Study on Coordinated Control Method of Reactor Power Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
-
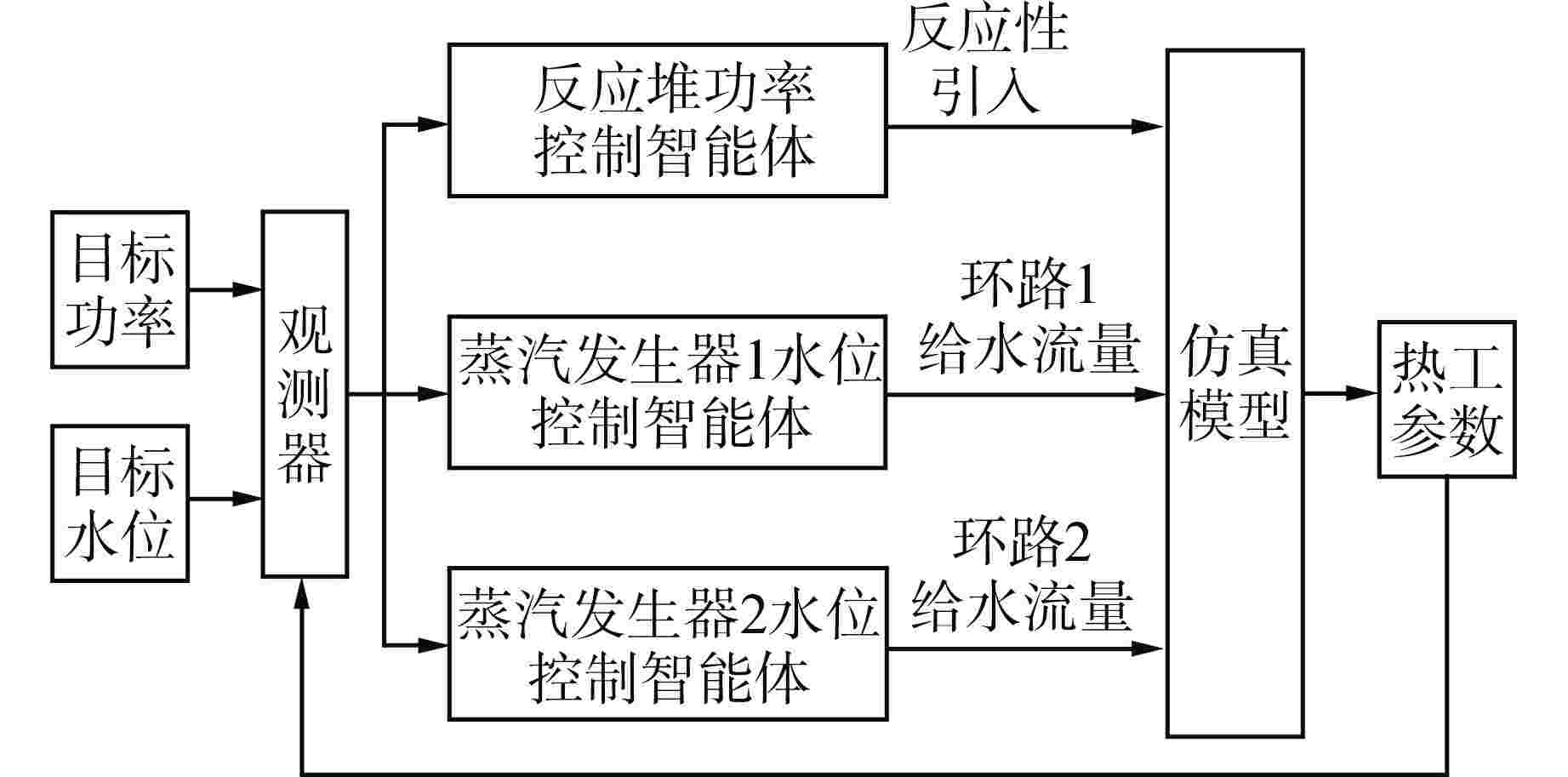
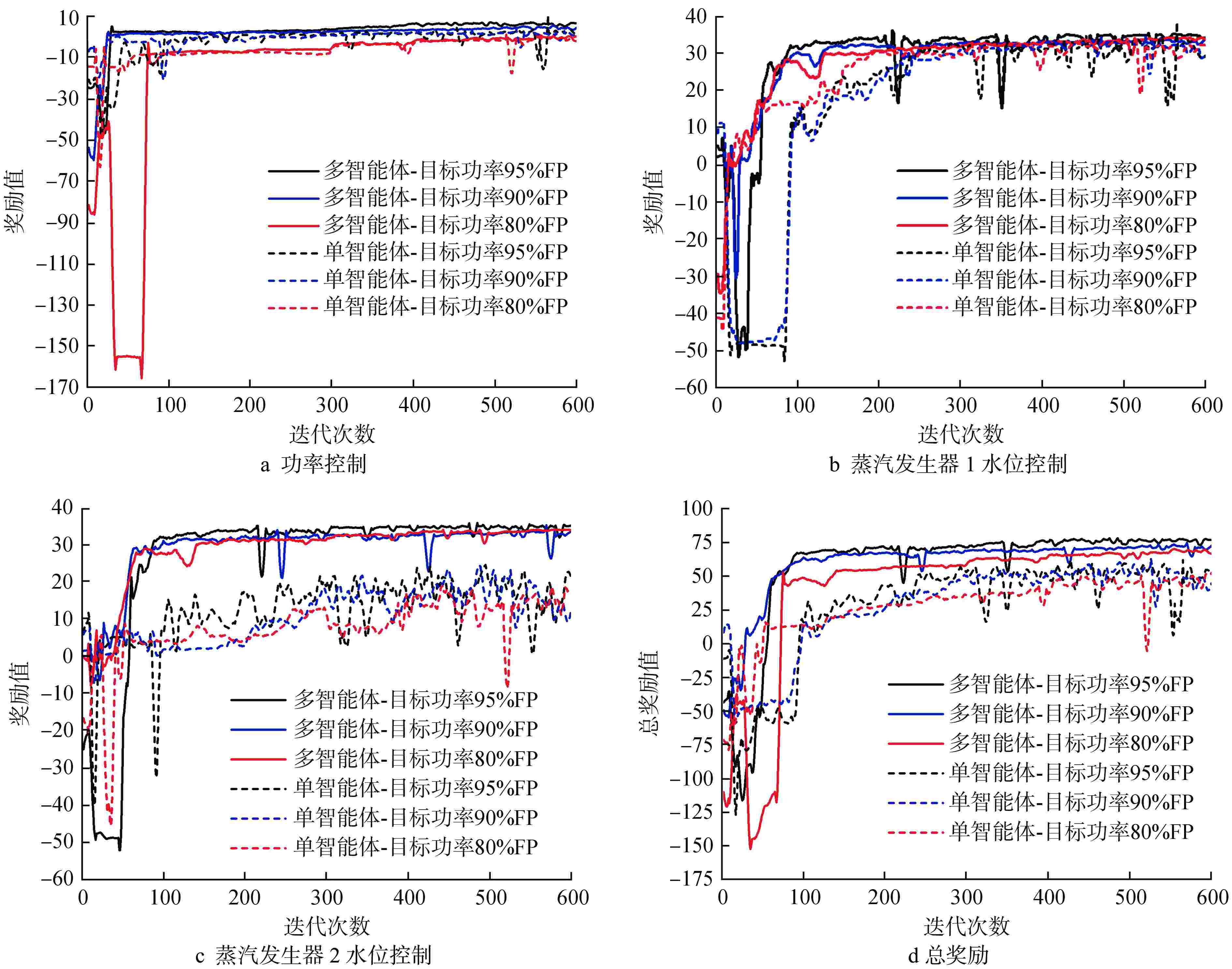
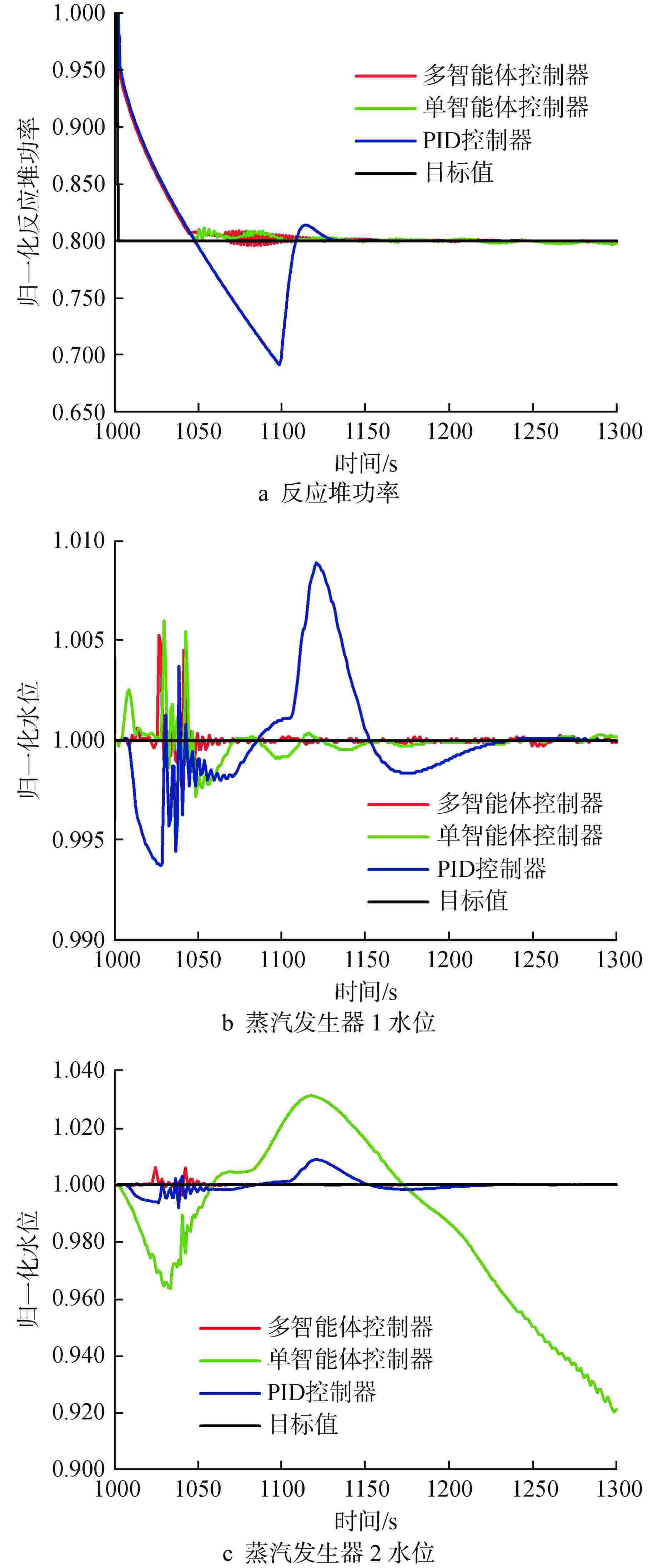
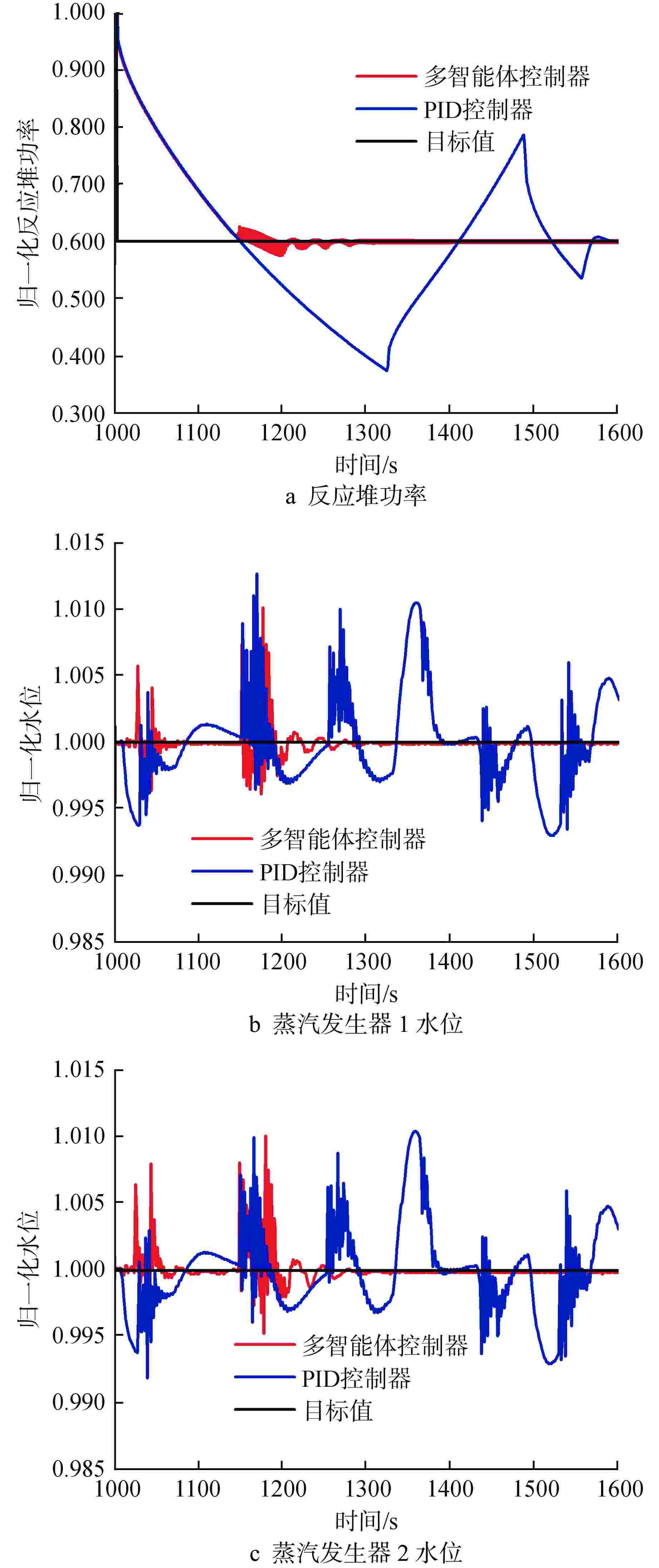
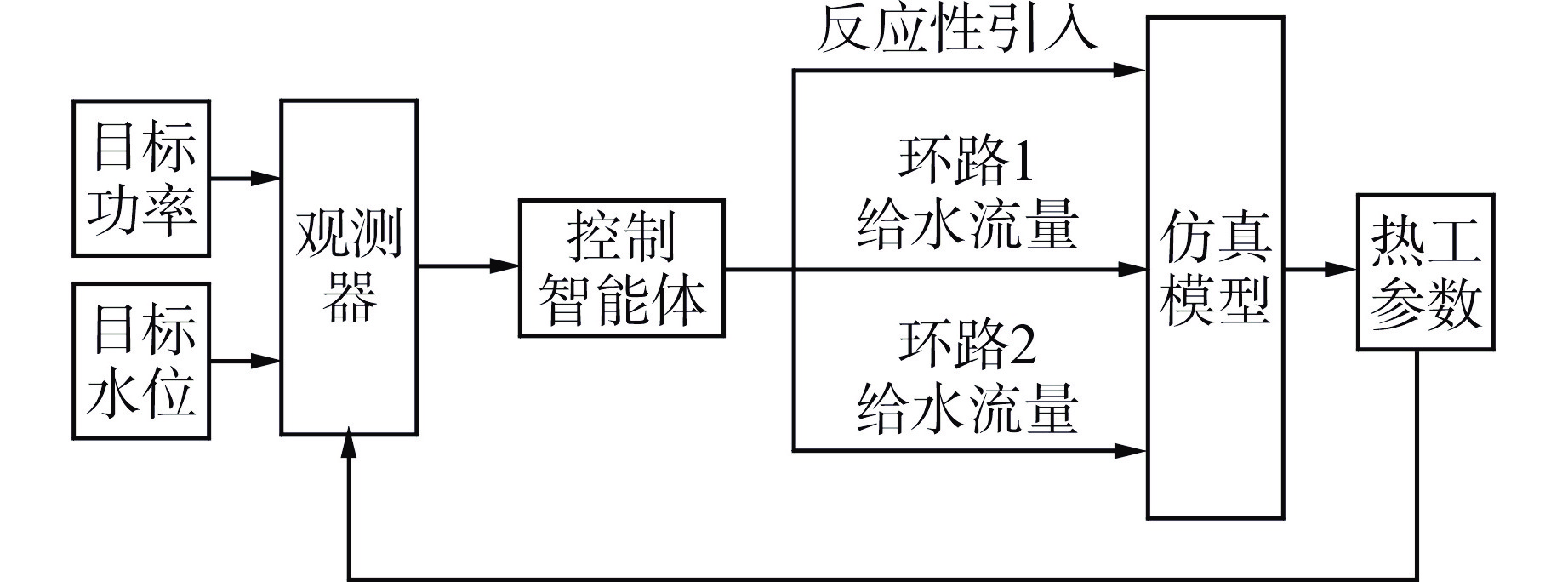
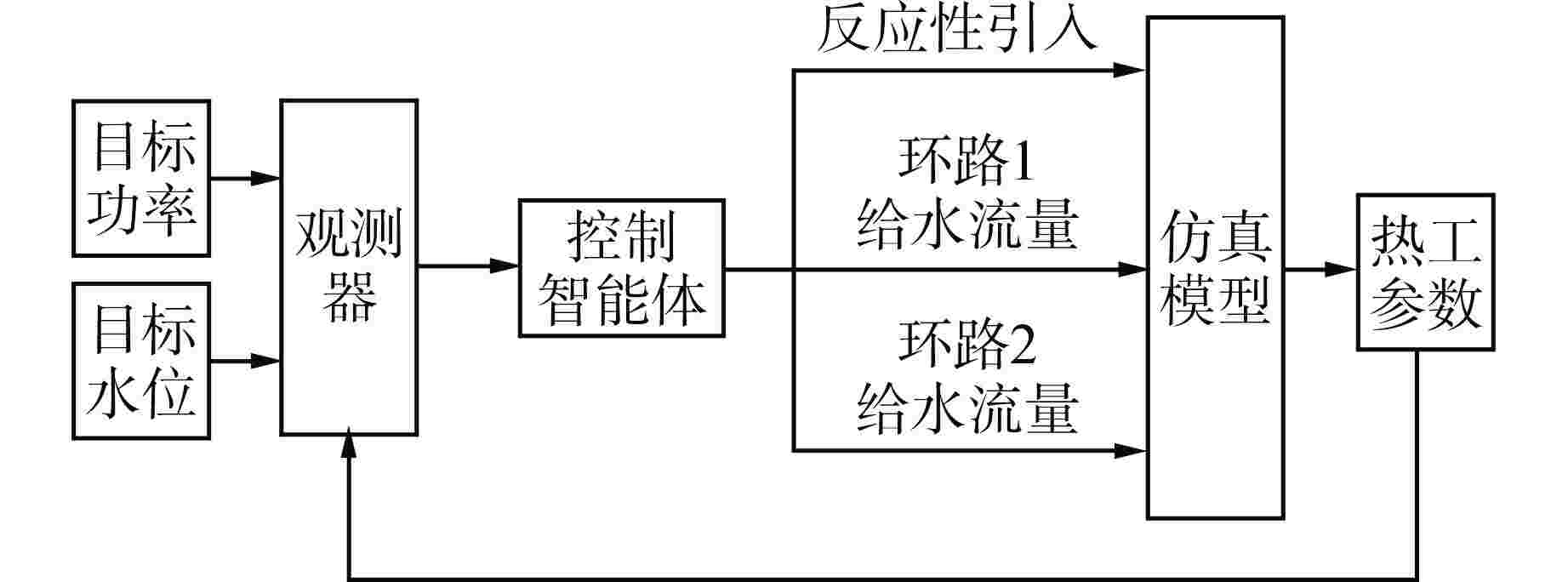
摘要: 为提高核电厂反应堆功率与蒸汽发生器水位的协调控制精度,本研究提出了一种基于双延迟深度确定性策略梯度(TD3)算法的多智能体强化学习协调控制框架,在该框架中,不同子任务被分配给相应的智能体,各智能体相互配合以准确协调反应堆功率和蒸汽发生器水位。通过一系列仿真实验,评估了该框架在不同工况下的性能表现,结果表明,多智能体控制框架在多种功率切换工况下显著提高了控制速度和稳定性,其超调量和控制时间均优于传统比例积分微分(PID)控制器,证明了该框架的有效性和优越性;此外,该框架在未经训练的新工况中也表现出优异的泛化能力,能够有效改善反应堆功率的协调控制精度与稳定性。
-
关键词:
- RELAP5协调控制 /
- 反应堆功率控制 /
- 蒸汽发生器水位控制 /
- 多智能体强化学习 /
- 双延迟深度确定性策略梯度(TD3)
Abstract: To improve the precision of coordinated control between reactor power and steam generator water levels in nuclear power plants, a multi-agent reinforcement learning coordination control framework based on Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3) is proposed in this study, in which various subtasks are assigned to the corresponding agents, and these agents cooperate with each other to accurately coordinate the reactor power and steam generator water levels. Through a series of simulation experiments, the performance of the framework under different operating conditions was evaluated. The experimental results demonstrate that the multi-agent control framework significantly improves the control speed and stability under various power switching conditions, with both overshoot and control time outperforming traditional proportional integral differential (PID) controllers. In addition, the framework also shows excellent generalization ability in untrained new conditions, which can effectively improve the precision and stability of coordinated control of reactor power. -
表 1 仿真参数与设计参数对比
Table 1. Comparison between Simulation Parameters and Design Parameters
参数名 设计值 计算值 相对误差/% 堆芯热功率/MW 966.00 966.00 0.00 堆芯入口温度/K 562.00 558.64 0.60 堆芯出口温度/K 588.40 584.96 0.58 环路冷却剂流量/(kg·s−1) 3333.30 3369.95 1.10 冷却剂压力/MPa 15.20 15.20 0.00 二回路系统压力/MPa 5.20 5.21 0.19 -
[1] 邱磊磊,张贤山,魏新宇,等. 自然循环蒸汽发生器的水位动态特性分析[J]. 核动力工程,2021,42(S2): 5-9. [2] 彭彬森. 基于多智能体的蒸汽发生器建模与水位控制策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2021. [3] 刘妍. 一体化反应堆协调控制技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2013. [4] 邓志光,青先国,吴茜,等. ALSTM-GPC在核电厂协调控制系统中的应用[J]. 核动力工程,2021,42(S2): 41-47. [5] 郭小梁. 船用核动力装置功率调节的协调控制方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学,2022. [6] 刘永超,李桐,成以恒,等. 基于深度确定性策略梯度算法的自适应核反应堆功率控制器设计[J]. 原子能科学技术,2024,58(5): 1076-1083. [7] LI C, YU R, YU W M, et al. Reinforcement learning-based control with application to the once-through steam generator system[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2023, 55(10): 3515-3524. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2023.06.001 [8] GU S D, KUBA J G, CHEN Y P, et al. Safe multi-agent reinforcement learning for multi-robot control[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 319: 103905. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2023.103905 [9] CHU T S, WANG J, CODECÀ L, et al. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for large-scale traffic signal control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(3): 1086-1095. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2901791 [10] YU L, SUN Y, XU Z B, et al. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for HVAC control in commercial buildings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(1): 407-419. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020.3011739 [11] KAZMI H, SUYKENS J, BALINT A, et al. Multi-agent reinforcement learning for modeling and control of thermostatically controlled loads[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 238: 1022-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.01.140 [12] LI F D, WU M, HE Y, et al. Optimal control in microgrid using multi-agent reinforcement learning[J]. ISA Transactions, 2012, 51(6): 743-751. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2012.06.010 [13] FUJIMOTO S, HOOF H, MEGER D. Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods[C]//Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. [14] 汪明媚,程启明,王映斐,等. 基于自适应GA自抗扰控制在蒸汽发生器水位控制中的应用研究[J]. 核动力工程,2011,32(6): 28-33. -





 下载:
下载: