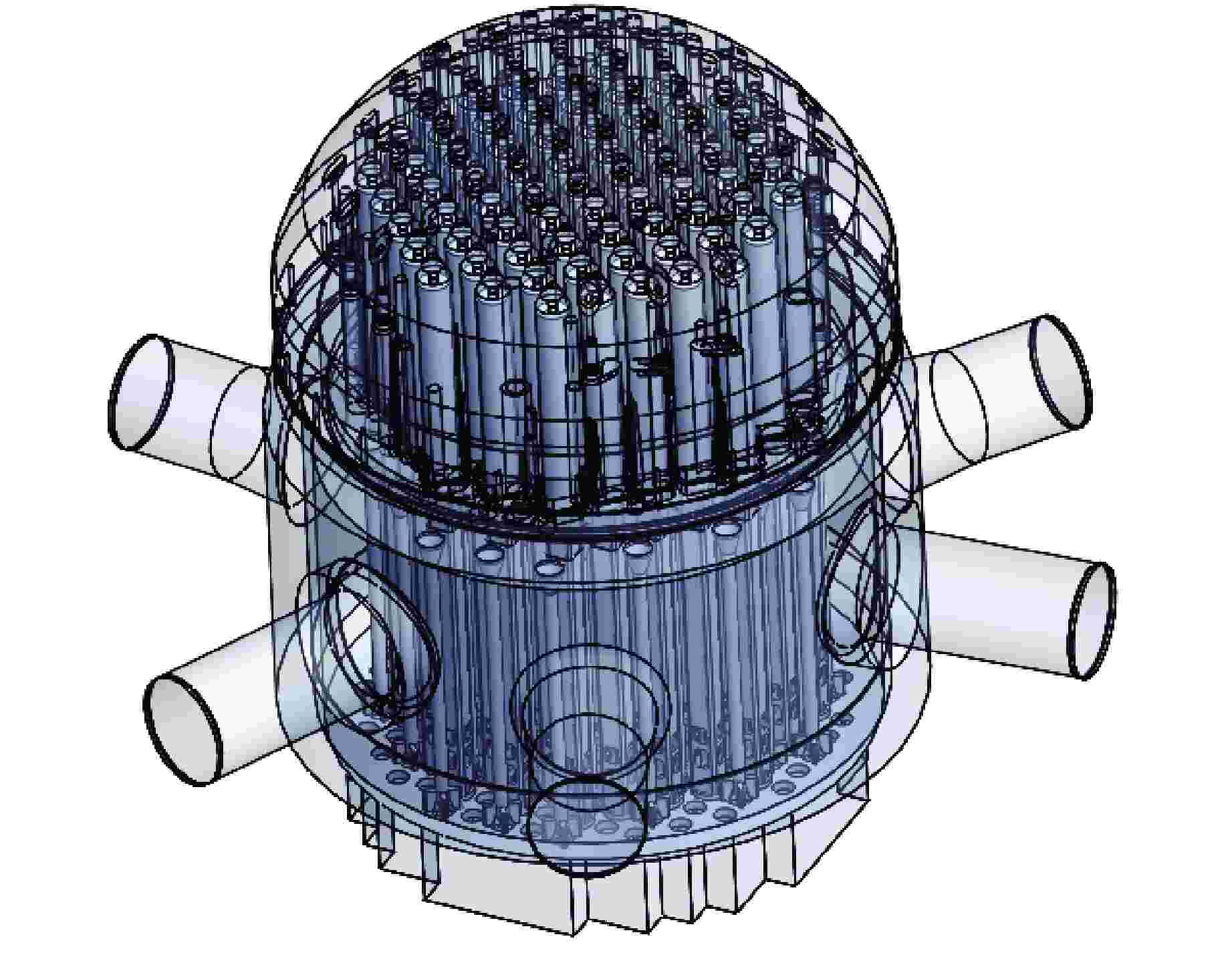
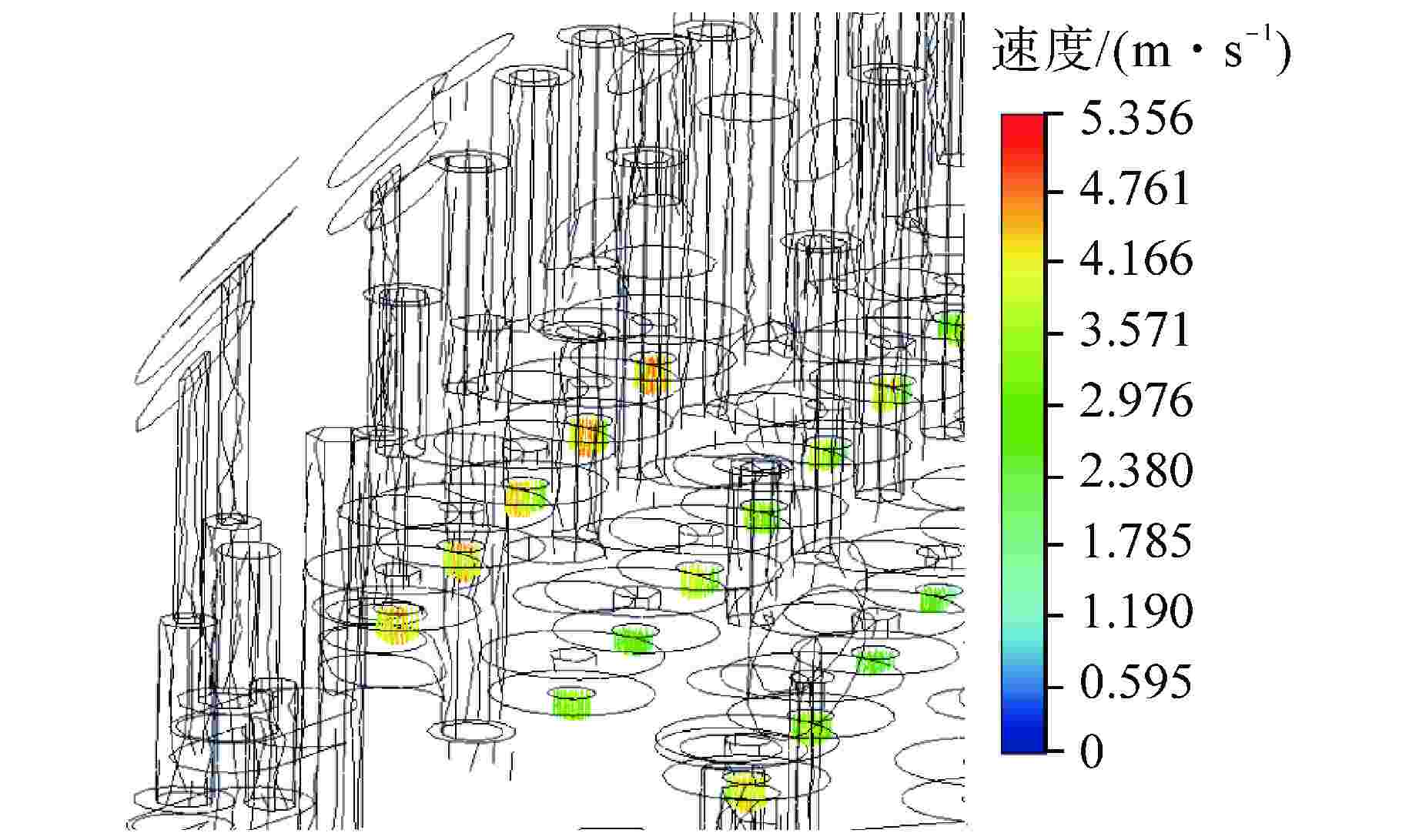
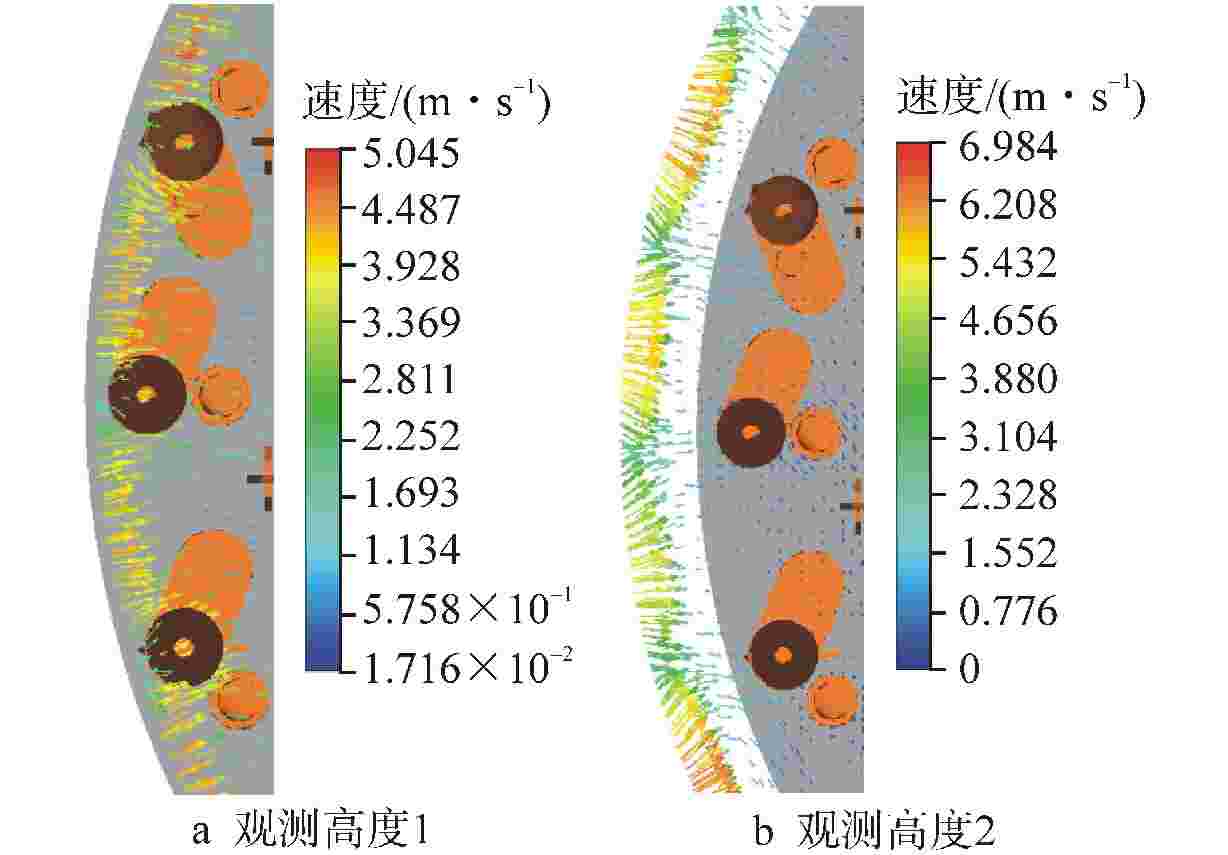
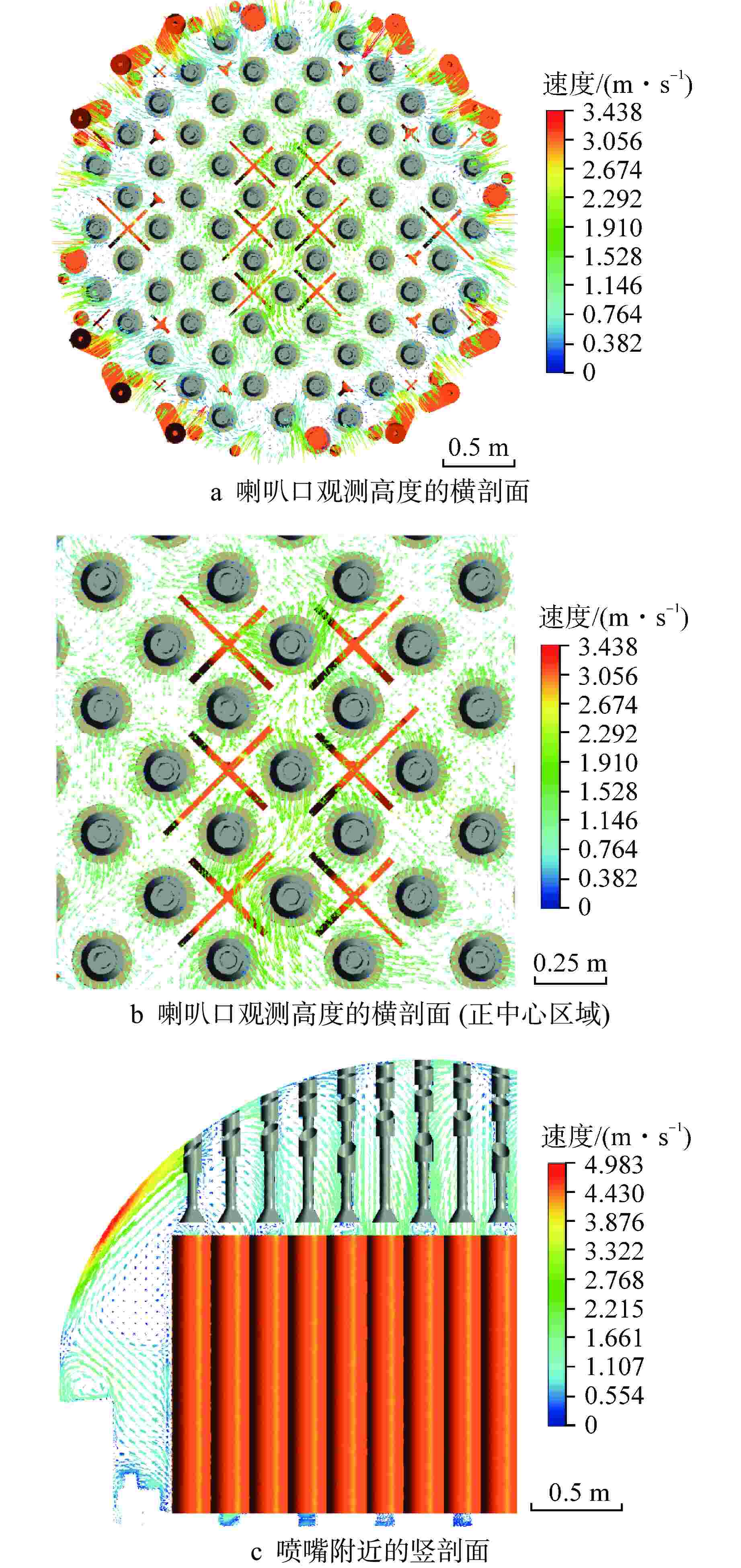
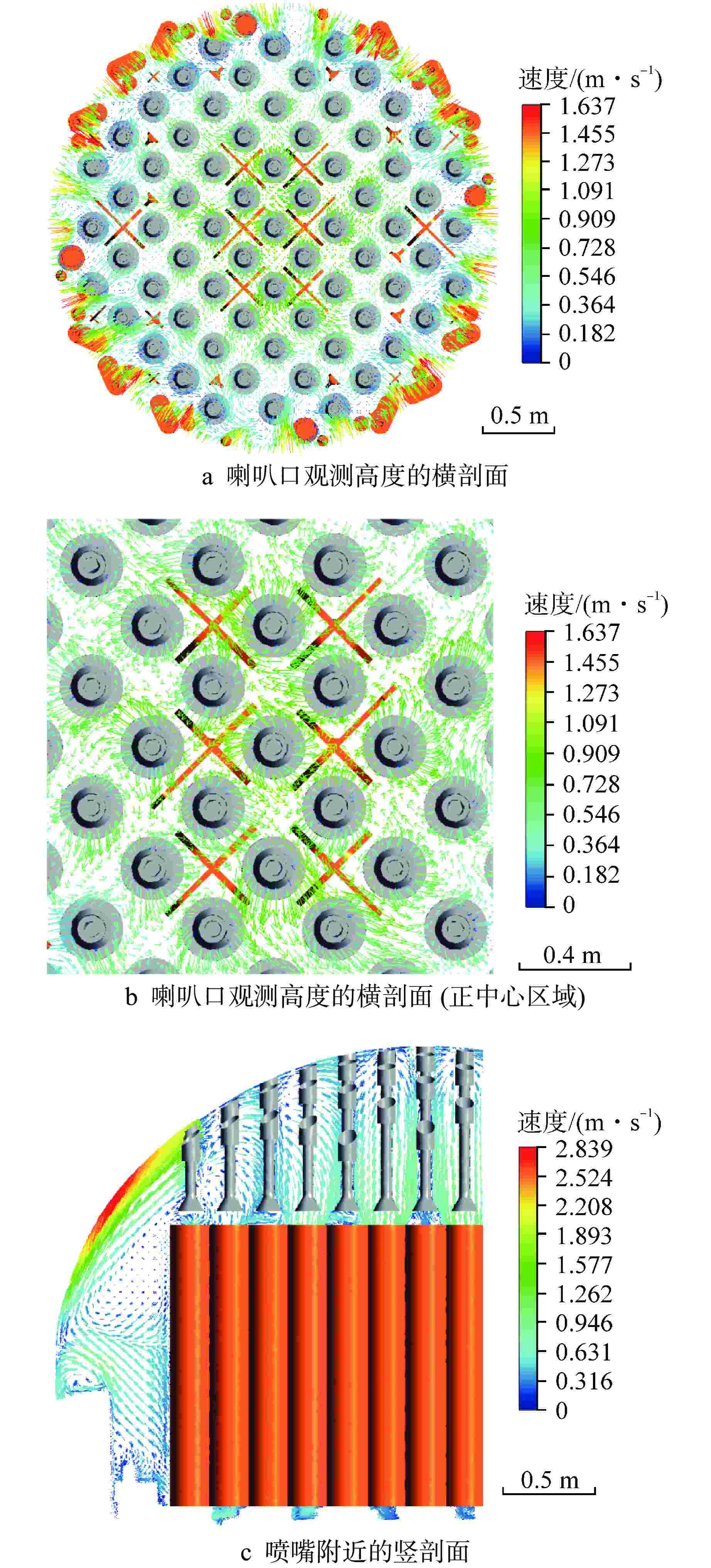
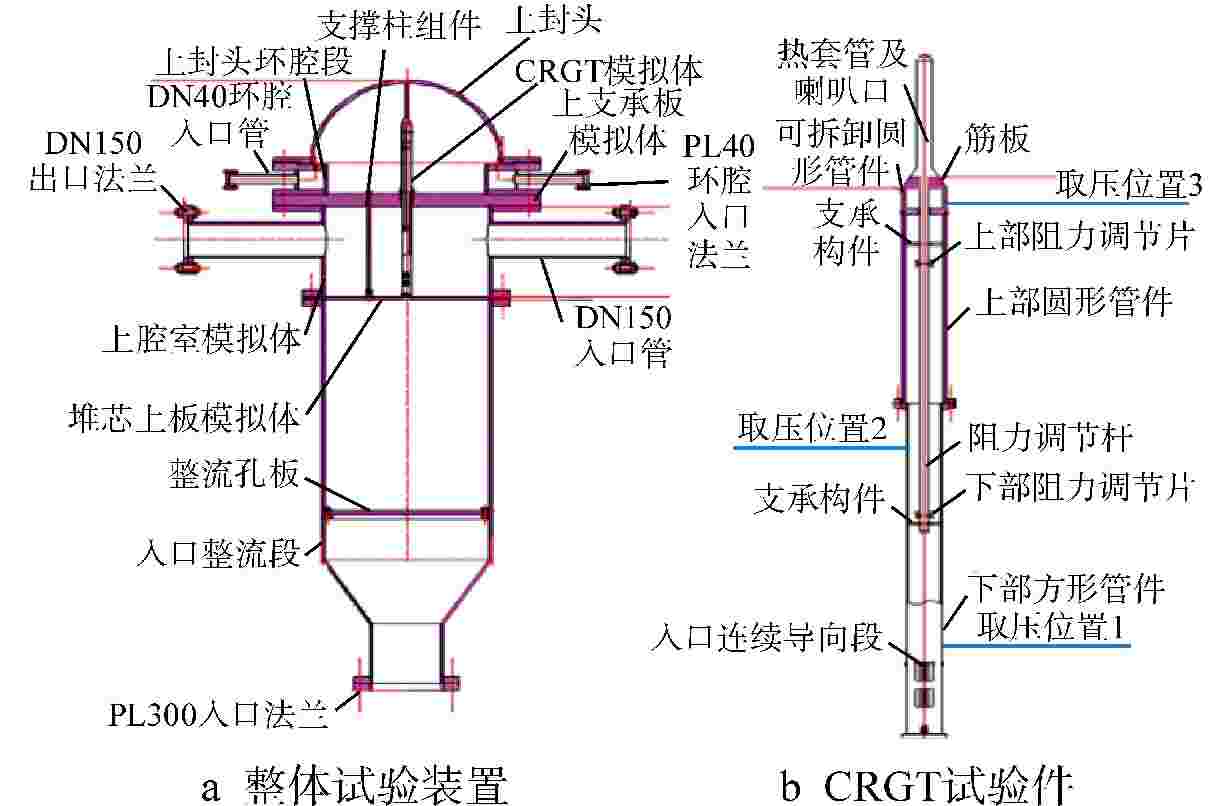
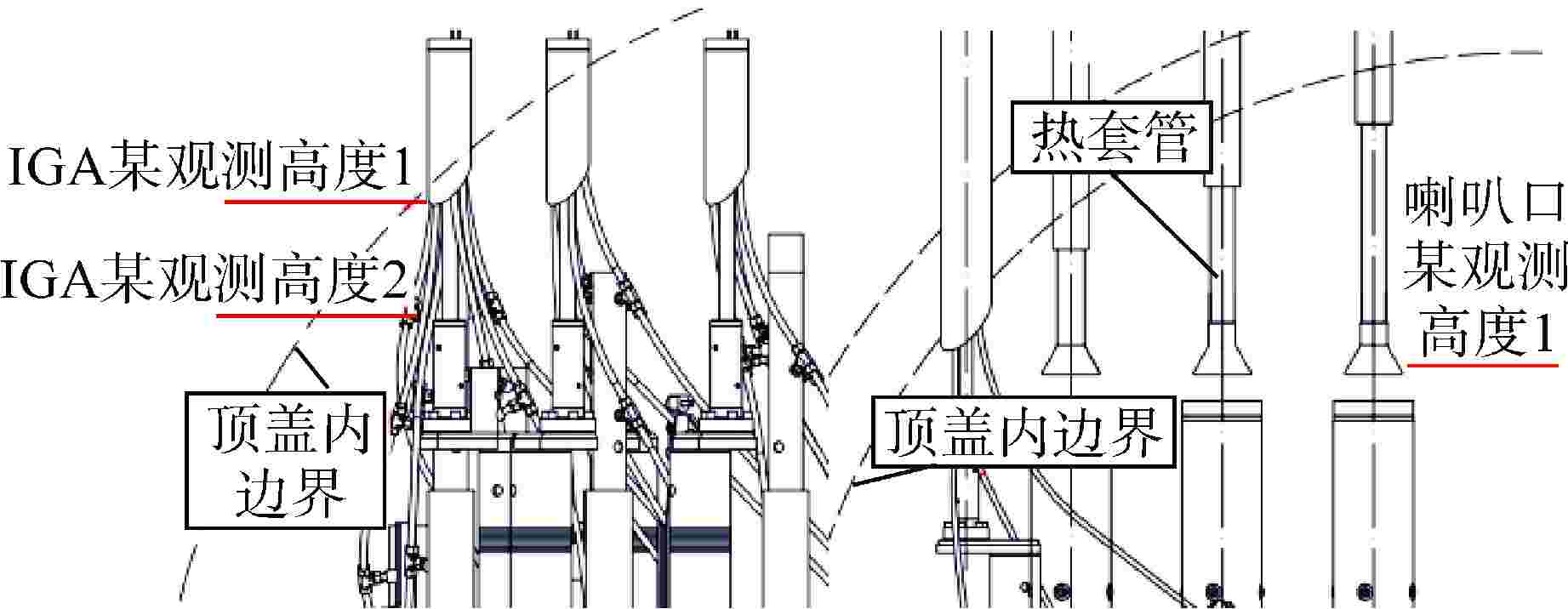
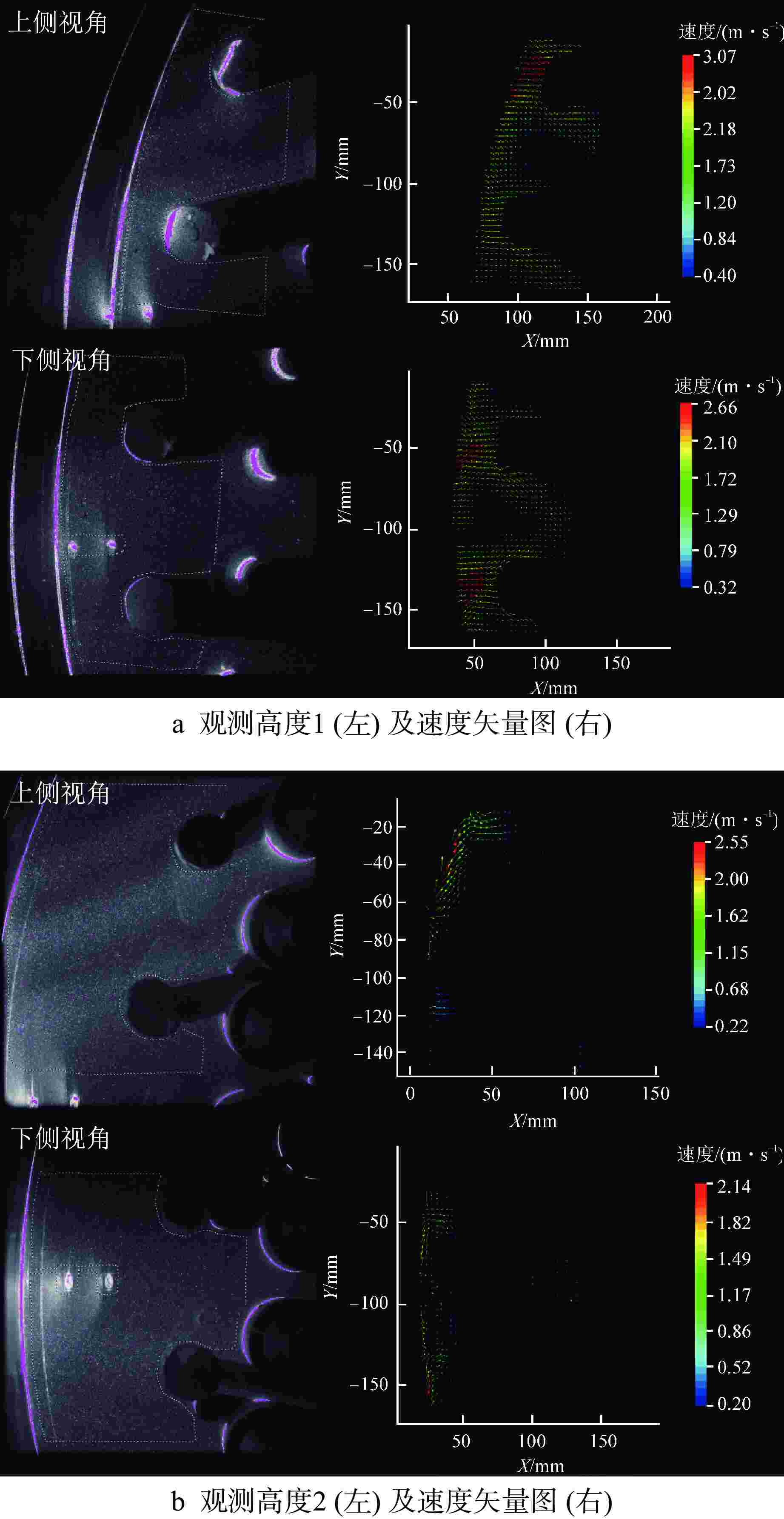
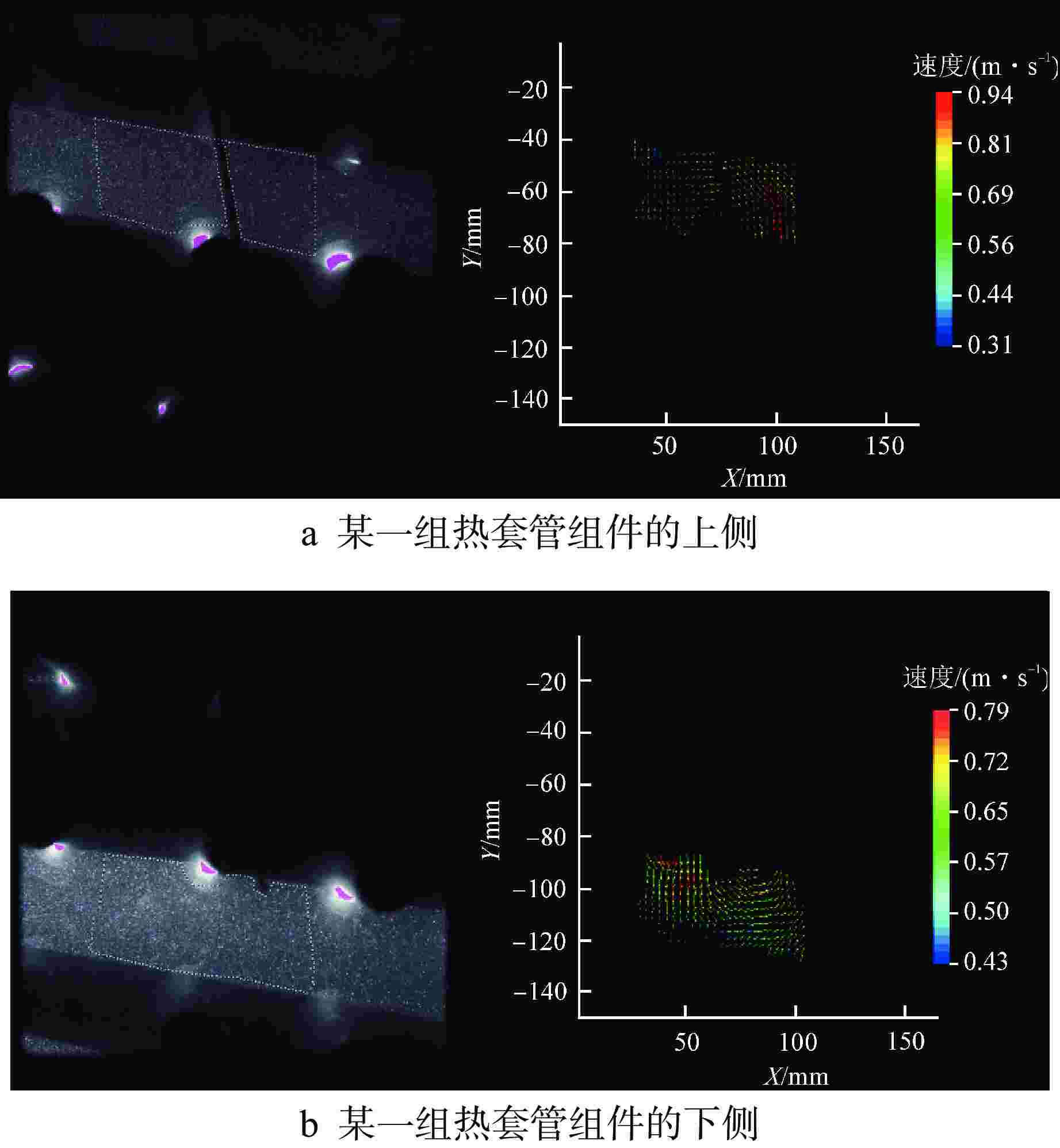
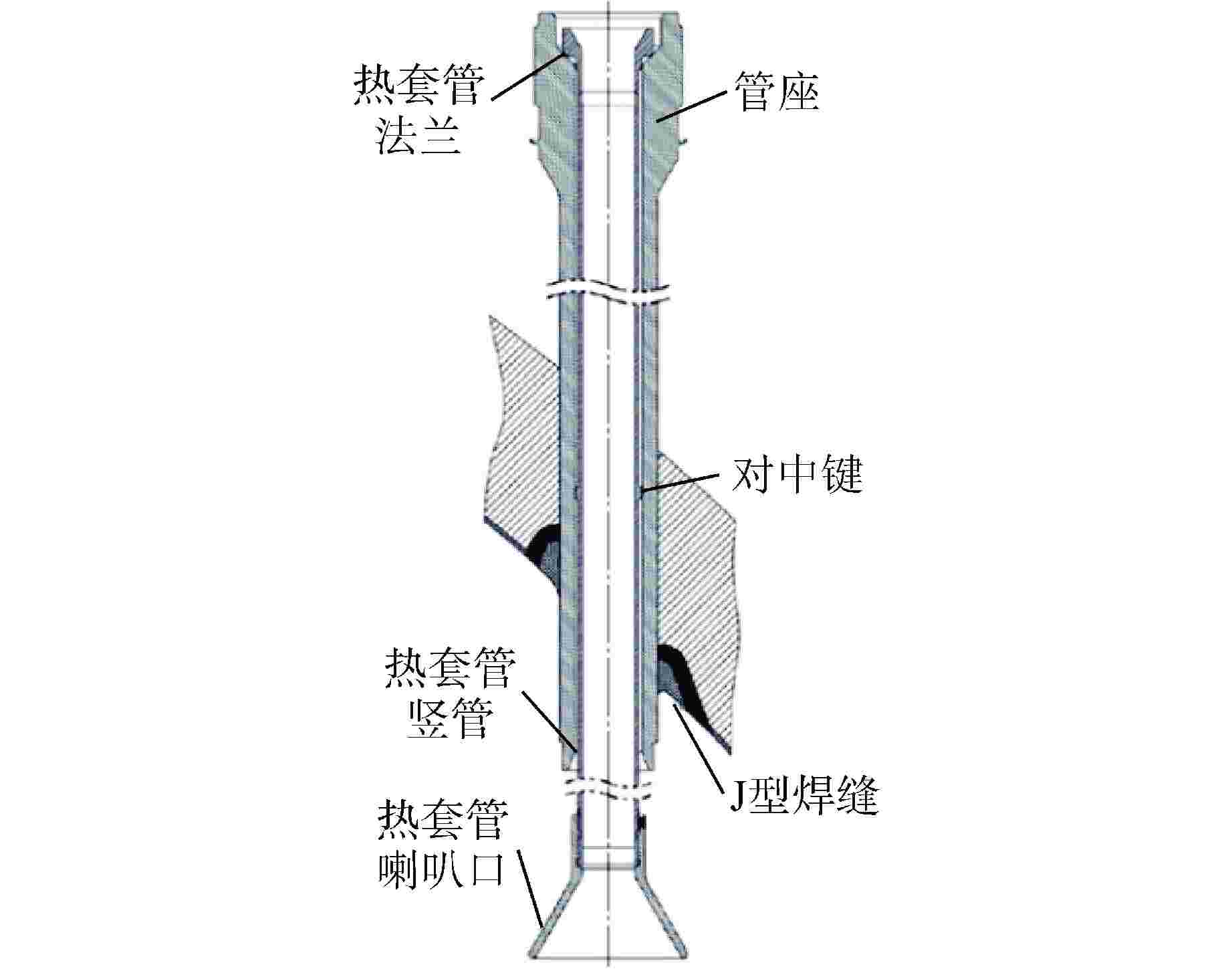
摘要: 为探究华龙一号反应堆压力容器(RPV)顶盖腔室区域的流动特征,为在役CPR1000压水堆核电厂的热套管磨损问题和华龙一号顶盖腔室结构的优化改进提供支撑。本文采用计算流体动力学(CFD)方法对顶盖腔室区域进行数值模拟,同时开展顶盖腔室模型水力模拟试验,获得顶盖腔室内流场分布及关键区域的水力特性参数。理论分析及试验结果表明:顶盖腔室关键区域的CFD结果和试验测得的横向流速偏差值在10%以内;正常工况下,顶盖腔室内整体流速较低,在顶盖喷嘴与内壁面附近流速较高;顶盖腔室内流体全部通过控制棒导向筒(CRGT)顶部流水孔进入上腔室,上腔室流体不会反向流入顶盖腔室,验证了华龙一号“冷顶盖”设计的有效性;顶盖腔室中心区域的热套管喇叭口附近存在漩涡且流速较外围区域更高,导致热套管承受的流体冲击更剧烈、磨损更严重。
-
关键词:
- 压力容器(RPV)顶盖腔室 /
- 计算流体动力学(CFD) /
- 模拟试验
Abstract: This paper aims to investigate the flow characteristics of the RPV Head Plenum region in the HPR1000 Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) to provide support for addressing the erosion of the Thermal Sleeve in operational CPR1000 PWR plants and optimizing the RPV Head Plenum region structures in HPR1000 PWR plants. This paper uses Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) methods to conduct numerical simulations of the RPV Head Plenum region and also carries out hydraulic model experiments of the RPV Head Plenum to obtain the flow distribution and hydraulic characteristics of key areas within the RPV Head Plenum region. The theoretical analysis and experimental results show that: The CFD results of the key areas in the RPV Head Plenum and the measured lateral velocity deviations from the experiments are within 10%. Under normal operating conditions, the overall flow velocity within the RPV Head Plenum is relatively low, but higher velocities are observed near the RPV Head nozzles and nearby surface. The coolant water in RPV Head Plenum flows downward through the holes at the top of CRGT and then flows into the Upper Plenum, which is consistent with the expectation of the HPR1000 “Cold RPV head”. Additionally, a vortex with higher flow velocity is present near the Thermal Sleeve Bell Mouth in the central region than in the peripheral area of the RPV Head Plenum, resulting in more severe fluid impact and wear on the thermal sleeves. -
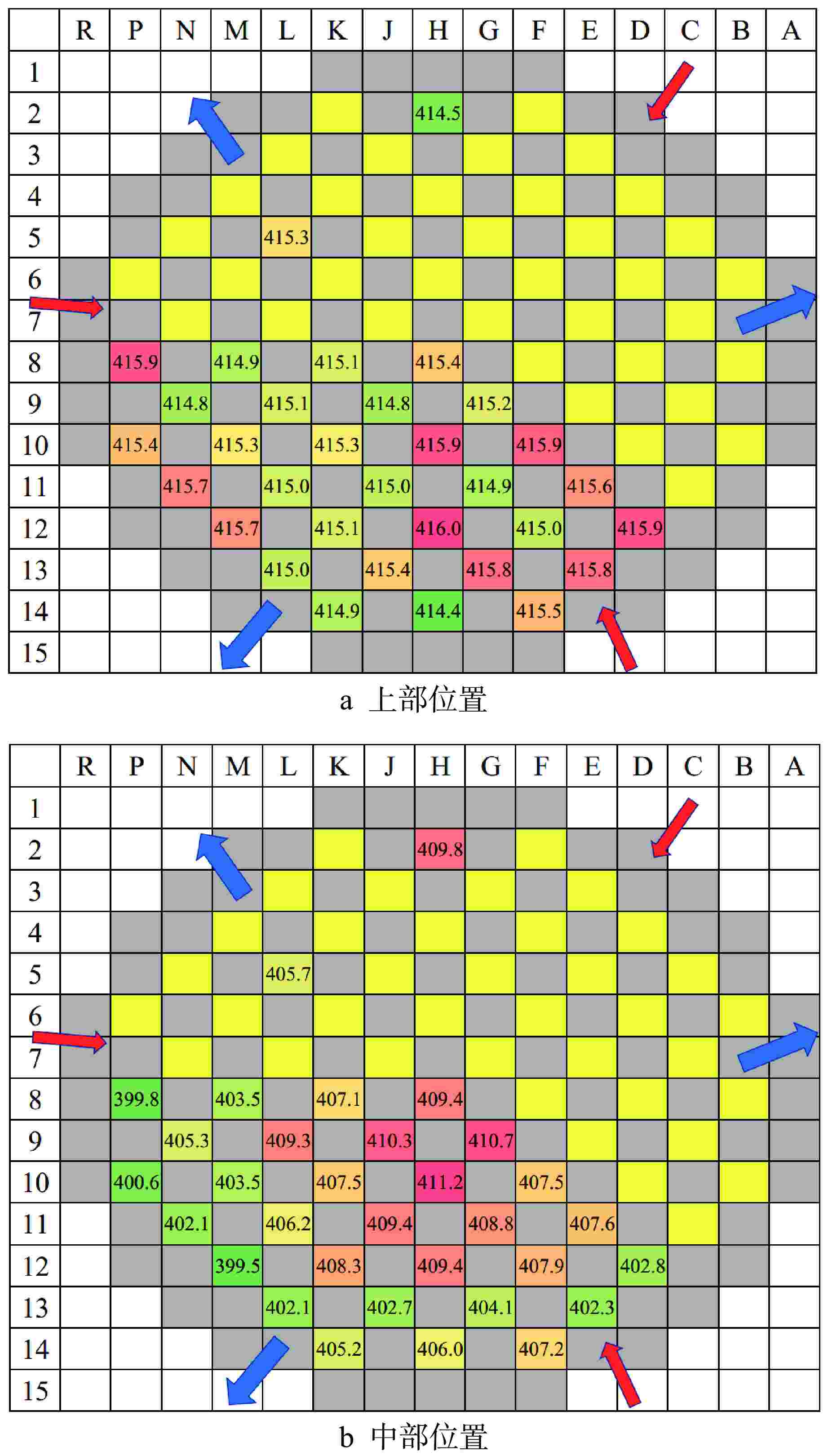
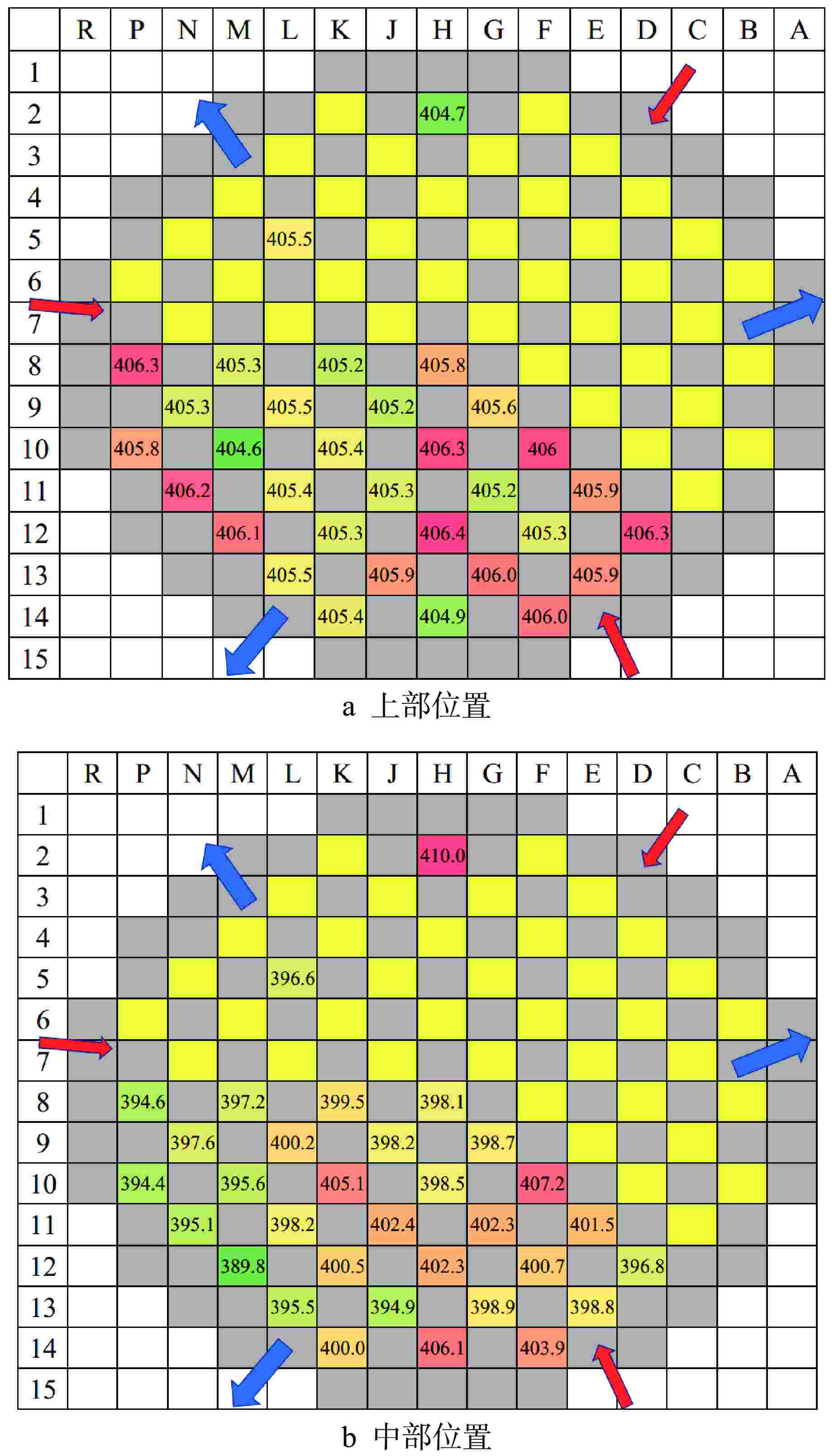
表 1 顶盖不同旁流量下试验结果(正常工况)
Table 1. Experimental Results with Different RPV Head Bypass (under Normal Condition)
旁流(Q)/Qnominal 0.60 0.66 0.72 0.92 1.00 下降流CRGT数量 68 69 69 69 69 上升流CRGT数量 1 0 0 0 0 表 2 顶盖不同旁流量下试验结果(假定工况)
Table 2. Experimental Results with Different RPV Head Bypass in Conservative Condition
Q/Qnominal 0.66 0.76 0.82 0.87 0.92 下降流CRGT数量 63 65 69 69 69 上升流CRGT数量 6 4 0 0 0 -
[1] 杨来生,宗桂芳,胡俊. 秦山核电二期工程反应堆水力模拟实验研究[J]. 核动力工程,2003, 24(S1): 208-211,226. [2] 李华奇,胡俊. 反应堆流场分布优化实验研究和理论分析[J]. 核动力工程,2002, 23(S1): 43-48,58. [3] 于浩,翁羽. 反应堆堆内构件上腔室流场初步分析研究[C]//第十六届全国反应堆结构力学会议. 深圳: 中国力学学会,中国核学会,2010: 315-324. [4] 杜思佳,刘余,李松蔚,等. “华龙一号”反应堆本体结构CFD模型研究[J]. 热科学与技术,2017, 16(5): 411-417. [5] 张明乾,段远刚,于晓雷,等. ACPR1000+反应堆整体水力特性数值分析与比较[J]. 核动力工程,2013, 34(6): 52-54,60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2013.06.013 [6] 张明乾,冉小兵,刘言午,等. CPR1000反应堆三维数值模拟分析及验证[J]. 核技术,2013, 36(10): 65-70. [7] 张明乾,黄美良,付月明,等. 堆芯中子注量率测量系统指套管磨损现象分析[J]. 核动力工程,2018, 39(6): 96-100. [8] 江帅,岳瑞博,郭贵申. 堆芯测量系统指套管磨损机理与处理方法分析[J]. 设备管理与维修,2023(15): 107-110. [9] 付先刚,濮继龙. 大亚湾核电站控制棒落棒时间超差问题的安全分析和审评[J]. 核动力工程,1997, 18(3): 2-8. [10] 王福军. 计算流体动力学分析——CFD软件原理与应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,2004: 120-125. -





 下载:
下载: