Design of Terminal Sliding Mode Controller Based on RBF Neural Network for Underwater Transportation System
-
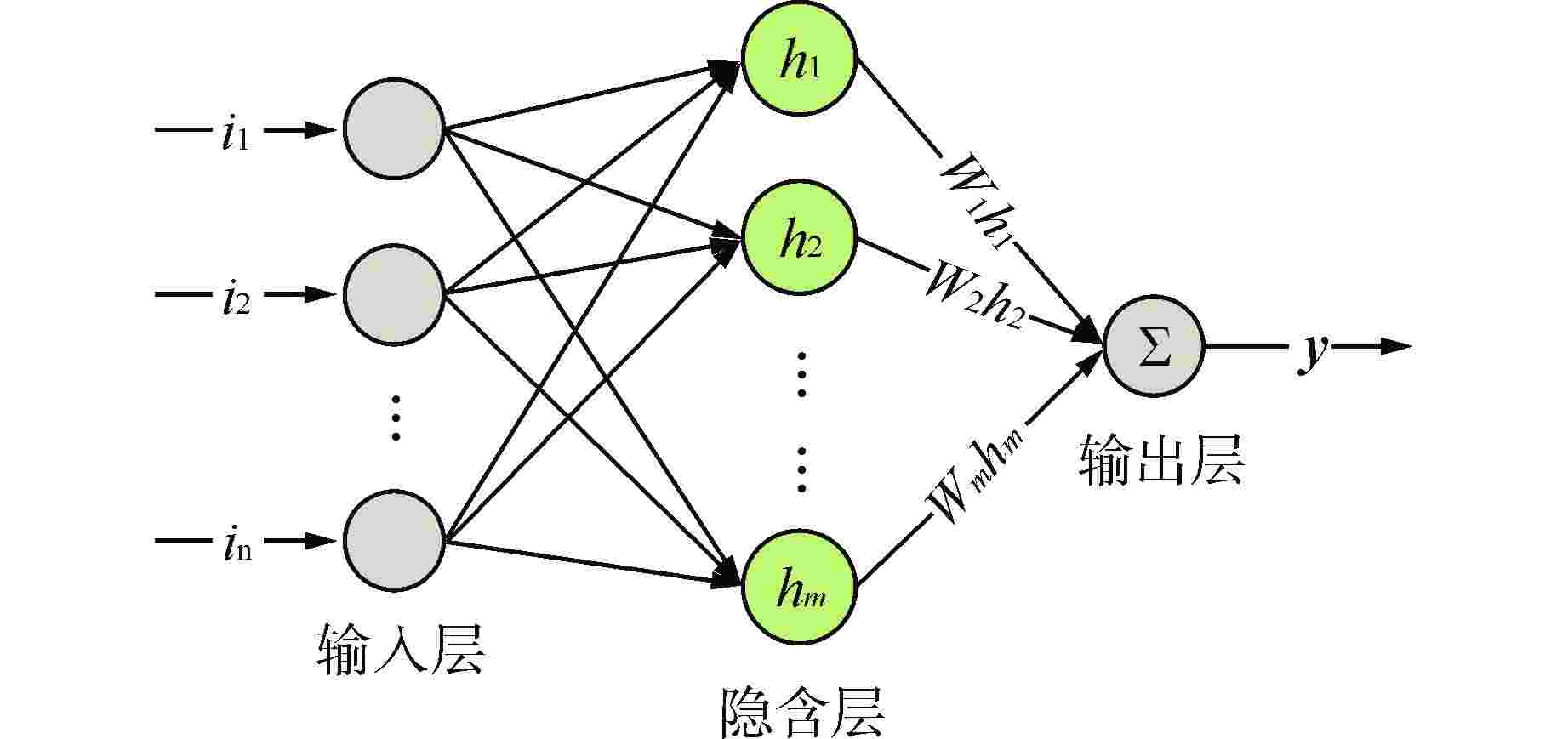
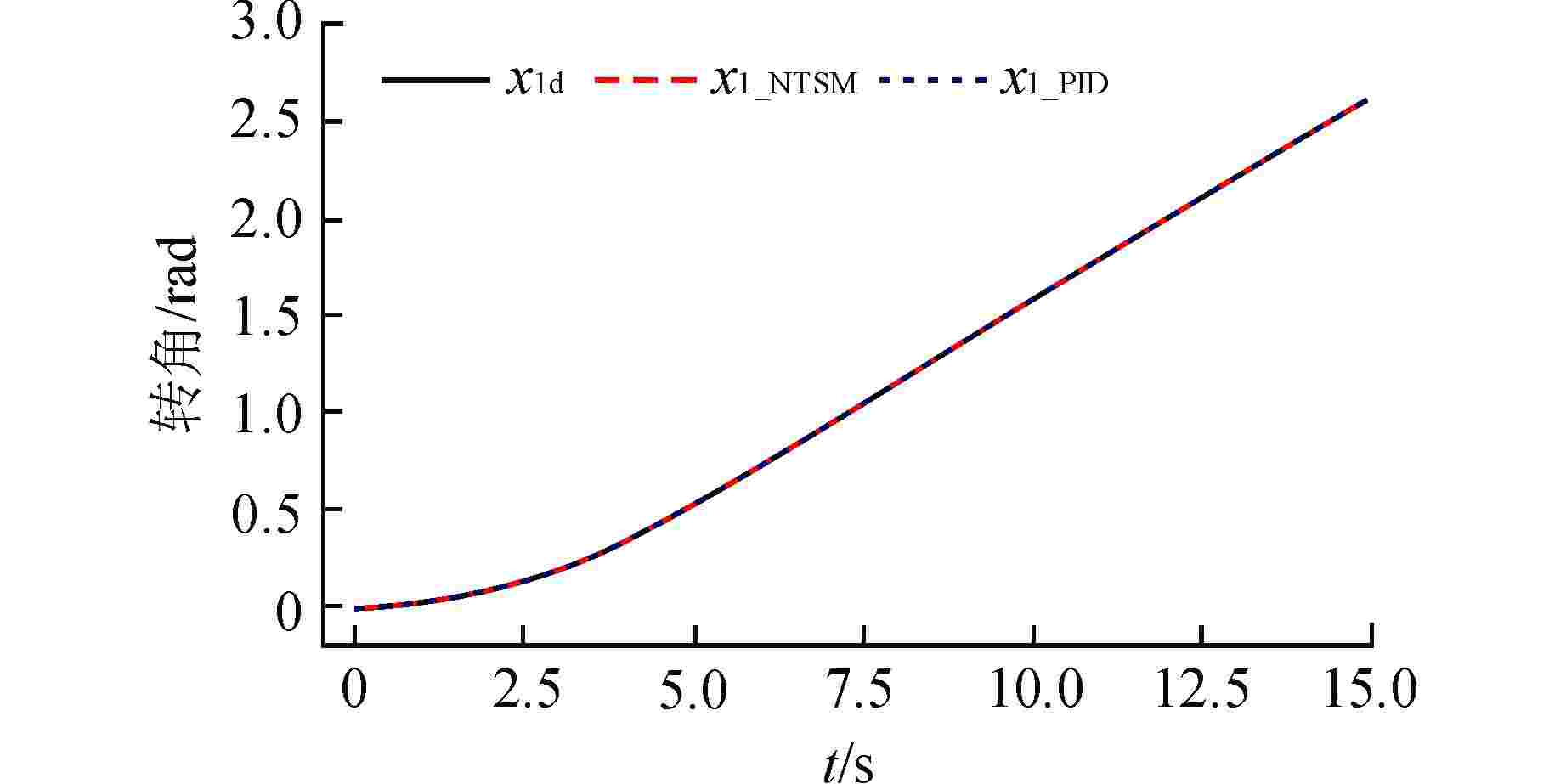
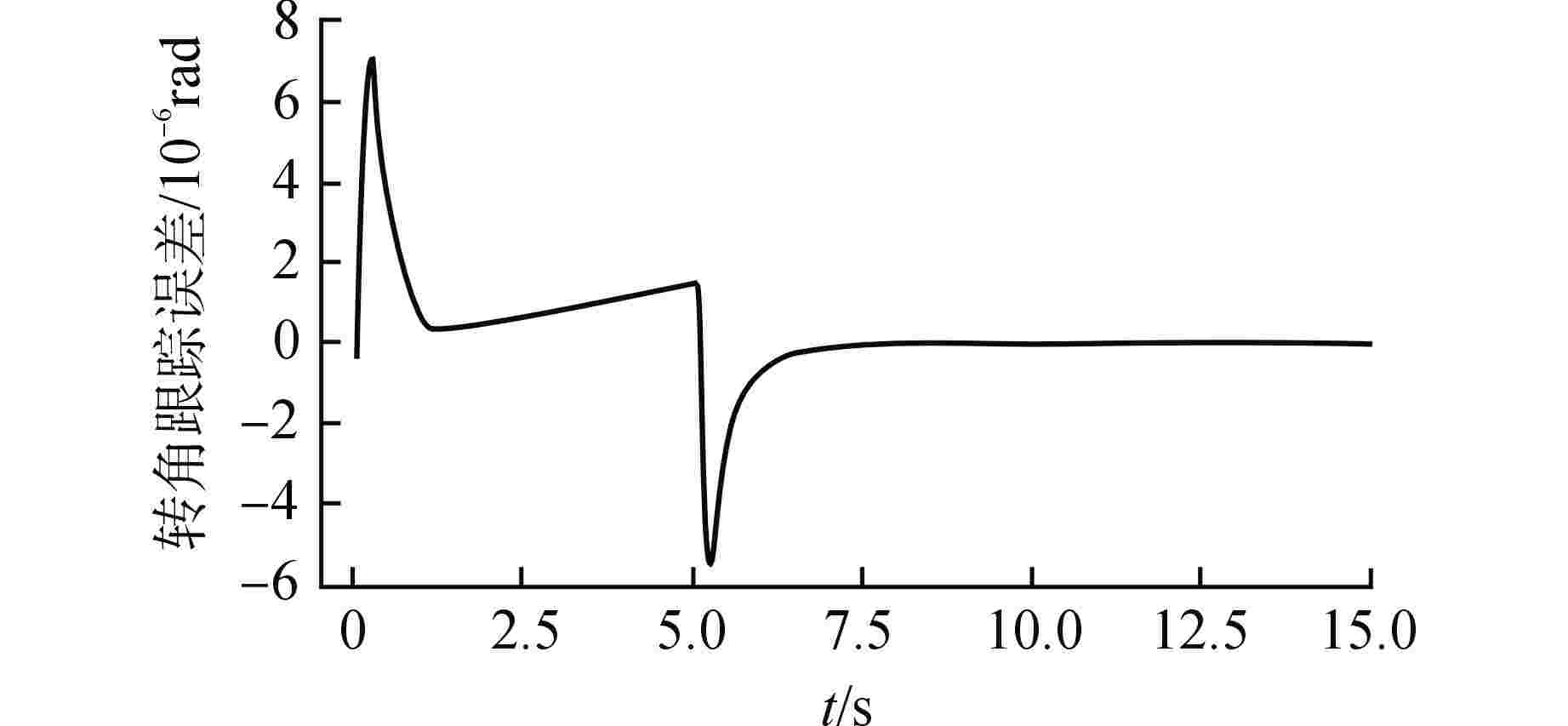
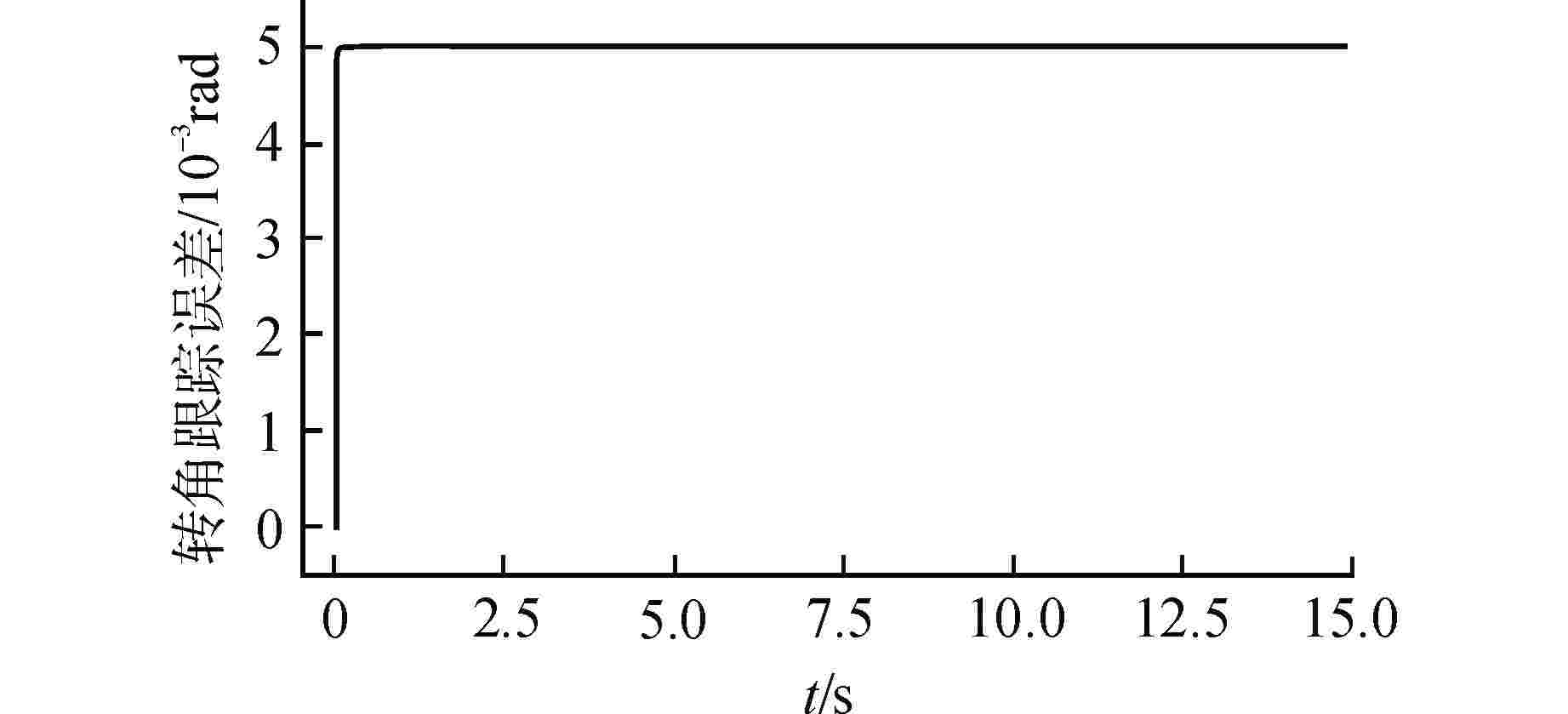
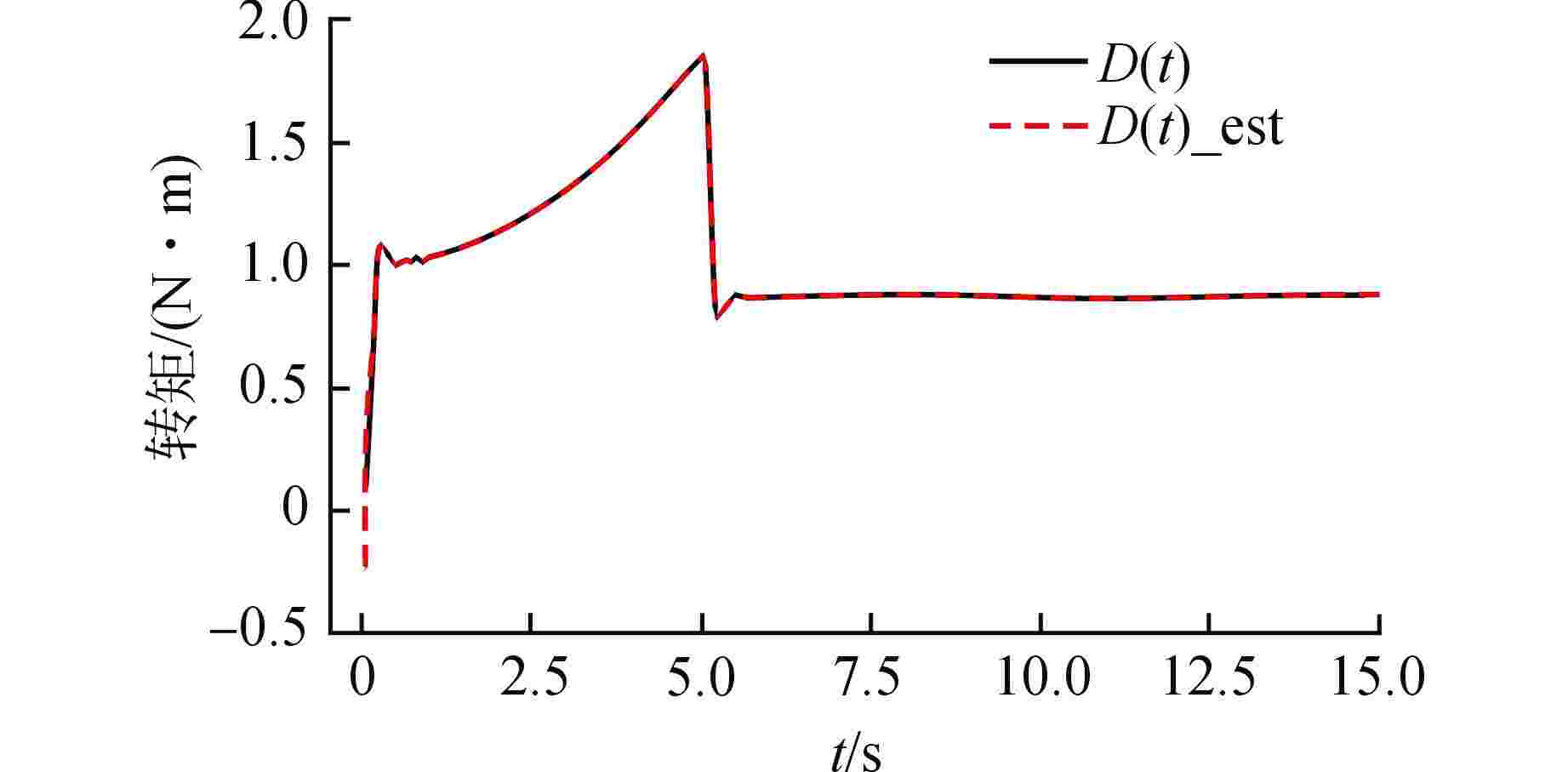
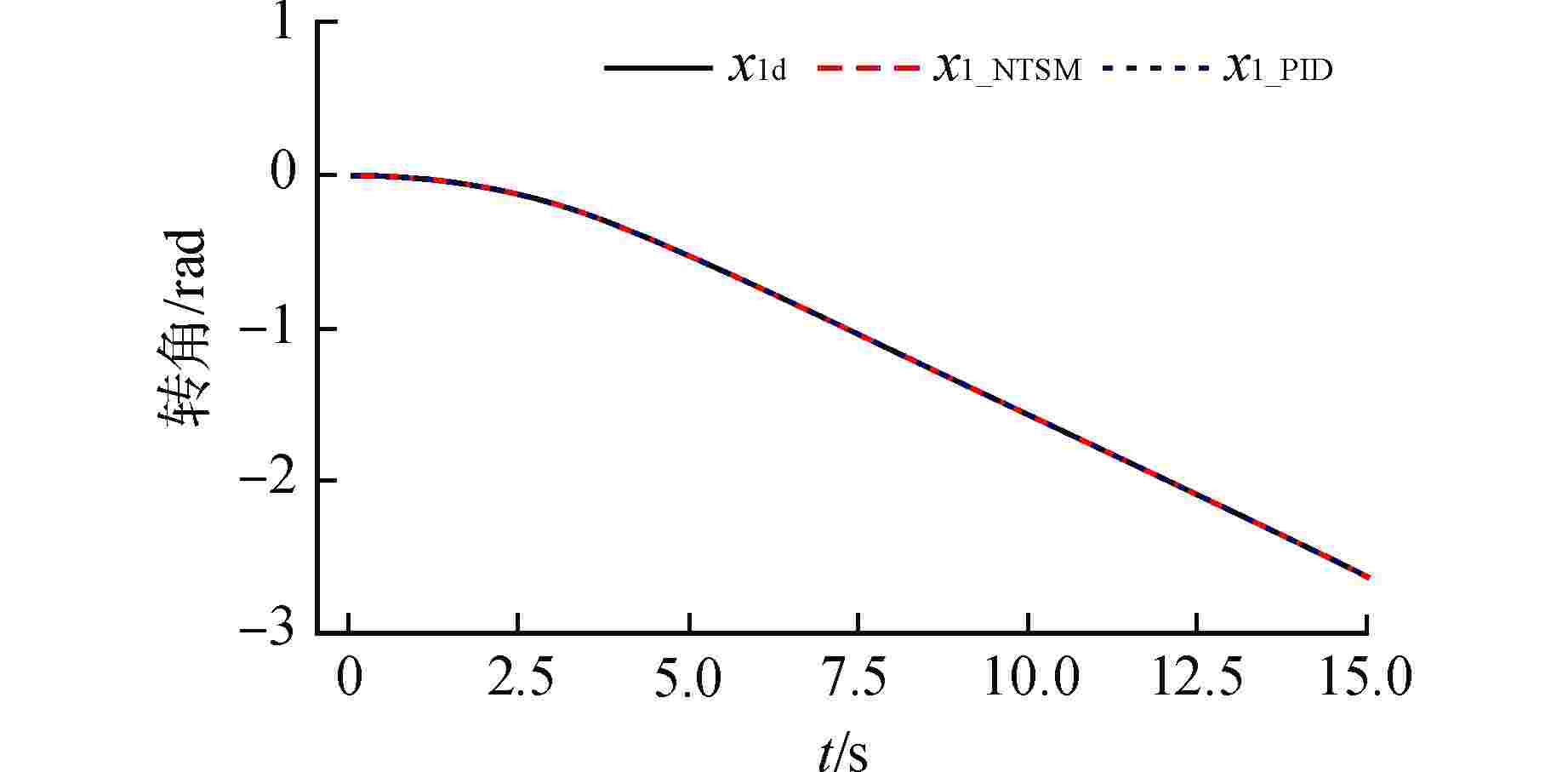
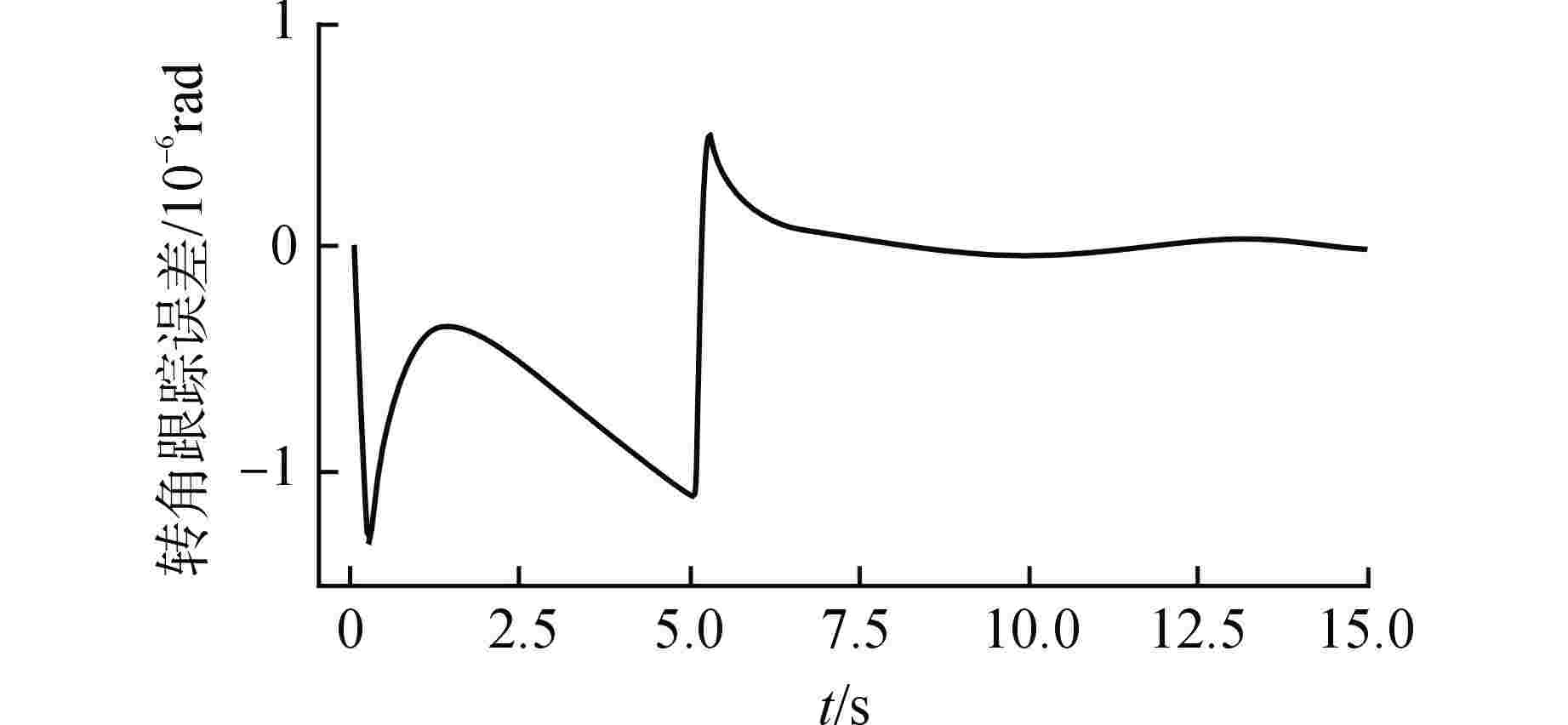
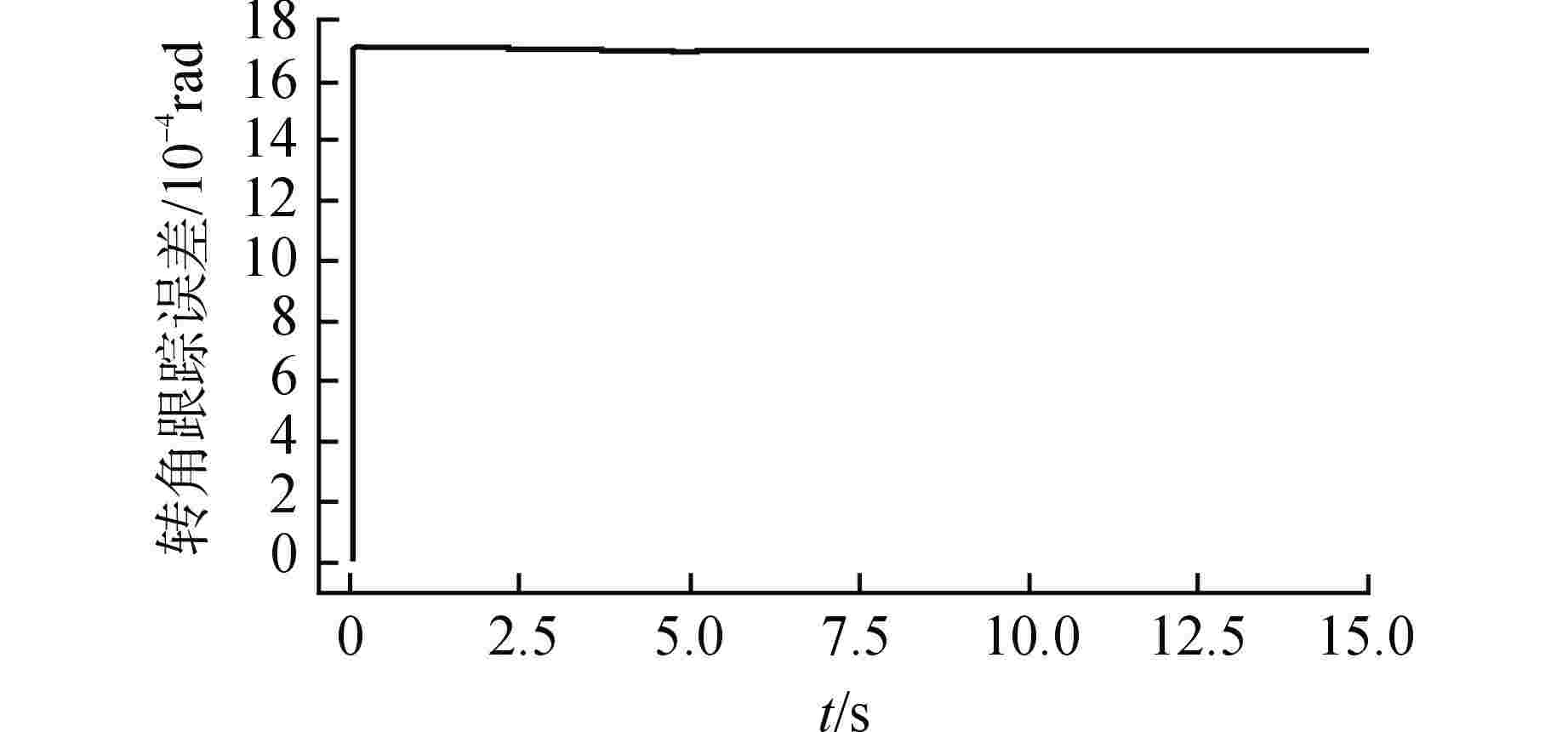
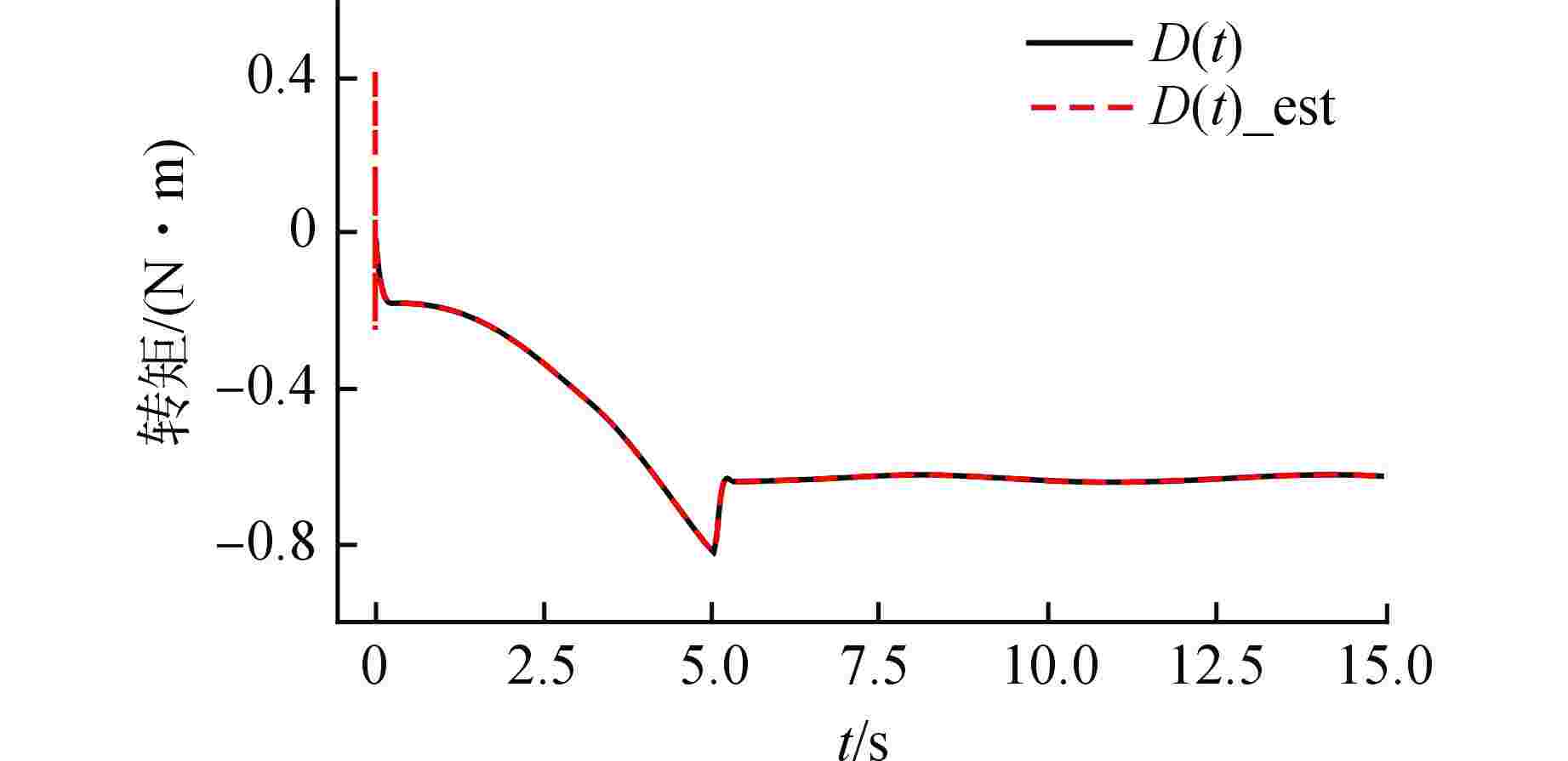
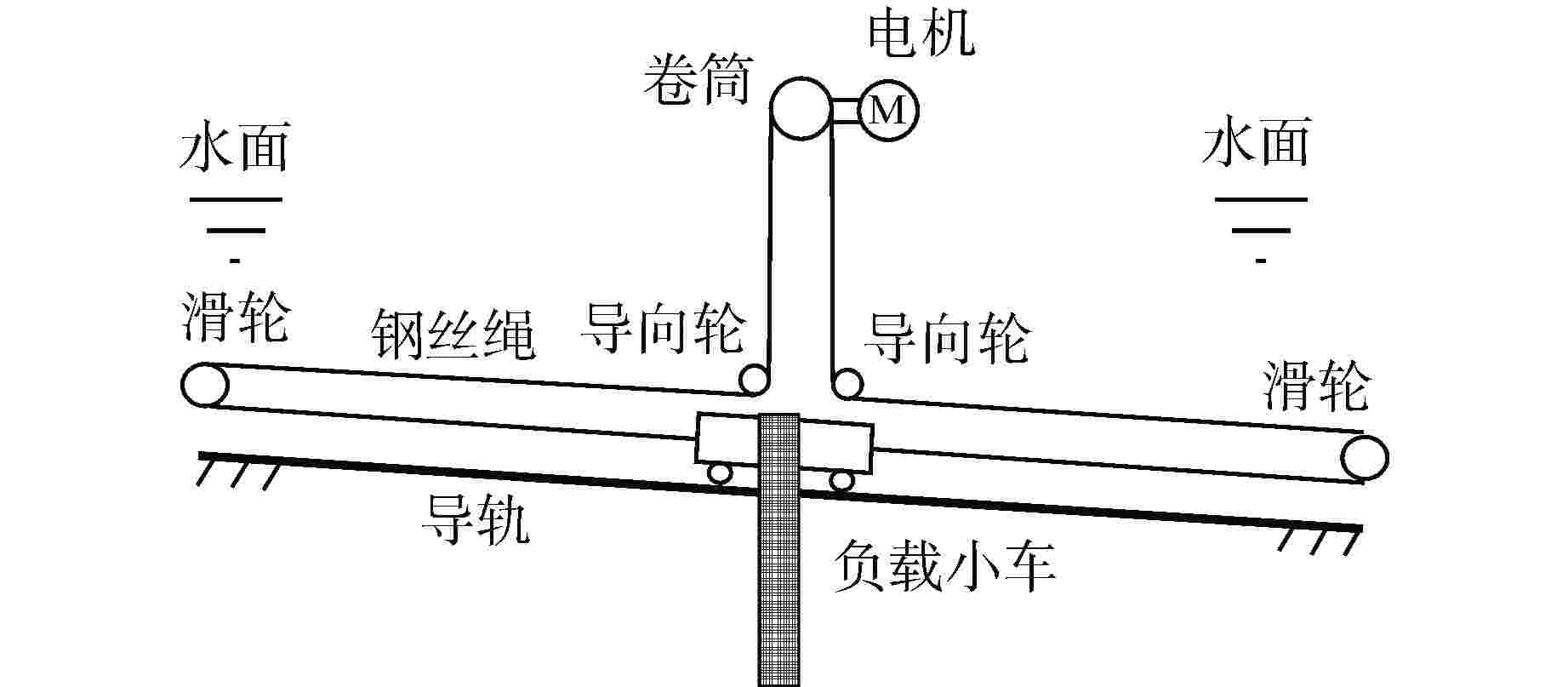
摘要: 水下运输系统在运输载荷时会受到水的不确定非线性和其他外部扰动影响。针对水下运输系统的运行控制问题,以核电厂燃料组件的水下运输系统为对象,设计了基于径向基函数(RBF)神经网络的非奇异终端滑模控制方法。首先,根据牛顿第二定律和Morison方程建立了系统的运动微分方程并推导其状态空间方程;其次,设计非奇异终端滑模控制器,并用RBF神经网络对未知非线性作用进行估计并在控制器中补偿,由Lyapunov稳定性理论推导了网络权值的自适应更新律;通过Lyapunov稳定性理论证明了所提控制策略可以实现对未知非线性估计的渐进收敛和对给定指令跟踪的有限时间收敛;分别对带载上行和空载下行两种工况进行仿真验证,仿真结果表明了所设计的控制器性能良好。
-
关键词:
- 水下运输 /
- 径向基函数(RBF)神经网络 /
- 终端滑模 /
- Morison方程
Abstract: The underwater transportation system will be affected by the uncertain nonlinearity of water and other external disturbance when transporting loads. Aiming at the operational control of underwater transportation system, a non-singular terminal sliding mode control method based on radial basis function (RBF) neural network is designed for the underwater transport process of nuclear power plant fuel assembly. Firstly, according to Newton's second law and Morison's equation, the kinetic differential equation of the system is established and its state-space equation is derived. Secondly, a non-singular terminal sliding mode controller is designed, and the unknown nonlinear effect is estimated by RBF neural network and compensated in the controller. The adaptive updating law of network weight is derived by Lyapunov stability theory. The Lyapunov stability theory proves that the proposed control strategy can achieve asymptotic convergence for unknown nonlinear estimation and finite-time convergence for given instruction tracking. Simulations is carried out for the two conditions of upgoing with load and downgoing without load respectively, and the results verify that the controller designed has good performance. -
表 1 模型参数表
Table 1. Model Parameters
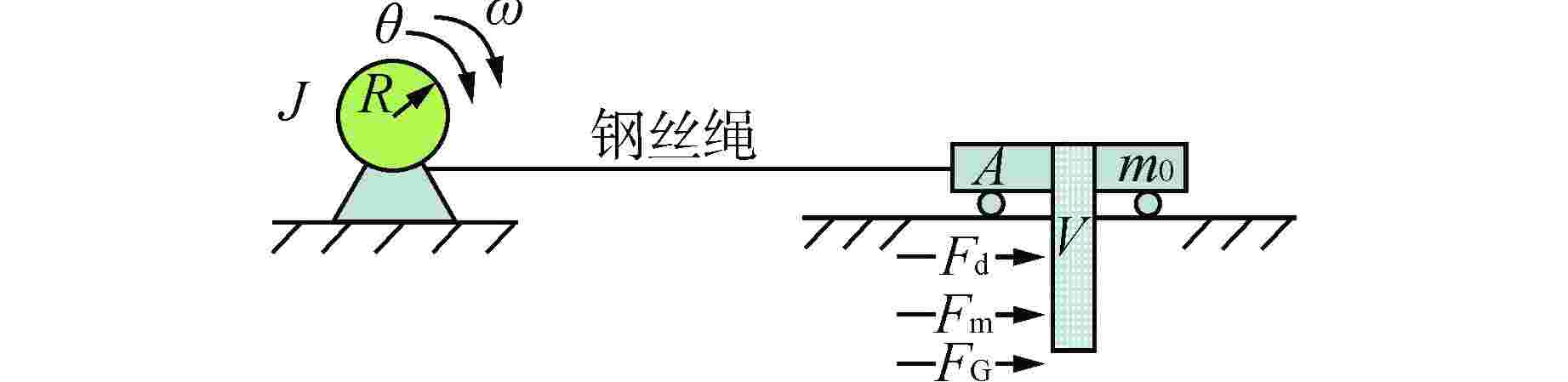
参数名 参数值 转动惯量J/(kg·m2) 0.006 带载质量mt/kg 966 空载质量mf/kg 296 卷筒半径R/m 0.325 阻尼系数bm 0.1 阻力面积(带载上行)Al/m2 1.1745 阻力面积(空载下行)Ad/m2 0.845 排水体积(带载上行)Vl/m3 0.224 排水体积(空载下行)Vd/m3 0.0377 导轨倾角φ 6° 水密度ρ/(kg·m−3) 1000 水的附加质量系数Cd 1.0 水的阻力系数Cm 1.0 -
[1] 王岳. 运输水下负载的海洋起重机轨迹规划与非线性控制[D]. 天津: 南开大学,2022. [2] 郭睿男. 水下生产设备吊装入水和水下拖航作业动力学特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2021. [3] 王书玉,张玮,李磊. 水下无人运输平台关键技术及发展趋势[J]. 舰船科学技术,2021, 43(21): 1-5. [4] 韩宪彬,王杰文,袁建斌. 海洋石油工程水下吊装[J]. 化学工程与装备,2023(5): 111-113. [5] 胡雪扬. 深水水下生产系统安装技术及其力学问题研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东),2016. [6] 任宪常,何英勇,王欢,等. 压水堆核电厂乏燃料转运系统工艺分析[J]. 起重运输机械,2014(4): 106-110. [7] 侯硕,贾晓峰. 压水堆核电站燃料厂房核燃料转运系统的抗震分析[J]. 核科学与工程,2013, 33(3): 314-320. [8] 袁占航,刘升,周洋. 乏燃料组件抓具混合双摆模型及地震响应分析[J]. 核动力工程,2020, 41(1): 59-64. [9] 陈飞,刘吉双,叶清,等. 压水堆燃料转运装置运输小车超载分析[J]. 核动力工程,2017, 38(3): 119-122. [10] AHMED S, WANG H P, TIAN Y. Model-free control using time delay estimation and fractional-order nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode for uncertain lower-limb exoskeleton[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2018, 24(22): 5273-5290. doi: 10.1177/1077546317750978 [11] 邹权,钱林方,徐亚栋,等. 链式回转弹仓的自适应鲁棒控制[J]. 兵工学报,2014, 35(11): 1922-1927. [12] 王杰,强宝民,何祯鑫,等. 欠驱动双摆吊车滑模控制研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报,2019, 40(12): 193-198,220. [13] 顾秀涛,洪梦情,陆玉叶,等. 基于固定时间终端滑模控制的塔吊防摆定位研究[J]. 南京理工大学学报,2023, 47(4): 533-541. [14] 谢政,谢建,杜文正,等. 大型发射装置液压起竖系统的滑模控制研究[J]. 兵工学报,2015, 36(4): 674-680. [15] BASU J K, BHATTACHARYYA D, KIM T H. Use of artificial neural network in pattern recognition[J]. International Journal of Software Engineering and its Applications, 2020, 4(2): 23-34. [16] PATEL S, SARABAKHA A, KIRCALI D, et al. An intelligent hybrid artificial neural network-based approach for control of aerial robots[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2020, 97(2): 387-398. [17] ZHANG M H, CHEN Y X. Link prediction based on graph neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal: Curran Associates Inc. , 2018: 5171-5181. [18] PEREIRA T D, ALDARONDO D E, WILLMORE L, et al. Fast animal pose estimation using deep neural networks[J]. Nature methods, 2019, 16(1): 117-125. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0234-5 [19] 张春雷,李鹤,董茂林,等. 燃料电池空气供应系统自适应神经网络滑模控制[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版,2022, 43(9): 1270-1276. [20] HUI J W, YUAN J Q. RBF-based adaptive sliding mode controller with extended state observer for load following of nuclear power plant[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2020, 360: 110465. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2019.110465 [21] FENG H, SONG Q Y, MA S L, et al. A new adaptive sliding mode controller based on the RBF neural network for an electro-hydraulic servo system[J]. ISA Transactions, 2022, 129: 472-484. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2021.12.044 [22] DONG R G. Effective mass and damping of submerged structures: UCRL-52342[R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Lab. , 1978: 10. [23] 沈勇,王昌明,狄长安,等. 水中弹丸运动状态分析及试验研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报,2002, 22(1): 45-47. [24] YU S H, YU X H, SHIRINZADEH B, et al. Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode[J]. Automatica, 2005, 41(11): 1957-1964. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2005.07.001 [25] FENG Y, YU X H, MAN Z H. Non-singular terminal sliding mode control of rigid manipulators[J]. Automatica, 2002, 38(12): 2159-2167. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(02)00147-4 -





 下载:
下载: